2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:30
Modern production equipment has a rather complex design. Friction mechanisms transmit motion with the help of friction force. These can be clutches, clamps, spreaders and brakes.
In order for the equipment to be durable, to work without downtime, special requirements are put forward for its materials. They are constantly growing. After all, technology and equipment are constantly being improved. Their capacities, operating speeds, as well as loads are increasing. Therefore, in the process of their functioning, various friction materials are used. The reliability and durability of the equipment depends on their quality. In some cases, the safety and life of people depend on these elements of the system.
General characteristics
Friction materials are integral elements of assemblies and mechanisms that have the ability to absorb mechanical energy and dissipate it into the environment. At the same time, all structural elements should not wear out quickly. To do this, the presented materials have certain properties.

Coefficient of friction of friction materialsshould be stable and high. The wear resistance index must also satisfy operational requirements. Such materials have good heat resistance and are not subject to mechanical stress.
So that the substance that performs frictional functions does not stick to the working surfaces, it is endowed with sufficient adhesive qualities. The combination of these properties ensures the normal operation of equipment and systems.
Material properties
Friction materials have a certain set of properties. The main ones have been listed above. These are service qualities. They determine the performance characteristics of each substance.
But all service characteristics are determined by a set of physical-mechanical and thermostatic indicators. These parameters change during the operation of the material. But their limit value is taken into account in the process of choosing a friction substance.

There is a division of properties into static, dynamic and experimental indicators. The first group of parameters includes the limit of compression, strength, bending and stretching. It also includes heat capacity, thermal conductivity and linear expansion of the material.
The indicators determined in dynamic conditions include thermal stability, heat resistance. The coefficient of friction, wear resistance and stability are established in the experimental environment.
Types of materials
Friction materials of the brake and clutch system are most often made on a copper or iron basis. Second groupsubstances is used in conditions of increased load, especially with dry friction. Copper materials are used for medium and light loads. Moreover, they are suitable for both dry friction and the use of lubricating fluids.

In modern production conditions, rubber and resin-based materials are widely used. Various fillers from metallic and non-metallic components can also be used.
Scope of application
There is a classification of friction materials depending on their area of application. The first large group includes transmission devices. These are medium and light loaded mechanisms that operate without lubrication.
Next are the friction materials of the brake system, designed for medium and heavy-duty mechanisms. These units are not lubricated.
The third group includes substances used in couplings of medium and heavy-duty units. They contain oil.

Also, brake materials containing liquid lubricant are also distinguished as a separate group. The main parameters of the mechanisms determine the choice of friction materials.
In the clutch, the load acts on the elements of the system for about 1 s, and in the brake - up to 30 s. This indicator determines the characteristics of the materials of the nodes.
Metal materials
As mentioned above, the main metal friction materials of the clutch system, brakes are iron andcopper. Steel and cast iron are very popular today.

They are applicable in different mechanisms. For example, friction materials for brake shoes that contain cast iron are often used in railway systems. It does not warp, but sharply loses its sliding qualities at temperatures above 400 °C.
Non-metallic materials
Friction materials for clutches or brakes are also made from non-metallic substances. They are created mainly on an asbestos basis (resin, rubber act as binders).

The coefficient of friction remains quite high up to a temperature of 220 °C. If the binder is resin, the material is highly wear resistant. But their coefficient of friction is somewhat lower relative to other similar materials. A popular plastic material on this basis is retinax. It contains phenol-formaldehyde resin, asbestos, barite and other components. This substance is applicable for units and brake mechanisms with severe operating conditions. It retains its qualities even when heated to 1000 °C. Therefore, retinax is applicable even in aircraft braking systems.
Asbestos materials are made by creating the fabric of the same name. It is impregnated with asph alt, rubber or Bakelite and pressed at high temperatures. Short asbestos fibers can also form non-woven linings. They add small metalshavings. Sometimes brass wire is introduced into them to increase strength.
Sintered materials
There is another variety of system components presented. These are sintered friction materials of the brake system. That this is a variety will become clearer from the way they are made. They are most often made on a steel basis. In the process of welding, other components that make up the composition are sintered with it. Pre-compressed blanks consisting of powder mixtures are subjected to high temperature heating.

Such materials are used most often in heavily loaded clutches and brake systems. Their high performance during operation is determined by two groups of components that make up the composition. The former materials provide a good coefficient of friction and wear resistance, while the latter provide stability and a sufficient level of adhesion.
Steel based materials for dry friction
The choice of material for various systems is based on the economic and technical feasibility of its manufacture and operation. Several decades ago, iron-based materials such as FMK-8, MKV-50A, and SMK were in demand. Friction materials for brake pads that worked in heavily loaded systems were later made from FMK-11.
MKV-50A is a newer design. It is used in the manufacture of linings for disc brakes. It has an advantage over the PMK group in terms of stability indicators,wear resistance.
In modern production, materials such as SMK have become more widespread. They have a high content of manganese. Also included are boron carbide and nitride, molybdenum disulfide and silicon carbide.
Bronze based materials for dry friction
Tin bronze materials have proven themselves well in transmission and braking systems for various purposes. They wear much less iron or steel mating parts than iron based friction materials.
The presented variety of materials is used even in the aviation industry. For special operating conditions, tin can be replaced by substances such as titanium, silicon, vanadium, arsenic. This prevents the formation of intergranular corrosion.
Materials based on tin bronze are widely used in the automotive industry, as well as in the manufacture of agricultural machinery. They withstand heavy loads. The 5-10% tin included in the alloy provides increased strength. Lead and graphite act as a solid lubricant, while silicon dioxide or silicon increases the coefficient of friction.
Operating in liquid lubrication conditions
Materials used in dry systems have a significant disadvantage. They are subject to rapid wear. When grease enters them from nearby nodes, their efficiency decreases sharply. Therefore, recently, materials designed to work in liquid oil have become more widespread.
Such equipment turns on smoothly, is characterized by highwear resistance level. It cools easily and simply seals.
In foreign practice, production volumes of such a product as asbestos-based friction material for brakes, clutches and other mechanisms have recently been growing. It is impregnated with resin. Formulated with high metal filler moldings.
Sintered materials based on copper are most often used for the lubricating medium. Non-metallic solid components are introduced into the composition to improve frictional characteristics.
Improve properties
First of all, improvement requires wear resistance, which friction materials have. The economic and operational feasibility of the presented components depends on this. In this case, technologists are developing ways to eliminate excessive heating on rubbing surfaces. To do this, they improve the properties of the friction material itself, the design of the device, and also regulate the operating conditions.
When materials are used in dry friction conditions, special attention is paid to their heat resistance and oxidation resistance. Such substances are less susceptible to abrasive type wear. But for lubricated systems, heat resistance is not so important. Therefore, more attention is paid to their strength.
Also, when improving the quality of friction materials, technologists pay attention to their degree of oxidation. The smaller it is, the more durable the components of the mechanisms. Another direction is to reduce the porosity of the material.
Modernproduction should improve the additional materials used in the manufacturing process of various movable, transmission devices. This will meet the growing consumer and performance requirements for friction materials.
Recommended:
Growing bulls for meat: choice of breed, living conditions, diet, sales, business profitability

Today, the process of reverse urbanization is noticeable in our country - we althy people move from stuffy, noisy, bustling cities to small villages and even villages. Many of them have their own businesses. For example, some are engaged in growing bulls for meat at home. This is hard work, but you can always provide yourself and loved ones with high-quality, clean products, at the same time making a good profit
Friction clutches: principle of operation, drawing
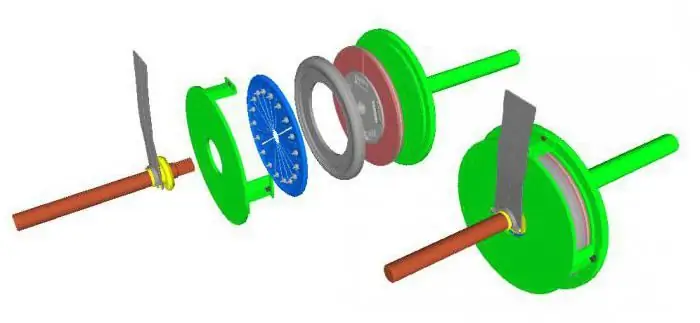
Friction type clutches are used in clutch mechanisms. The devices differ in parameters as well as design. There are many types of friction clutches
Anti-friction materials: overview, properties, application

The article is devoted to antifriction materials. Their properties, features, varieties, as well as areas of application are considered
Materials released to production (posting). Accounting for the disposal of materials. accounting entries

Most of all existing enterprises can not do without inventories used to produce products, provide services or perform work. Since inventories are the most liquid assets of the enterprise, their correct accounting is extremely important
Friction joints on high-strength bolts

Friction joints on high-strength bolts: design features, manufacturing and assembly requirements. Methods for obtaining the necessary roughness of mating surfaces. Calculation of the main parameters of the connection. Quality control

