2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:43
Prototyping in the general sense is one of the varieties of design and research modeling. The task of such a study is the possibility of a visual study of the properties of the designed object, structure or product. Modeling is the process of creating a three-dimensional image that allows you to determine the parameters of the spatial structure, dimensions, plasticity and proportions of surfaces. When creating a layout, the designer is primarily determined by its scale, as well as color and texture, which could reflect the main features of the finished product.
Goals and objectives
The need for professional prototyping exists in many areas of activity: in architectural construction, in the initial production stages in industry, in the advertising business and demonstration activities of companies. In some areas of activity, a higher degree of rigor in the work is required.
For example, the task of creating industrial layouts usually consists in visual demonstrationthe functioning of various parts and assemblies in miniature, as well as the representation of the dynamic processes occurring in them. In the commercial or advertising direction of this activity, the qualitative perception of the object at the visual level is rather important. Modeling in design often requires finding a compromise solution between the author's idea and technical limitations when creating a layout.
Process Features
First of all, the parameters and nuances during development depend on the area in which the layout is created. However, there are a number of generic features suitable for each type of layout. The designer will certainly consider the following questions before starting development:
- Determining the typology of an object or layout objects.
- Calculation of all design stages, setting work tasks.
- Choosing the most suitable material and layout technology.
- Approximate estimate of the complexity and real complexity of the project.
- Finding the design features of the layout. Determination of sufficient granularity for each object.
- Finding a suitable production area for assembly. Schedule the nuances during transportation and long-term storage of the finished layout.
- Comparison of your own established traditions, preferences and personal experience with current methodological recommendations and current production standards.
The layout basics listed above allow the designer to decide on the right scale. It is worth noting,that this moment is one of the key and affects all future work.
To better understand the features of such activities, you should consider several basic types of layouts. At the same time, there is no unambiguous classification, because each development can be attributed to several types and types at once, depending on the field of activity, as well as the methods and technologies used.

Paper color layouts
Paper prototyping uses a range of materials, including cardboard, foam board, styrofoam and, of course, plain paper. Later, the finished layout is pasted over with a colored film on top. The scope of this type of application can be anything, but it is worth noting that the detail of paper products is worse than that of similar projects made of plastic or other hard materials.
Among other things, paper layouts are less durable and more susceptible to temperature changes and fluctuations in indoor humidity than any other. Frequent transportation can also be fraught with such materials. At the same time, paper and cardboard prototyping has one significant plus - it is very profitable if you have a small budget and only need one demonstration.
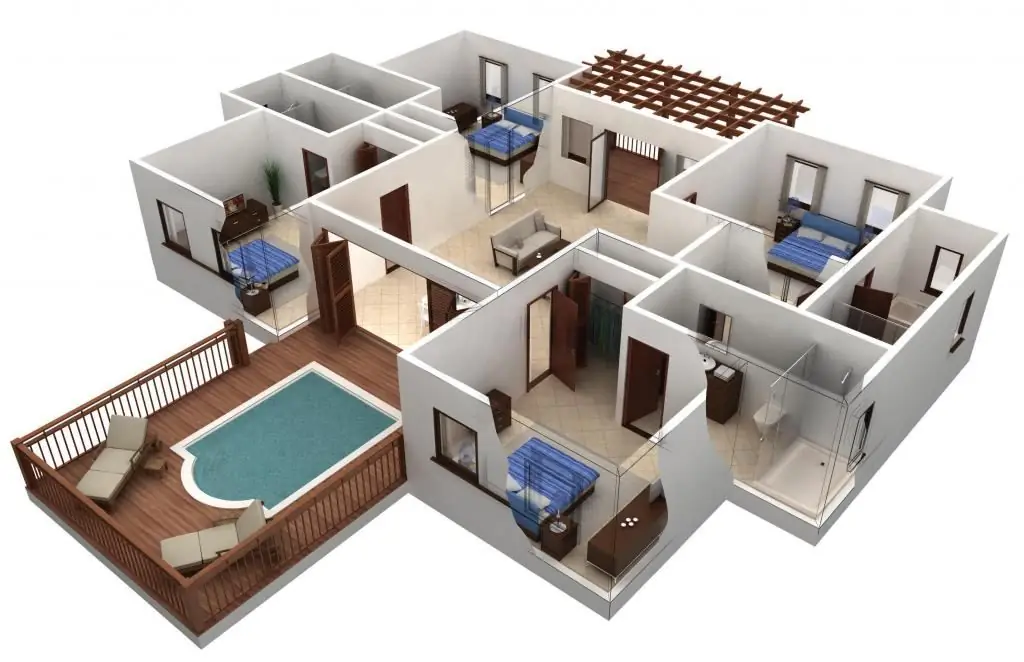
Interior layouts
Designed for composition visualization and interior design. Models of interior spaces are made on a scale from 1:10 to 1:50. Often the outer walls and ceiling are not shown as the main purpose is to emphasize the interior finish and layout. Furniture, machines andother content of the interior is depicted very schematically, that is, without observing the exact form.
Foam plastic is preferred as a material, although paper layout is also acceptable. Exhibition projects are made from hard materials like plexiglass and plastic and then painted. Preliminary sketch-graphic modeling is usually carried out immediately before the layout of equipment and other pieces of furniture.

Architectural models
In construction, the exact correspondence between the prototype and the final structure is paramount. Architectural layout allows some degree of distortion of proportions, but only within normalized limits. Basically, designers create such layouts according to pre-prepared sketches and draft designs. The resulting models can be both collapsible and monolithic. The ability to remove the roof or several floors of the building allows you to better study the internal structure and layout.
In architecture, prototyping is, first of all, the creation of an accurate or as close as possible to a real spatial and volumetric model of a building on a certain scale. In addition, this type applies to other related areas: investment, marketing and advertising. In such a layout, a whole group of structures or just a single fragment of a building, such as an apartment or a room, can be shown.
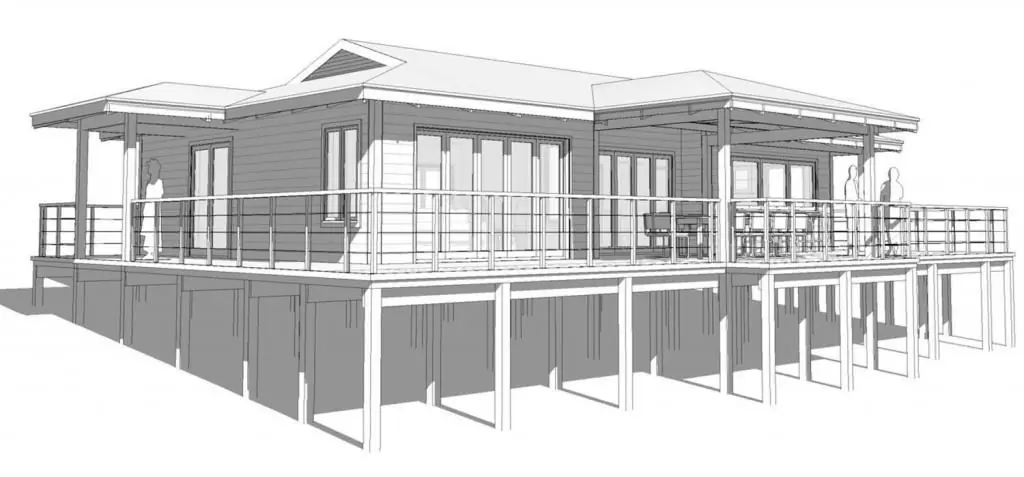
Planning layouts
Such layouts closely intersect with architectural layouts, but implya copy of the whole site with the districts or groups of structures located on it. This category includes plans for cottage settlements, urban planning projects and landscape panoramas. A feature of the manufacture of such layouts is considered to be the mandatory presence of several sub-models.
Demand for this type increases in preparation for development or for solving certain economic problems, for example, optimizing road traffic or laying new communications. The marketing industry also uses such layouts, but does not require the designer to observe special accuracy and proportions.
Special attention should be paid to the convenience of transportation, because large-scale projects of entire cities can take up significant space. In such cases, the working canvas is divided into several parts in advance.
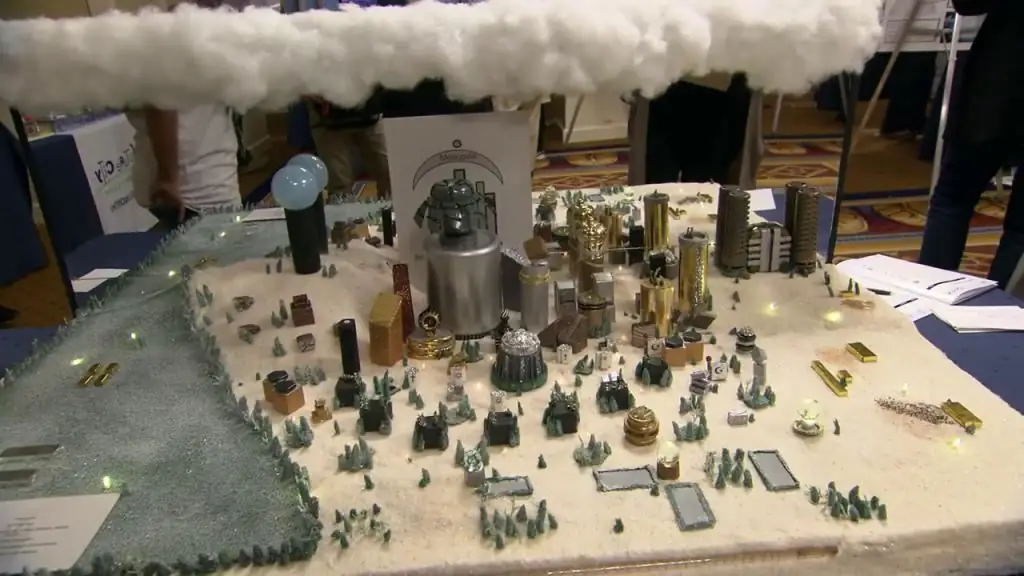

Technical and mechanical layouts
Basically, this type is represented by various modes of transport with functioning nodes: cars, yachts and ships, as well as aircraft. Technical prototyping is the creation of a fully functioning prototype with all mechanical and electrical elements. It is possible to face such works in domestic conditions. For example, a toy railway with a train running along it, in which the lighting is fully functional.
However, models of cars and other vehicles for children, although they are an example of technical prototyping, in no way reflect its technological processes and methodsmodeling while working on professional projects.
Mechanical mock-ups are often visual miniatures that demonstrate various technological processes in real time. Large overall projects, in turn, show the functional or motor capabilities of devices and mechanisms.

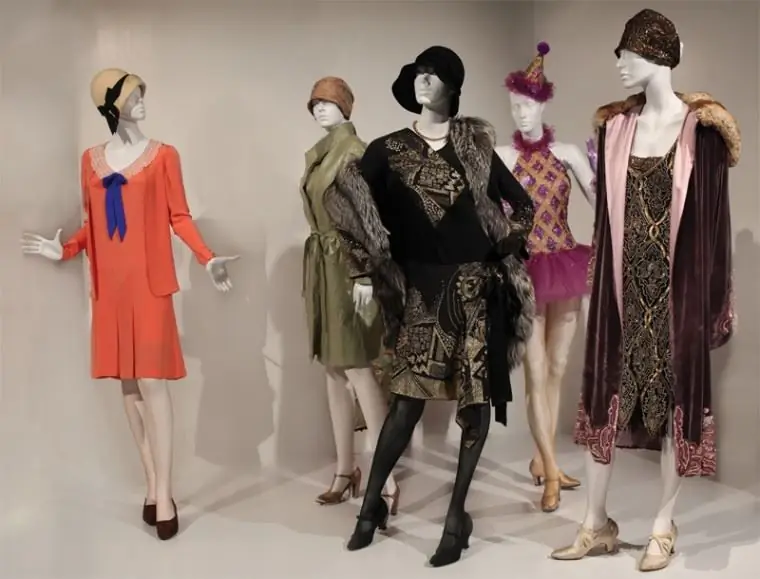
Clothing design
Otherwise, this method of modeling is also called the tattooing method. The conceived project is carried out by the designer directly on a mannequin or a person. The master forms a ready-made layout from the selected fabric using pins. In the future, the material is removed and placed on the table, and the designer proceeds to the next step - adjusting the created lines according to the patterns and the ruler.
Most often this method is used in the manufacture of outerwear with a complex cut, various dresses, skirts and jackets. The designer, as a rule, has in his arsenal several tricks that give clothes a voluminous shape. When prototyping, there is no need to design patterns on paper. Among other things, this option allows you to take into account the individual characteristics of the figure and perform better tailoring.

Composite layout
The main elements that are reproduced when building a composition should be considered the volumetric and spatial structure of the object, its tectonics and layout, the proportions of the main parts and dominants, as well as rhythmic and plastic layers.
Organization of a properly builtCompositions are one of the main design tasks when developing a layout. At the same time, you need to pay attention not only to the main constituent elements. In particular, not only the layout itself, but also the sub-layout can be called the compositional basis of layout, because its size will determine the force of the impact of the composition on space in the same way as a real object of architecture does it in life.
Among other basics of composition, the following are distinguished:
- observance of the proportions of all elements and parts;
- creating harmonic plastic transitions between surfaces;
- determination of exact spatial and dimensional characteristics;
- identifying the correct figurative-plastic character, texture and color graphics.
Main materials used
The capabilities of modern specialists are expanding significantly due to the active introduction of industrial and even household 3D printers. The list of various synthetic materials for 3D printing is quite wide and is limited only by the goals and capabilities of a single device.
Of course, traditional paper and cardboard are used in some cases. However, the most relevant materials are considered to be polystyrene and plastic. Prototypes of gift and art models, future architectural and industrial objects are often made of metal and wood. Clay, gypsum, plexiglass and plasticine are other common materials for prototyping.
Main layout functions
The role of the design functions of layouts is the formation and implementation of the idea, the rationale for design decisions, the transformation and detailing of the author's vision. The prototype is brought into line with the chosen thinking system and adjusted to ideal forms.
Exploratory layout function - a design search carried out by iterating through different directions to transform an object. Thus, there is a basis for analysis, development of a modeling strategy and making adjustments.
In fact, prototyping is a means for carrying out project activities and monitoring their results. The corrective function allows you to set in this case the possibility of implementing plans and ideas, as well as to combine various requirements. It indicates the need for changes and reduces the number of possible errors to a minimum.
Heuristics and learning functions
No less interesting is the heuristic function. It is based on the presence of a feedback between what is visually demonstrated and what a person feels at that moment. Experts believe that it is this function that encourages designers to invent, activates their creativity and provides other ways to overcome difficulties in the course of solving design problems.
The educational function works just as effectively, thanks to which the designer masters the technique of thinking and developing in three-dimensional space, develops imagination and a sense of plastic, proportional-rhythmic and geometric harmonies.
Recommended:
Timekeeper: job responsibilities, required education, conditions of admission and features of the work performed

For the first time, the profession began to be mentioned at the end of the 18th century in connection with the formation of the largest enterprises and a large staff. A specialist was needed who would monitor the attendance of employees at work. The job responsibilities of the timekeeper included monitoring the stay of workers at the enterprise
Profession nutritionist: concept, definition, required education, admission conditions, job responsibilities and features of the work performed

Dietology is a section in medicine that is dedicated to the organization of proper and rational nutrition. Therapeutic diets help people overcome existing he alth problems and achieve good results in the treatment and prevention of various diseases. That is why proper and balanced nutrition is the source of well-being and he alth
Senior cashier: concept, definition, required education, admission conditions, job responsibilities and features of the work performed

The general list in the job description of the senior cashier as a whole comes down to knowledge of the main rules of the organization (trade, banking, etc.), sanitation, safety, and the rules for operating the equipment used in the work. This employee is endowed with great powers, responsibilities, rights, so it is so important to draw up a job description as fully as possible. Otherwise, the employee may not live up to the expectations of management
Materials released to production (posting). Accounting for the disposal of materials. accounting entries

Most of all existing enterprises can not do without inventories used to produce products, provide services or perform work. Since inventories are the most liquid assets of the enterprise, their correct accounting is extremely important
Pharmacologist is The concept, definition, required education, admission conditions, job responsibilities and features of the work performed

Who is this? Differences between a pharmacologist and a clinical pharmacologist, a pharmacist and a pharmacist. Features of pharmacological education. The main tasks and job responsibilities of a specialist, his basic skills. Place of work of a pharmacologist, interaction with colleagues and patients. Area of professional activity. When to contact a pharmacologist?

