2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-06-01 07:12:56
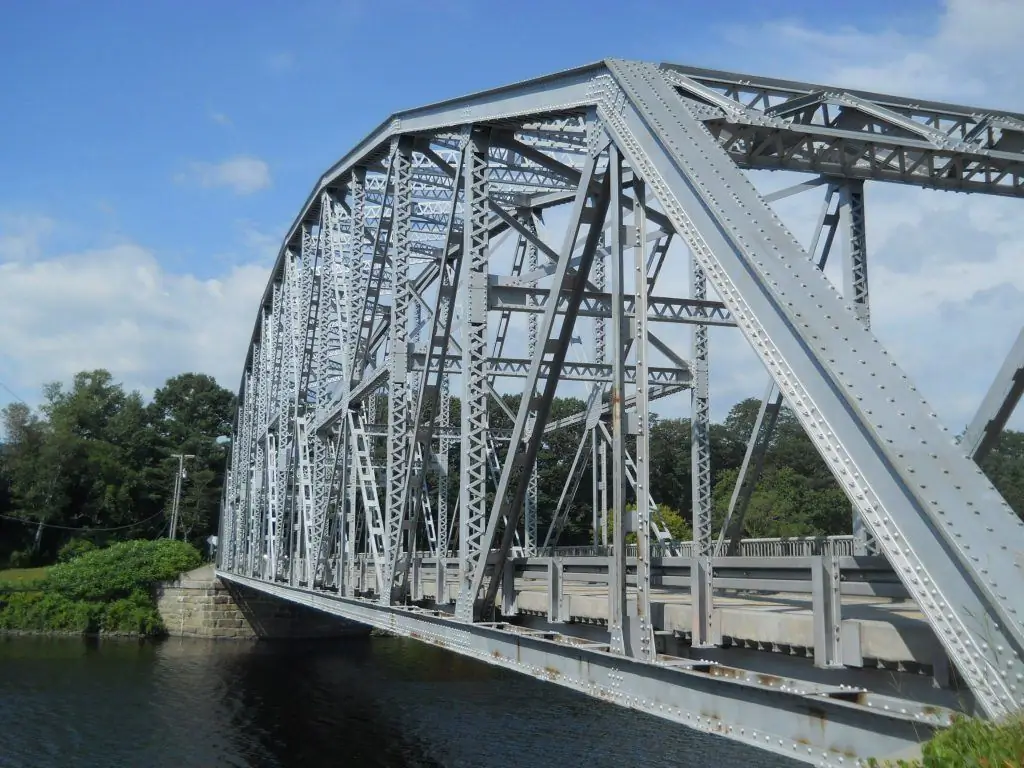
Friction joints have a high bearing capacity and are less labor intensive than welded ones. Due to this, they are widely used in the production of building steel structures. Obtaining the necessary friction forces in the joint is achieved in various ways - abrasive blasting and flame treatment, as well as using adhesive compositions.
Description and application
In mechanical engineering, there are 2 types of bolted connections according to the nature of the force transfer in them:
- Shear resistant. Most often they are designed on bolts of coarse, normal and increased accuracy (rarely high-strength). The tightening force is not controlled. Calculations take into account the internal tensile, crushing and shear stresses, but do not take into account frictional forces.
- Friction (shear resistant). The external force is counteracted by the friction forces arising in the contact planes of the parts to be joined. The friction is due to the preload of the fixing bolts, which should be maximum. Therefore, in such joints, high-strength hardware with thermalprocessing.
The last type is divided into 2 subcategories: friction and friction-shear joints, in which one part of the forces is transmitted through friction, and the other through crushing.
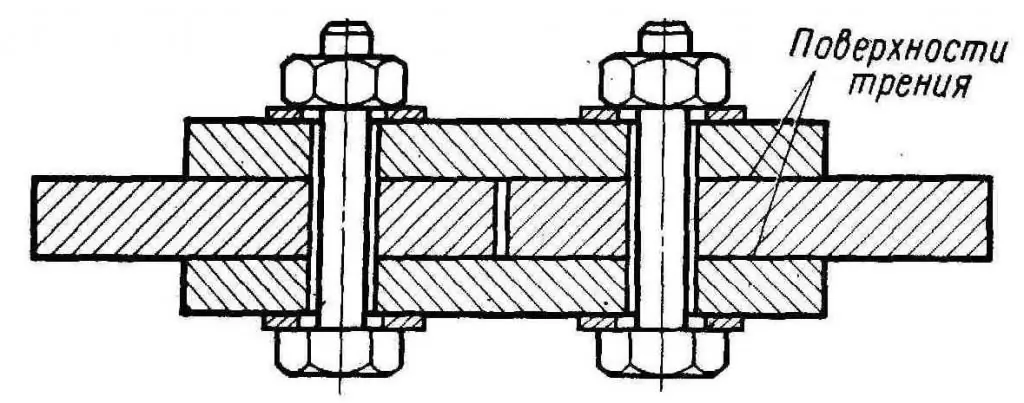
The disadvantage of these connections is the high cost of fasteners. On the other hand, the use of friction joints on high-strength bolts improves reliability and reduces the number of field welds. Accordingly, the complexity of the assembly is reduced by almost 3 times. This type of connection is used in the construction of industrial buildings, in the construction of bridges, cranes, and other lattice structures that experience vibration or dynamic loads.
Promising directions in the development of this constructive solution are the use of removable conservation coatings and the use of "block" manufacturing technology, when the assembly and painting of enlarged units is carried out at the plant, and only the final installation is done at the construction site.
Roughness factor
The required surface roughness, which provides the calculated friction force, is achieved by abrasive, flame treatment of mating surfaces or by using special coatings. The coefficient of friction for calculations is taken from the table below.
| Processing type | Coefficient of friction |
| No Preservation | |
| Brushing | 0, 35 |
| Shot blasting | 0, 38 |
| Cut flame | 0, 42 |
| Shot- or sandblasting | 0, 58 |
| Shot blasting, cleaning of both parts, flame heating up to 300°C around the bolt holes. Heat treatment area - not less than washer size | 0, 61 |
| With subsequent preservation | |
| The first detail is sand or shot blasting, preservation with glue. Second mating part - brushed, no further preservation | 0, 5 |
The type of processing must be indicated on the drawings. The mating surfaces are completely free of ice, snow, oil, scale, rust and other contaminants before bolt assembly.
Sandblasting
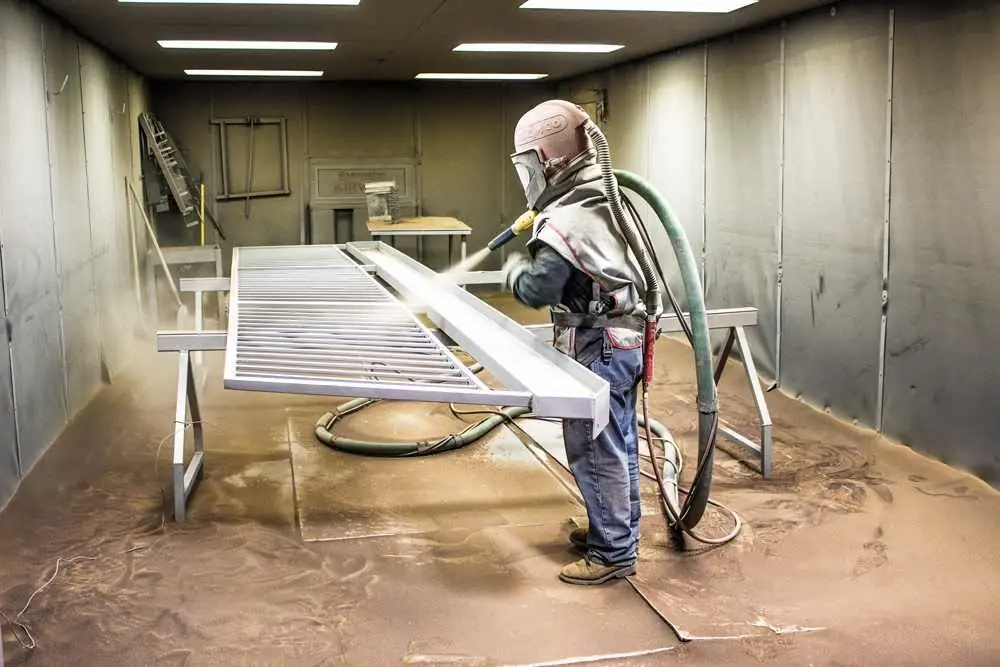

The following requirements apply to the cleaning of metal structures with friction joints using sandblasting technology:
- roughness of the prepared surface - no more than Ra 6, 3;
- complete elimination of oxides and rust (2nd degree of purification according to GOST 9.402-2004);
- degree of surface degreasing - the first (water film break time - more than 1 minute, no oil stains on filter paper);
- preliminary cleaning of compressed air entering the sandblaster from oil and moisture (this is controlled at least 1 time per shift);drying quartz sand to a moisture content of not more than 2%.
After sandblasting, dust must be removed from surfaces by blowing air or wiping with a clean cloth.
Flame treatment
The torch uses an oxy-acetylene flame when cleaning parts. Combustion products (oxides) are subsequently removed with wire brushes. In this case, you can not bring the metal to a shine. Flame cleaning can only be used for parts with a thickness of at least 5 mm, in order to avoid their thermal warping. Processing is carried out in the following modes:
- oxygen pressure - 0.6 MPa, acetylene in cylinders - 0.05 MPa;
- oxygen supply - maximum (the core of the flame should come off the heater nozzle, but not go out);
- torch travel speed - 1 m/min (for thin-walled metal structures 5-10 mm - 1.5-2 m/min);
- next pass should overlap the previous one by 15-20mm;
- torch angle up to 45°.
When carrying out this technological operation, special burners with a wide flame are used.
Shot and brush cleaning

Before processing with metal brushes (brushing), the paint is removed from the surfaces with solvents or in a gas-flame method. It is impossible to clean parts to a metallic sheen, as this prevents the formation of the proper coefficient of friction. Work is carried out using a mechanized pneumatic or electrictool. Remaining dust is removed by blowing with air or a hair brush.
For shot blasting, steel or cast iron chipped (chopped) shot with a fraction of 0.8-1.2 mm is used. Shot blast machines use cast iron shot.
Coatings
To increase frictional forces in flange and friction joints, adhesive substances are also used - glues. As a friction coating, compositions are used, the main component of which is epoxy resin, and the additional ones are a hardener, solvent, accelerator or isopropanol.
Assembly work is carried out in the following order:
- Large-sized structural elements are cleaned by one of the methods described above, except for gas-flame, and also degreased. The time interval between cleaning and gluing should not exceed 0.5 days. Storage at the same time is carried out in conditions of humidity no more than 80%.
- Glue is prepared immediately before use.
- Adhesive composition is applied to the surface of smaller elements and filled with silicon carbide powder 2 mm thick, rolling with a metal roller. It is allowed to glue both contacting parts with glue. Within 1-2 hours, freshly prepared glue should be completely used up.
- Remove excess powder by turning the part and making a few taps.
- Keep time until the epoxy is fully cured.
- The friction joint is assembled on high-strength bolts.
Hardware quality

Fasteners for friction joints must be accompanied by a quality certificate. Bolts, washers and nuts are prepared as follows:
- cleaning of conservation grease in an alkaline solution (exposure in a container for 15-20 minutes);
- drying, blowing with compressed air;
- threading with wrenches or on a lathe;
- mineral oil lubrication;
- complete set of bolts with paired nuts that were used during running;
- storage until assembly work (no more than 10 days).
Calculation of friction connection

The most important connection parameters of this type are:
- friction coefficient Μ on the contact surfaces, determined from the table above, depending on the type of processing;
- bolt torque ratio;
- bolt tightening force;
- torque required to obtain the required value of the previous indicator.
The calculated torque value is found by the formula:
M=K∙N∙dnom, where K is the torque factor determined according to GOST 22356-77;
N - bolt tension force, kN;
dnom - its nominal diameter, mm.
The value of N is determined by the formula:
N=σr∙Sn∙ k,
where σr is the tensile strength of the bolt material, N/mm2;
Sn - bolt cross-sectional area,net, mm2;
k - working conditions coefficient (for steel structures and road bridges it is equal to 1).
The force generated in one bolt contact is found by the formula:
N1=N∙Μ/ɣ, where ɣ is the coefficient of reliability, selected depending on the number of bolts in the connection.
The minimum required number of high strength bolts is determined as follows:
n=P/(k∙N1∙s), where P is the acting longitudinal load, kN;
s - number of contacts in the connection.
Assembly
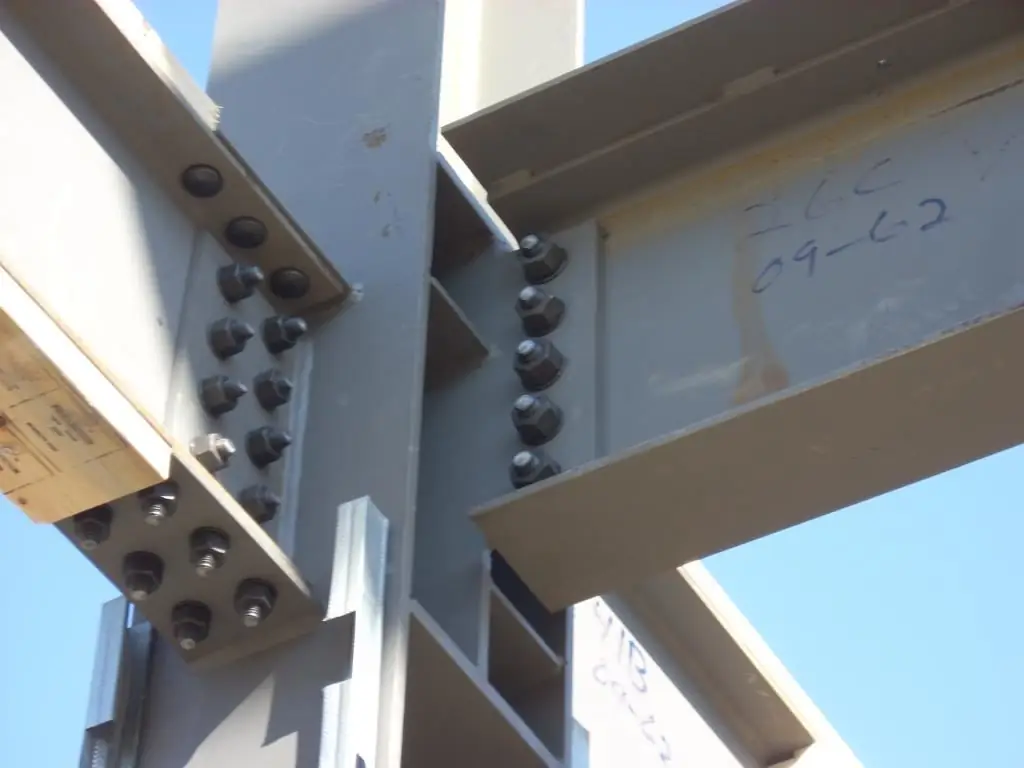

The rules for making a friction connection are to comply with the following technical requirements:
- Before assembly, it is necessary to prepare the surface using one of the above methods (according to the project documentation), remove bumps and burrs that prevent the parts from fitting snugly.
- During transportation and intermediate storage of parts, oiling or contamination of prepared surfaces should be excluded. If this could not be avoided, then a second cleaning procedure is necessary.
- At the first stage of assembly, the parts are aligned with holes using mounting plugs.
- Install bolts with washers (no more than one under the bolt head and nut), tighten them with nuts by 50-90% of the calculated force and check the tightness of the connection.
- Adjust the calculated tightening torque with torque wrenches.
- Apply putty or primer mixed withcement, white clay, chalk. This is done to seal the connection from moisture.
Quality check
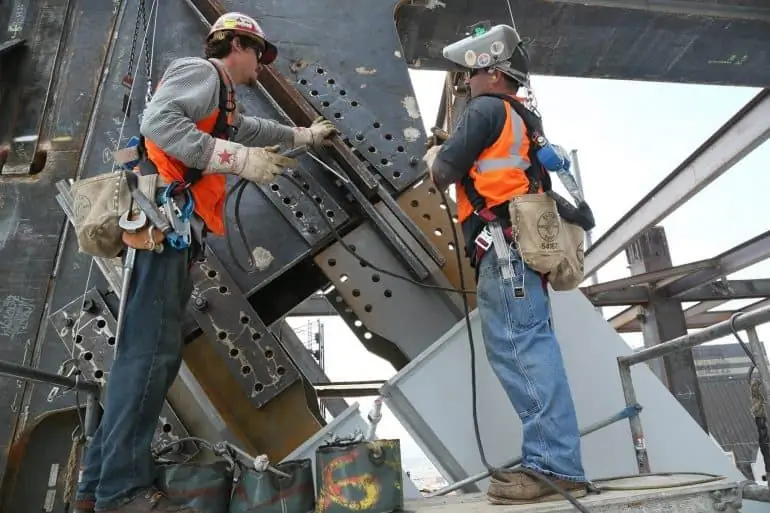

Quality control is carried out at all stages of preparation and assembly. The results of inter-operational checks are recorded in the field connection manufacturing log.
The complex of such works includes the following operations:
- incoming quality control of raw materials, components, purchased products;
- checking tool condition, tare torque wrenches;
- control of surface cleaning and hardware preparation;
- Checking the density of joints tightening (using probes);
- selective tightening torque control;
- pressure control;
- test samples (as required by the customer of civil works).
Recommended:
High-speed trains. high speed train speed

Today there are express trains in almost every country. Let's see which is the fastest train in Russia and the world. Here is a rating of express trains that can reach speeds of over 300 kilometers per hour
Friction clutches: principle of operation, drawing
Friction type clutches are used in clutch mechanisms. The devices differ in parameters as well as design. There are many types of friction clutches
Friction materials: choice, requirements

Modern mechanisms have a complex design, high speeds. Therefore, they use various high-quality friction materials. What they are, what types there are, as well as what are the features of their application, are discussed in the article
Anti-friction materials: overview, properties, application

The article is devoted to antifriction materials. Their properties, features, varieties, as well as areas of application are considered
High-explosive projectile. High-explosive fragmentation projectile. artillery shell

When back in 1330, Berthold Schwarz, a German monk, discovered the throwing properties of gunpowder, he did not imagine that he would become the progenitor of a new god - the god of war

