2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:33
Each organization, regardless of whether it works under the general taxation system (OSN) or under the simplified one (STS), is required to submit annual accounting and tax reporting (hereinafter, reporting documentation - OD). Annual reporting is the most capacious in terms of information on the operation of the enterprise included in it, therefore it is considered very important. The compilation of OD has many goals. The accounting OD of a firm is of interest not only to the authorities, but also to the enterprise itself.

The meaning of drawing up OA
Any OD, whether quarterly or annual, contains information about the current financial position of the company. This information is necessary for state bodies (hereinafter referred to as GO) to present the situation about the real state of affairs of the enterprise. On the basis of reports from firms, the authorities compile general statistics, which are the basis for the analysis and adoption of various decisions at the state level. Also, GOs, using the information provided, monitor the conduct of the company's activities, and in the event of anydefects, omissions or violations impose various pen alties on the enterprise.
In addition to civil defense, ML is also necessary for enterprises themselves. Obtaining regular information about the financial situation of the organization helps its leaders to make various management decisions. OD is very important for the stable operation of the entire enterprise and the realization of its development prospects.

Users of accounting information
Quarterly and annual reports are a summary form of accounting information about the enterprise. Accounting information always has users, that is, those who use this information for various purposes, which were announced above. All users of accounting information are divided into internal and external. The internal ones include heads of firms, higher organizations (if any), management units (if the enterprise is large). External users include the Federal State Statistics Service (Rosstat), the Federal Tax Service (FTS), the Pension Fund (PFR), the Social Insurance Fund (FSS). External users also include any individuals and legal entities, since the accounting OD of any company must comply with the principles of transparency and accessibility to any user.
The above external users of accounting information, with the exception of individuals and not specified legal entities, impose liability on the firm if it does not submit the OD on time. In case of delay, the GO has the right to impose a fine not on the company.

Types of OD
OD is divided into types: statistical, operational, accounting, tax. Statistical OD is intended to be submitted to the statistical authorities. The purpose of operational OD is operational accounting at the enterprise. This type of OD includes those things that are not reflected in the accounting OD, but are also necessary for the normal operation of the company. These things include employee turnouts, production capacity, and the like. A characteristic feature of operational OD is the time of its provision, which, as a rule, is equal to one working day. Accounting OD reflects the financial state of affairs of the enterprise. Tax OD is formed for the purposes of tax accounting at the enterprise.
Accounting OA, in turn, is subdivided by frequency and volume. According to the frequency, OD is quarterly (intra-annual) and annual. In accordance with the law, accounting OD must be incremental, that is, documentation for the first quarter must include information only from the first quarter of the year, OD for the second quarter must contain information from the first and second quarters, and so on. Annual reporting includes information for all four quarters.

In terms of volume, the organization's quarterly and annual reporting can be primary and consolidated (consolidated). If the enterprise has subsidiaries, then the accounting OD within a single subsidiary or within itself will be primary. Consolidated OD is compiled from all primary securities of subsidiaries and the parentorganizations inclusive.
ML Requirements
The main requirements for the preparation of OA are relevance, integrity, reliability, comparability, timeliness.
- Relevance of data characterizes OD as a set of information about the state of the enterprise on a specific date. You cannot provide OD, for example, for the third quarter, in which information for the second will be given.
- Integrity means reporting information about the operation of an enterprise, covering all areas of its activities and the financial position of subsidiaries (if any).
- Reliability of OD enables any user of this information to be sure that it reflects the real state of affairs of the enterprise.
- For the purpose of comparing the work of a company in different periods of time, the OD must comply with the principle of comparability, that is, have units of measurement common to all periods of its work.
- The timeliness of quarterly or annual financial statements obliges an enterprise to provide ML within periods strictly defined by law.
In addition to the above requirements, OD must also meet such principles as mandatory, unity of forms and methods, simplicity, public accessibility, brevity, clarity, publicity.
The procedure for compiling OD
The order of compilation can be conditionally divided into two stages: preparation and formation. At the preparation stage, all the necessary information is collected to form the OD. Also at this stage it is very important to detect and correct (if identified) various errors in accounting, sincetheir presence in the quarterly or annual tax reporting may cause fines from the tax authorities for misrepresenting the true state of affairs of the organization. At the stage of formation, the process of compiling the OD takes place. After completion of both stages, the documentation must be signed by the head, the chief accountant of the company and have seals.

Errors in ML
All errors identified at the stage of preparation of the OD, the organization must correct. Errors are divided into significant and insignificant. An error that affects the management accounting of internal users of this accounting information is recognized as significant. That is, if it is able to greatly change the strategy of the economic activity of the enterprise. Similarly, a significant error is defined for external users. In other cases, the error is regarded as insignificant, but it also needs to be corrected.
Any errors can be freely corrected before the annual accounts are submitted and approved by the GO or other internal or external users. If the OD has already been handed over to users, but has not yet been approved by them, then it is necessary to send the corrected OD to them with a note that the old version has been replaced.
There are two options for fixing major bugs. By reflecting the identified results of errors on account 84 "Retained earnings" or retrospective recalculation.

Basic forms of annual reporting
OD forms, which all enterprises are required to provide to the civil defense: both large and small,are completed form buch. balance sheet (No. 1) and the form of the report on financial results (No. 2, otherwise called the report on loss and profit). In addition, investments must be attached to the balance sheet: form of the report on changes. capital (No. 3) and the form of the report on the movement. den. funds (No. 4). An explanatory note should also be attached to the balance sheet, highlighting those things in the activities of the company that cannot be represented by numbers. Enterprises operating under the simplified tax system may not provide forms 3 and 4. These reports must be submitted to the Federal Tax Service and Rosstat at the end of the year or at the beginning of the next (for the previous one). At the same time, an individual entrepreneur, regardless of his taxation system (DOS or STS), may not provide an annual balance sheet and investments to the Federal Tax Service, but must also submit them to Rosstat once a year.

The above composition of the annual accounts is basic but not exhaustive.
List of annual OD for DOS firms
Below is the list and timing of annual reporting for organizations operating under DOS:
- VAT declaration - until the end of January (FTS).
- Forms 6-NDFL, 2-NDFL - until the beginning of April (FTS).
- Form 3-NDFL (for individual entrepreneurs) - until the beginning of May (FTS).
- Form 1-IP (for individual entrepreneurs) - before the beginning of March (Rosstat).
- Form 4-FSS - until the end of January (FSS).
- Form RSV-1 - until mid-February (PFR).
- Average number of employees - until the end of January (FTS).
- Three types of tax declarations (property tax, transport tax, land tax) - until the end of January (FSS).
- Confirmationmain activity (not for individual entrepreneurs) - until mid-April (FSS).
- Balance sheet and investments - until the end of March (FTS, Rosstat).
List of annual OD for firms on the simplified tax system
Below is the list and terms of annual reporting for organizations operating under the simplified tax system:
- Form 4-FSS - until the end of January (FSS).
- Form RSV-1 - until mid-February (PFR).
- Average number of employees - until the end of January (FTS).
- Two types of tax declarations (transport tax, land tax) - until the end of January (FSS).
- Declaration of the USN - until the end of March (FTS).
- Forms 6-NDFL, 2-NDFL - until the beginning of April (FTS).
- Confirmation of the main activity (not for individual entrepreneurs) - until mid-April (FSS).
- Form PM (for small businesses) - until the end of January (Rosstat).
- Balance sheet and investments - until the end of March (FTS, Rosstat).
Recommended:
Rules for filling out a certificate 2 personal income tax: step by step instructions, required forms, deadlines and delivery procedure

Individuals are required to transfer taxes accrued on their income to state budget funds. To do this, a certificate of 2 personal income tax is filled out. This document displays data on income and tax deductions of individuals. The employer is obliged to submit this documentation annually to the relevant regulatory authorities at the place of its registration. Instructions and rules for filling out certificate 2 of personal income tax will be discussed in the article
A bank statement is The concept, necessary forms and forms, design examples
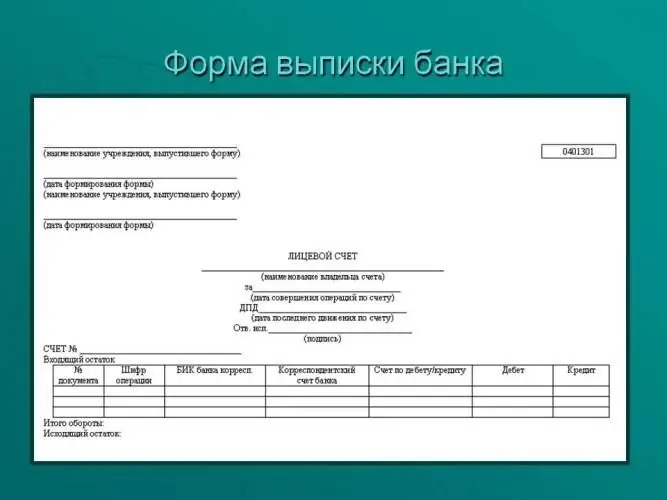
When purchasing any banking product, any client, sometimes without knowing it, becomes the owner of an account with which you can carry out income and debit transactions. At the same time, there must certainly be a certain tool that allows any client to exercise control over the movement of their own funds. This is a bank statement. This is a document that is usually issued upon request to the client. However, not everyone is aware of this possibility
Interim accounting reporting: features, requirements and forms

The Tax Code establishes the obligation of economic entities to form annual and interim financial statements. The purpose of the first document is clear - it contains information about the facts of the economic activity of the enterprise for the reporting period. These data are necessary to verify the correctness of the compilation of records, the reliability of the reflection of operations. As for the preparation of interim financial statements, not all experts understand its importance
Mutual settlements between organizations: drawing up an agreement, necessary documents, forms of forms and rules for filling out with examples

Settlement transactions (offsets and settlements) between business entities are quite common in business practice. The result of these operations is the termination of the mutual rights and obligations of participants in civil relations
FSS reporting: form, deadlines and delivery procedure. Reporting to the Social Insurance Funds: registration rules

Regardless of the taxation regime, all entrepreneurs are required to submit a quarterly report to the Social Insurance Fund in the prescribed form (4-FSS). The report is submitted even if the activity was not carried out and the employees were not paid wages. Such reporting is called zero and is mandatory

