2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:37
To regulate and optimize the functioning of boiler units, technical means began to be used even at the initial stages of automation of industry and production. The current level of development in this area can significantly increase the profitability and reliability of boiler equipment, ensure the safety and intellectualization of the work of maintenance personnel.
Objectives and goals
Modern boiler room automation systems are able to guarantee trouble-free and efficient operation of equipment without direct operator intervention. Human functions are reduced to online monitoring of performance and parameters of the entire complex of devices. Automation of boiler houses solves the following tasks:
- Automatic start and stop of boilers.
- Regulation of boiler power (cascade control) according to the given primary settings.
- Control of feed pumps, control of levelscoolant in the working and consumer circuits.
- Emergency stop and activation of signaling devices, in case the operating values of the system go beyond the established limits.
Automation Object
Boiler equipment as an object of regulation is a complex dynamic system with many interrelated input and output parameters. The automation of boiler houses is complicated by the fact that the speed of technological processes in steam units is very high. The main adjustable values include:
- flow rate and pressure of the coolant (water or steam);
- discharge in the furnace;
- feed tank level;
- In recent years, increased environmental requirements have been imposed on the quality of the prepared fuel mixture and, as a result, on the temperature and composition of smoke exhaust products.
Automation levels
The degree of automation is set when designing a boiler house or when overhauling/replacing equipment. It can range from manual control according to indications of instrumentation to fully automatic control according to weather-dependent algorithms. The level of automation is primarily determined by the purpose, capacity and functional features of the operation of the equipment.
Modern automation of the boiler room implies an integrated approach - the subsystems for monitoring and regulating individual technological processes are combined into a single network with functionalgroup control.
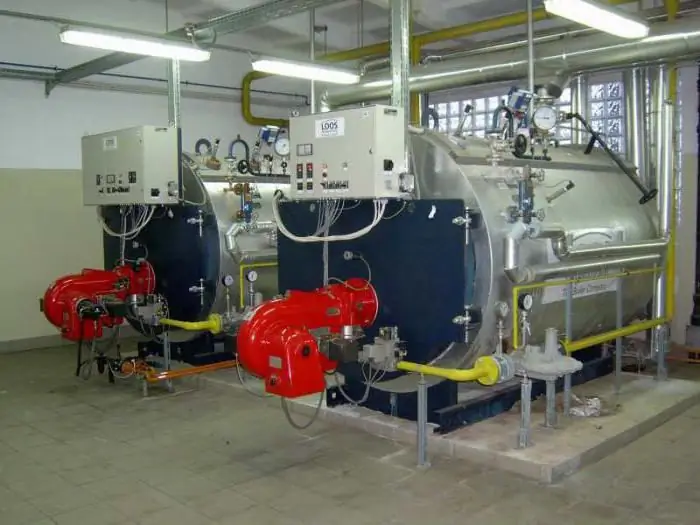

Overall structure
Automation of boiler houses is built on a two-level control scheme. The lower (field) level includes local automation devices based on programmable microcontrollers that implement technical protection and blocking, adjustment and change of parameters, primary converters of physical quantities. This also includes equipment designed to convert, encode and transmit information data.
The upper level can be represented as a graphical terminal built into the control cabinet or as an operator's workstation based on a personal computer. It displays all the information coming from the lower-level microcontrollers and sensors of the system, and enters operational commands, adjustments and settings. In addition to process dispatching, the tasks of optimizing modes, diagnosing the technical condition, analyzing economic indicators, archiving and storing data are solved. If necessary, information is transferred to the general management system of the enterprise (MRP / ERP) or locality.
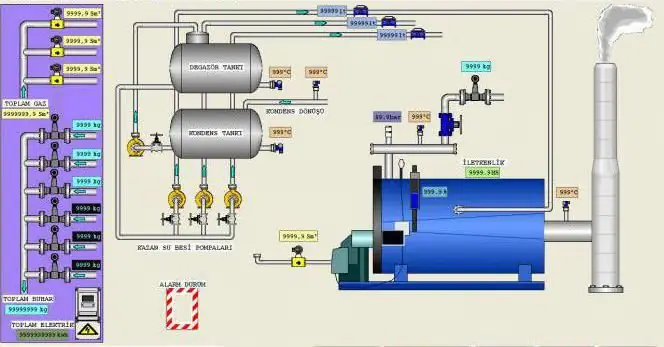
Automation of boiler equipment
The modern market is widely represented by both individual instruments and devices, as well as domestic and foreign-made automation kits for steam and hot water boilers. Automation tools include:
- ignition and flame control equipment, starting andcontrolling the process of fuel combustion in the combustion chamber of the boiler unit;
- specialized sensors (draft and pressure gauges, temperature and pressure sensors, gas analyzers, etc.);
- actuators (solenoid valves, relays, servo drives, frequency converters);
- control panels for boilers and general boiler equipment (panels, touch screens);
- switching cabinets, communication lines and power supply.
When choosing technical means of control and monitoring, the closest attention should be paid to safety automatics, which excludes the occurrence of emergency and emergency situations.

Subsystems and functions
Any boiler room automation scheme includes control, regulation and protection subsystems. Regulation is carried out by maintaining the optimal combustion mode by setting the vacuum in the furnace, the primary air flow rate and the coolant parameters (temperature, pressure, flow rate). The control subsystem outputs the actual data on the operation of the equipment to the human-machine interface. Protection devices guarantee the prevention of emergency situations in case of violation of normal operating conditions, the supply of a light, sound signal or the shutdown of boiler units with fixation of the cause (on a graphic display, mnemonic diagram, shield).

Communication protocols
Automation of boiler plants based on microcontrollers minimizes the use in functionaldiagram of relay switching and control power lines. To connect the upper and lower levels of the automated control system, transfer information between sensors and controllers, to translate commands to actuators, an industrial network with a specific interface and data transfer protocol is used. The most widespread standards are Modbus and Profibus. They are compatible with the bulk of the equipment used to automate heating facilities. They are distinguished by high rates of reliability of information transfer, simple and understandable principles of operation.

Energy saving and social effects of automation
Automation of boiler houses completely eliminates the possibility of accidents with the destruction of capital buildings, the death of service personnel. ACS is capable of ensuring the normal functioning of equipment around the clock, minimizing the influence of the human factor.
In light of the continuous rise in fuel prices, the energy-saving effect of automation is not the least important. Saving natural gas, reaching up to 25% per heating season, is provided by:
- optimum "gas/air" ratio in the fuel mixture in all operating modes of the boiler house, correction by the level of oxygen content in the combustion products;
- the ability to customize not only boilers, but also gas burners;
- regulating not only the temperature and pressure of the coolant at the inlet and outlet of the boilers, but also taking into account environmental parameters(weather-compensated technology).
In addition, automation allows you to implement an energy-efficient algorithm for heating non-residential premises or buildings that are not used on weekends and holidays.
Recommended:
Aircraft device for dummies. Aircraft device diagram

Few people know how an airplane works. Most don't care at all. The main thing is that it flies, and the principle of the device is of little interest. But there are people who cannot understand how such a huge iron machine rises into the air and rushes at great speed. Let's try to figure it out
Nuclear power plants. Nuclear power plants of Ukraine. Nuclear power plants in Russia

Modern energy needs of mankind are growing at a gigantic pace. Its consumption for lighting cities, for industrial and other needs of the national economy is increasing. Accordingly, more and more soot from burning coal and fuel oil is emitted into the atmosphere, and the greenhouse effect increases. In addition, there has been more and more talk in recent years about the introduction of electric vehicles, which will also contribute to the increase in electricity consumption
The largest power plants in Russia: list, types and features. Geothermal power plants in Russia
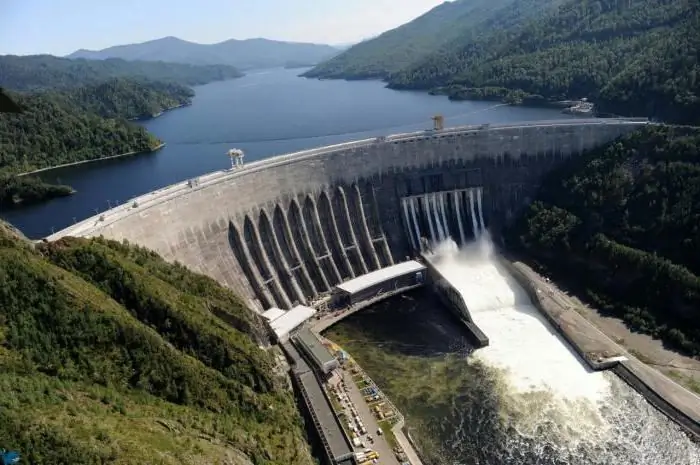

Russia's power plants are scattered in most cities. Their total capacity is enough to provide energy for the entire country
Aeration plants: definition, types, principle of operation, production plants and do-it-yourself tips
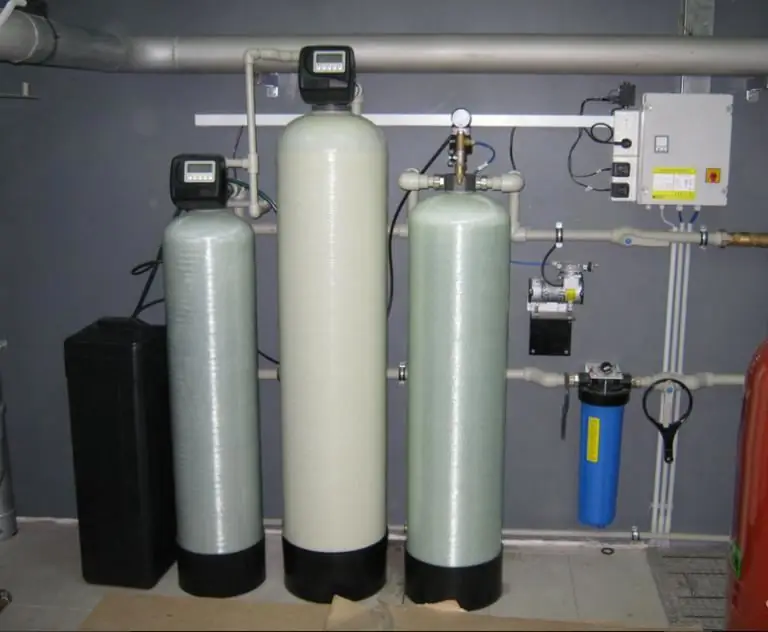

Installation of the aeration column provides for the connection of a sump so that it has two flushing modes - direct and reverse. Combined use allows you to wash the filter element more efficiently. It is better to take a bigger mud trap. Small filters become clogged within a short time and require frequent rinsing. It is better to use a glass flask
Variable capacitor: description, device and diagram

Currently, people almost everywhere use radio-electric devices and other things powered by electricity. However, few people wonder how it all works. One of the small elements is a variable capacitor, but it performs a rather important function