2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:41
The idea of defeating aircraft and lightly armored vehicles led to the creation of heavy machine guns with a caliber of more than 12 mm. Such machine guns were already able to hit a lightly armored target, reach a low-flying aircraft or helicopter, as well as shelters behind which there were infantry.
According to the classification of small arms, the 14.5-mm KPVT machine gun is already adjacent to artillery weapons. And in design, heavy machine guns have much in common with automatic guns. At the same time, individual modifications of large-caliber machine guns have more shot energy than small-caliber automatic guns.
Design task
Before designing the KPVT (Machine gun designed by Vladimirov), it was necessary to choose the concept of the weapon. The 20-mm V-20 aircraft gun of its own design was taken as a basis.
The first machine gun was presented for factory testing in November 1943. The weapons acceptance commission noted a number ofnew design benefits such as:
- seriously designed automation;
- The strength of the machine gun components meets the requirements of combat anti-aircraft weapons.
At the same time, the commission especially emphasized the possibility of using a machine gun in air defense. By April 1944, the People's Commissariat ordered Plant No. 2 to produce for military testing:
- machine guns (under the designation KPV - 44) - 50 pieces;
- anti-aircraft gun - 1 pc.
When the Great Patriotic War ended, both the machine gun and the anti-aircraft gun were sent for military trials in May 1945. And already in 1946 they were put into service, and the production of 14.5-mm infantry PKP and its anti-aircraft version was launched at the plant. Degtyarev. By 1952, eight thousand installations of the anti-aircraft version of the KPV were delivered to the armed forces.
Also, synchronously, work was underway to create a KPVT (14.5 mm machine gun) to install an upgraded version (with electric drive) on tanks and various types of infantry fighting vehicles.
Machine gun device
Automatics have been redesigned so that the recoil of the barrel during a short stroke uses the energy of powder gases, which are discharged through a special muzzle device (recoil amplifier).
The weighted barrel of Vladimirov's machine gun is made for firing a cartridge with a large charge of gunpowder. The movable barrel during the operation of the machine gun made it possible to make the operation of the automation smooth, which, in turn, does not increase the stroke length of the entire system.

The design of the trigger provides only automatic fire when firing from the rear sear. As soon as the drive of the movable system is locked into the extreme forward position, a shot is fired.
KPVT - a machine gun with automatic safety locks that prevent the bolt from locking and firing a shot when the barrel is not attached correctly. The fuse also blocks the feed of the tape into the machine gun if the cartridge has not been removed from the link.
It was possible to switch the feed direction of the tape, which made it easier to install the machine gun on complex installations. Accordingly, the reload handle can be easily installed on the left or right side. Also, the advantages include the presence of a quick-detachable barrel, which is removed along with the casing, for which a handle is provided on the latter.
KPVT in numbers
Vladimirov's machine gun is so powerful that a bullet fired from it retains its lethality over the entire flight distance, which is from 7 to 8 km!
But since the dispersion of bullets increases at such large distances, and it is difficult to monitor the results of shooting and its adjustment, it is recommended to limit the aiming range to 2000 m.
KPVT - a machine gun, the performance characteristics of which are shown in the illustration below.

The mass of the mobile system and the rollers on its elements ensure the smooth operation of the automatic machine gun.
Also, the advantages of the system include the fact that there is no need for accurategap adjustment, which ensures high reliability despite various operating conditions.

Interesting facts
The KPVT tank machine gun during combat operations showed such a high armor-piercing ability on NATO-standard RHA steel armor that starting from the 1970s. and to this day NATO countries, issuing those. the assignment for the design and creation of new military equipment, took into account the damaging effect of an armor-piercing bullet fired from a KPVT!
And this is not surprising, since at distances from 500 to 800 m, the KPVT confidently pierced the frontal armor of the main types of armored personnel carriers of a potential enemy. The most common M113 armored personnel carrier (USA) was also under threat of defeat.
Based on this penetrating ability, the combat weight of the main NATO infantry fighting vehicles "Marder A3" (Germany) and "M2A2 Bradley" (USA), relative to Russian infantry fighting vehicles, was doubled.

Twin installation
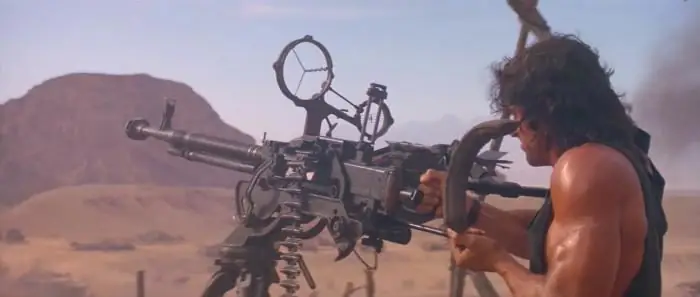
KPVT - a machine gun, the photo of which is presented in the article, has found its use as an anti-aircraft weapon for hitting air targets with single (ZPU-1) and twin installations (ZPU-2, ZU-2).
At the ZU-2 installations, an automatic type anti-aircraft sight was installed, equipped with a second (right) gunner's seat and an additional frame for a cartridge box. In this version, it was put into service in 1955.

The installation had wheels for towing over long distances, but by calculation forcesthe installation could also be moved across the field for short distances.
Mountain modification
For use in mountain conditions, ZGU-1 was used because of the possibility of its disassembly for movement in the mountains by crew forces. The mining installation was developed back in 1954, but its adoption was suspended due to the "rocket mania" then fashionable in the government of the USSR.
But in 1968, the collapsible ZGU-1 was put into service, and at first it passed a combat test in the Vietnamese army as an aid to this country in the fight against American aircraft.
Also in later military conflicts in Afghanistan and in the Chechen company ZGU-1 were widely used.

Quad antiaircraft machine gun
The quadruple anti-aircraft gun from large-caliber KPV ZPU-4 was put into service in 1949 under the designation GAU 56-U-562. ZPU-4 entered service with air defense to protect tank, motorized rifle regiments and airborne divisions from air attacks.
For firing from the ZPU-4, the APO-3-S automatic sight was put into use. Due to the calculation-solving mechanism, the calculation of the task of hitting the target was accelerated, taking into account the speed, heading and dive angle.
All these parameters had to be entered manually by the gun crew, which, in the face of rapidly growing aircraft speeds, reduced the possibility of installation. But at that time it was a significant step forward when compared to previous anti-aircraft sights.

But also the 14.5 mm KPVT machine gun on the ZGU-4 for this arrangementcan also be called its main drawback, since the installation showed a low "survivability" of its main armament. And this is due to the fact that the machine gun itself was originally developed as a tank gun.
What the KPVT is for
KPVT itself is a machine gun, the characteristics of which were originally laid down with the expectation of installation on tanks. Moreover, the idea of \u200b\u200bcreation was such that it was used in pair with a tank gun.

The option, in which the KPVT was located on the tower as a turret, was not excluded.
The tank version received an electric trigger from a 21-V source and an impulse shot counter, respectively, based on tank use, the spent cartridges were withdrawn. He also had a detachable receiver.
In addition to domestic armored vehicles, the KPVT (machine gun) was also installed on the armored vehicles of the Warsaw Pact countries.
When using the KPVT on armored vehicles, it turned out to be the most "long-lived" weapon, since, as a rule, all the armored vehicles of the Armed Forces of the Soviet Union were equipped with it.
Recommended:
Large-caliber machine guns of Russia and the world. Comparison of heavy machine guns
Even in the First World War, a fundamentally new and terrible weapon appeared on the battlefield. Large-caliber machine guns. In those years, there was no armor that could protect against them, and the shelters that were traditionally used by the infantry (made of earth and wood) generally made their way through with heavy bullets
NSVT heavy machine gun: overview, characteristics and description

Machine guns at the time of their appearance were not accidentally classified as artillery: the power of such weapons still amazes. Moreover, heavy "machine gunners" allow even mounted shooting, so that they can be attributed to artillery systems, albeit with tension, even today
Diesel gun: reviews and selection criteria. Diesel gun of indirect heating: technical characteristics

The diesel heat gun is ideal for quickly heating a construction site, agricultural, warehouse or industrial premises. Since its operation is carried out on diesel fuel, it consumes electricity exclusively for the operation of automation and a fan. As the main advantages of such a technological solution, one can name a relatively high thermal power with rather small dimensions
Kolomensky Heavy Machine Tool Plant

Kolomensky Heavy Machine Tool Plant (Kolomna) is Russia's leading manufacturer of presses and machine tools for various purposes. Included in the structure of the production center "Stankotekh"
RPK-16 machine gun: specifications. Kalashnikov light machine gun

At the international presentation of weapons "Army-2016", held in September 2016, the RPK-16 machine gun, the brainchild of domestic gunsmiths, was demonstrated. It will be discussed in this article

