2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:33
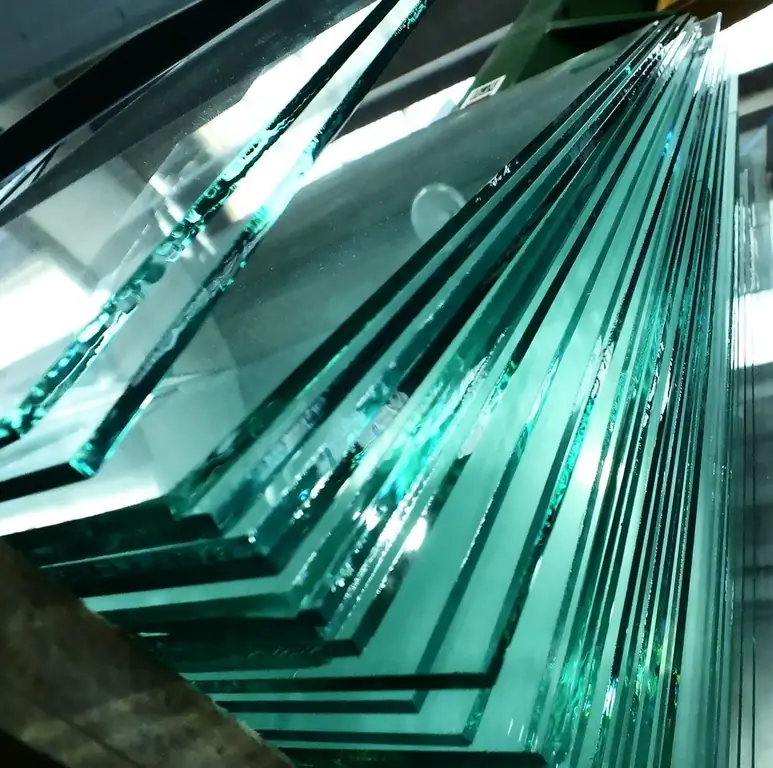
Glass is one of the most ancient and versatile materials. Glass products are all around us, but usually we do not think too much about its characteristics. They can vary greatly depending on the purpose of using the future product. One of the most common types is heat-resistant glass. Let's find out how it differs from the usual one and where it is applied.
Heat-resistant glass
Glass is an inorganic substance. It is characterized by the properties of a solid body; in the molten state, it is a superviscous liquid. Its brittleness, strength, density and heat capacity vary greatly and depend on impurities.

Recently, materials have been developed that have properties that are not typical of glass, such as fire resistance. The main parameter that distinguishes heat-resistant glass from other glasses is the temperature at which it retains its properties. It withstands heat even at 1000degrees Celsius, while his "colleagues" crack already at 80 degrees.
Refractoriness is affected by the composition and thickness of the material. If the glass is thick and contains a large proportion of alkali oxides, then it will be strong. The most resistant heat-resistant glass is quartz. It withstands large temperature differences and has a high boiling point (2230 degrees).
Production of heat-resistant glass
As a rule, glass is a mixture of several components. For standard material, quartz sand, lime and soda are taken. They are heated to very high temperatures (from 1700 degrees), which is why they melt and mix with each other. After that, the mixture is poured into molten tin (they do not mix due to the difference in density), and then gradually cooled.
To give the necessary properties, other substances are added to these components. To make heat-resistant glass, various oxides are used. So, borosilicate material contains boron oxide, quartz - silicon oxide.

Additional strength it will have if you use several layers. For this, it is allowed to cool completely. Finished sheets are ground, cleaned and cut to the required dimensions. Then several sheets of glass are glued together with a special polymer. The final touch is firing the glass "sandwich" at 660-680 degrees.
Application
Heat-resistant glass is popular in the kitchen. Ovens and dishes are made from it. common productof this material is also a fireplace. Quartz glass is used in the production of optical fibers, Fresnel lenses, crucibles, insulators, etc. Borosilicate glass is used for optical glasses, glassware, reflecting telescopes.
There are many advantages to fire-resistant glassware. It withstands even open fire, is durable. The material is quite inert and does not oxidize when heated, so it does not change the taste of the dish. It does not corrode or scale.

Of course, even heat-resistant glass has drawbacks. It does not respond well to a sharp increase or decrease in temperature. Dishes made of such material should not be placed on high heat immediately after the freezer. In addition, fire-resistant glass is not shockproof and should not be dropped.
Recommended:
How to make glass? Glass production technology. glass products
Glass is familiar to everyone. But the process of making it is extremely exciting. Each stage is important and affects the quality of the final product. The basis is sand, soda, lime. The process is almost entirely automated. Surprisingly, glass can even be made at home
Heat energy tariff: calculation and regulation. Heat energy meter

Who approves and regulates heat tariffs? The main factors affecting the cost of the service, specific figures, the trend of increasing cost. Thermal energy meters and self-calculation of the cost of the service. Prospects for billing. Varieties of tariffs for organizations and citizens. Calculation of REC tariffs, documentation required for this
Heat resistance and heat resistance are important characteristics of steels
Ordinary structural steels, when heated, abruptly change their mechanical and physical properties, begin to actively oxidize and form scale, which is completely unacceptable and creates a threat of failure of the entire assembly, and possibly a serious accident. To work at elevated temperatures, materials engineers, with the help of metallurgists, created a number of special steels and alloys. This article gives a brief description of them
Heat shrink tube: characteristics, scope and benefits

Heat shrink tubing is one of the most popular and widespread types of heat shrinkable materials on the Russian market. By its design, this element is characterized by high qualities of reliability and is used to change the diameter of the part (on which it is mounted) to one degree or another
Glass blasting. Manufacturing Methods and Applications

Modern designers' quest for perfection has enabled manufacturers and processors to introduce methods such as sandblasting glass and mirrors. This method is not too complicated and does not require highly skilled workers

