2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:32
The basis for monitoring and analyzing the financial, economic, investment activities of an organization are accounting data. Their reliability and timeliness determine the relationship of the enterprise with regulatory authorities, partners and contractors, owners and founders. The main source of information about the state of all types of company assets, settlements, debt obligations and capitals is financial statements. Its first and main form is the balance, it is calculated on a specific reporting date according to accounting registers, which are called synthetic accounts.
General definition
The movement of all types of enterprise funds until the end of the reporting period is carried out in the appropriate units of measurement on the accounts of accounting. They are grouped according to the principle of homogeneity of assets or capital. The system of registers provides the possibility of constant data control, which is necessary for making adequate and timely management decisions. Synthetic accounts are a unit of accounting accountinginformation on a particular type of funds. They reflect all changes in the availability of the object, the interim balance, sources of income and expense items. Synthetic and analytical accounts look like a two-sided statement (table), which has a name and a number corresponding to the approved system. On the territory of our country, a unified list is used, which can be finalized by the enterprise, depending on the economic need.

Chart of Accounts
The correspondence of reporting indicators and the actual presence of a certain type of asset (debt, capital, settlements) should be easily determined based on the relevant register. Due to the unified chart of accounts operating on the territory of the Russian Federation, this requirement is observed. The current document was approved by the order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 under the number 94-n, in fact, the November 2010 edition is used. The chart of accounts is a grouping of accounting objects involved in business transactions with the definition of their balance sheet. It reflects synthetic accounts and sub-accounts recommended for detailing, i.e. accounting positions of the first and second levels. Each of them has a unique number and name of the object of economic activity. Based on a unified list, each business entity determines a working chart of accounts in accordance with the areas of its main activity.
Classification
Accounting accounts are systematized by groups of objects: current, non-current assets,calculations, production costs, capital, financial result. Each of the sections contains a list of registers, which are classified according to various criteria: in relation to balance, purpose, degree of detail, economic content. Accounts are inventory, calculation, distribution, off-balance sheet, stock, resultant, etc. Important for the application of the principle of double entry is the division into active (50, 10, 01, 20), active-passive (60, 76, 62, 71) and passive (84, 96, 80, 75) accounts. Belonging to a group determines the properties of the register and the procedure for conducting operations on the object by means of the organization. According to the degree of detail of information, the following division is accepted:
- Synthetic accounts.
- Subaccounts.
- Analytical.

In the chart of accounts, there is a list of recommended sub-accounts, which are opened additionally in case of economic need. The enterprise develops analytical accounting registers independently. Through internal documents, an accounting policy is formed in the field of detailing accounting information. Accounts of synthetic and analytical accounting are interconnected, a transcript is created for a larger object, the data of which corresponds to the head register. In this case, it is necessary to observe the sequence of control of accounting objects. Information posted on analytical accounts is transferred to a sub-account, the sum of indicators of the second stage is the value for recording in the corresponding synthetic number and contentregister.
Characteristic
Synthetic accounting accounts are a general register for all objects of the organization's activities. Their main characteristic is a direct connection with reporting and balance sheet, so accounting is kept exclusively in monetary terms. Any enterprise is obliged to open synthetic accounting accounts on the basis of the initial (opening) balance sheet of assets and sources of their formation. In the process of movement of funds arising from the implementation of activities, the corresponding changes are reflected in the debit and credit of the register. The calculated indicators of the balance are transferred to the next type of accounting documents, on the basis of which all types of reporting are formed. The asset and liability sections of the balance sheet consist of positions whose names correspond to such an information storage unit as a synthetic account. Correspondence example: 80 “Authorized capital” is located in the 3rd section of the liability “Capital and reserves”, 10 “Materials” is the 2nd section of the asset “Working capital”, etc. This reporting procedure is based on the accounting movement registers objects greatly facilitates the control and analysis of the company's work for a certain period.

Doing Order
At the initial stage of activity, each organization evaluates the availability of assets, capital, investment funds and borrowed funds at its disposal in monetary terms. These indicators form a balance, on the basis of which it is necessary to open synthetic accounting accounts. In the ledgerthe amount of the value of the asset or debt will appear as a balance (balance) at the beginning of the activity. Each accounting object is assigned a number in accordance with the working chart of accounts approved by the enterprise.
For example, the fixed production assets owned by LLC "X" are valued at 10 conventional units, respectively, register number 01 "Fixed assets" is formed. Its initial balance is 10 c.u. That is, this entry is posted in the balance sheet and is reflected in the "active synthetic account" register. An example for a passive account: the amount invested by the founders as the authorized capital of the enterprise is 5 conventional units. A synthetic passive account No. 80 “Authorized capital” is opened, the value of its initial balance is 5 conventional units. In the future, changes in the register occur on the basis of relevant accounting documents, certificates, calculations. At the end of the billing period, a closing balance is formed on the accounts, which characterizes the availability of assets and their sources on a certain date. Its value is reflected in the balance sheet, or chess sheet, which, in turn, serves as a data source for the General Ledger and balance sheet.
Documents
The process of reflecting all movements and business transactions in accounting is unified by the relevant legislative acts. Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 173n dated December 15, 2010 regulates the list of primary documentation, which is the basis for making changes to synthetic and analytical accounts. For every change in registerthere is a form. For example, a cash receipt order is used to process cash receipts at the cash desk, and a payroll is used to reduce debt to employees. For analytical accounting, the list of documents has been significantly expanded, the enterprise selects the forms necessary for detailing synthetic accounting data. For example, a time sheet or payroll is used by an accountant when generating transcripts for account No. 70.

Subaccount
Depending on the main activity, an enterprise can use a large amount of assets and attract various sources for this. For their detailed accounting, transcripts for synthetic accounts are provided. The numbers of such registers correspond to the head object, the level of detail varies depending on the number of subaccounts. Regulatory documents regulate their number and names, records are made in monetary terms. The greatest number of clarifications require accounts that reflect assets (08, 10, 41, 55) and performance indicators (91, 98, 90). The use of these registers in full or in part, the company decides independently, depending on the economic situation. With automated accounting, subaccounts are included in the standard chart of accounts, the 1C Accounting program allows you to activate the required number of used registers through the settings.
Relationship
Sub-accounts are second-order registers, they are not reflected in the balance sheet, but their results are summarized for eachsynthetic account to which they refer. During control, three equalities must be observed:
- Synthetic account balance at the beginning of the period=the sum of the balance of open sub-accounts.
- Turnover on the debit and credit of the synthetic account=the sum of the values of turnover on sub-accounts.
- Balance at the end of the period=the sum of the balances at the end of the period for sub-accounts.

Analytics
Synthetic accounting accounts reflect the total monetary amount of the presence of an object of assets or the source of their formation. Sub-accounts allow you to detail their content, but for a complete analysis of the availability of certain resources, calculations are not enough. Therefore, enterprises use analytical accounting, which allows you to track the movement of objects in kind and in cash. Before opening synthetic accounts, the organization allocates all available assets to analytical positions, which together give an indicator reflected in the balance sheet. The need to create and maintain detailed registers depends on the direction of the company and its size. Not all synthetic accounting accounts need to be detailed, for some open sub-accounts are sufficient, and advanced analytics of the third and fourth levels is used only for a large range. All opened registers are interconnected by a certain economic object. An example of the broadest detail is account 10 "Materials". 11 sub-accounts are opened for it, each of which is deciphered by analytical accounting of several levels. Schemeaccount looks like this:
- Warehouse X (Quantitative Accounting).
- Financially responsible person (quantitative and monetary accounting).
- Brick (quantitative and monetary accounting).
- Building materials (cash accounting).
- Materials, synthetic account No. 10 (cash account).

Analytics by types of companies is used to account for settlements with various counterparties. For example, account No. 62 "Settlements with buyers" may contain more than 100 accounting positions, the debt or advances of which are important for controlling the turnover of the company's funds. Analytics in this case provides an opportunity for extended control over contracts and counterparties.
Doing Order
Synthetic and analytical accounts are opened simultaneously for positions requiring decryption. All types of movement of detailed information are reflected in parallel in registers of three orders. The number of analytical accounts and their names are not regulated by law, the enterprise independently develops this type of registers. To formalize the processes of movement of accounting objects, there are a number of documents that can be filled out by the accounting department or a financially responsible person. For example, inventory cards, registers, time sheets, etc. The resulting volume of documents is quite difficult to process without the use of modern computer technology. Analytical accounting data are summarized in turnover sheets, which are compared with synthetic accounting data and sub-accounts. Detailed information allowsrespond more quickly to changes in asset inventories, simplifies the inventory of goods and materials, settlements, capital.
Interaction

All steps of one accounting object are vertically dependent. Analytical accounting data are summarized and reflected in the corresponding sub-account. If there are several open registers of the second order, their values are added up and reflected in a synthetic account, from which they are transferred to the company's balance sheet. When controlling credentials, the following groups of equalities must be observed:
- Synthetic account balance initial=amount of balance initial for open sub-accounts.
- Balance initial on sub-account=sum of balance initial on open analytical accounts.
In this case, the revolutions for dt and tot must correspond to the same sequence. The balances of synthetic accounts that do not have sub-accounts, but have a large number of analytical registers, are calculated as the sum of the balances of all open positions. Verification of data consistency should be carried out regularly, using turnover sheets or chess sheets.
Automation
Large volumes of accounting information are quite difficult to process, so modern enterprises install computer and computing equipment equipped with appropriate programs. For our country, the most popular product in this market is "1C Accounting". This program is based on the nationallegislation, taking into account the requirements of the tax inspectorate and in accordance with all regulations. For an enterprise of any form of ownership and activity, it is easily regulated. To account for synthetic accounts and analytics of any level, settings are provided that allow not only to keep current records, but also to receive information on any position in the context of interest at the current moment.
Recommended:
Bank accounts: current and current account. What is the difference between a checking account and a current account

There are different types of accounts. Some are designed for companies and are not suitable for personal use. Others, on the contrary, are suitable only for shopping. With some knowledge, the type of account can be easily determined by its number. This article will discuss this and other properties of bank accounts
Synthetic fibers. Synthetic polyamide fiber

Synthetic fibers began to be produced industrially in 1938. At the moment, there are already several dozen of them. All of them have in common that the starting material for them is low molecular weight compounds that are converted into polymers through chemical synthesis. By dissolving or melting the resulting polymers, a spinning or spinning solution is prepared. Fibers are formed from a solution or melt, and they are only then subjected to finishing
Accounts receivable and accounts payable is The ratio of accounts receivable to accounts payable. Inventory of receivables and payables

In the modern world, various accounting items occupy a special place in the management of any enterprise. The material presented below discusses in detail the debt obligations under the name "receivables and payables"
What is the difference between an apartment and an apartment? The difference between an apartment and an apartment

The residential and commercial real estate market is incredibly vast. When offering housing, re altors often refer to an apartment as an apartment. This term becomes a kind of symbol of success, luxury, independence and we alth. But are these concepts the same - an apartment and an apartment? Even the most superficial glance will determine that these are completely different things. Consider how apartments differ from apartments, how significant these differences are, and why these concepts should be clearly distinguished
Balance: types of balance. Types of balance sheet
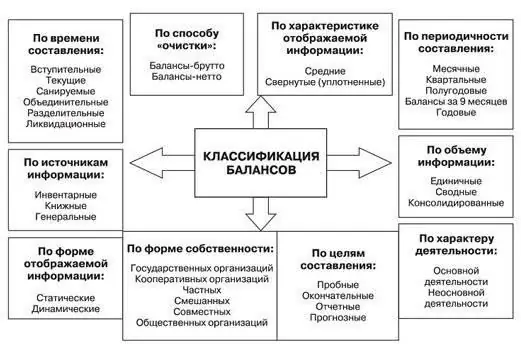
The balance sheet is the most important accounting document of an institution. What is it, what are the rules for filling it out, types and classification

