2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-06-01 07:12:56
The idea of creating a submersible moving under water, actually a prototype of a submarine (hereinafter referred to as a submarine), arose long before their actual appearance in the 18th century. There are no exact descriptions of underwater vehicles either in numerous legends or in the Renaissance genius Leonardo da Vinci. The first actually created and had an accurate description of the submarines were:
- Design of Cornelius Van Drebel made of leather and wood, actually floating at a depth of 4 meters during the time of King James I of England (first quarter of the 17th century);
- Papen tin submarine (late 17th century), rectangular shape (1.68 × 1.76 × 0.78 meters);
- Submarine Turtle Tower, which took part in the hostilities during the Civil War in North America (the last quarter of the 18th century);
- American Fulton's 1801 copper submarine, on which the first successful attack was carried out in France, however, a demonstration one;
- the first iron underwater carrier of mines on muscular strength (at the same time it was a “rocket carrier”) built in Russia in 1834 (authorSchilder);
- Submarines with pneumatic propulsion appeared almost simultaneously in Russia (1863, Alexandrovsky) and France (1864, Bourgeois and Brun).
Diesel-powered submarines (DPL) appeared at the beginning of the last century, then diesel-electric (DES) and nuclear submarines (NPS) were invented.
The history of the creation of DPL and DEPL, as well as their confrontation in the era of superpowers
In the last century, a small flotilla of Russian submarines in the Russo-Japanese War of 1905 gained its first combat experience. The Japanese did not use submarines. Practical success was not achieved: the concept of their application was formulated and practical combat experience was gained.
In the First World War, as well as in the subsequent - the Second, the German submarine fleet distinguished itself, on which the bet was made in the battle on the seas. German submarines actively destroyed not only merchant ships, but also warships of the coalition. In total, 160 warships were sunk during the First World War, and 395 during the Second World War, including 75 submarines, as well as merchant ships with a cargo of more than 30 million tons. On the part of the USSR, the most active were the actions of submarines of the "Pike" type, 2/3 of which died in the Black and B altic Seas.
In 1955, the USSR launched project 641 of the second generation of diesel-electric submarines - the famous "Insects" or in the Western "Foxtrot" (in total, ¾ hundred pieces of such submarines were produced), which "reigned" in the open spaces for more than 10 years seas and oceans, although they were opposed by American diesel submarines.
A radical change in the strategy for the use of diesel-electric submarines
It was a time of ambiguous attitude towards the fleet in generaland to the submarine fleet in particular, since with the advent of atomic weapons, opinions were expressed that the task of destroying enemy naval forces could be solved with the help of nuclear weapons. However, the reasonable point of view still prevailed that even under these conditions the fleet would solve the assigned tasks, and with the advent of the third component of the nuclear triad - nuclear submarines, this issue was finally resolved. Diesel-electric submarines began to be created not only with mixed weapons (torpedoes plus missiles launched through torpedo tubes) and attack diesel-electric submarines with cruise missiles, but also with ballistic nuclear missiles, including those with underwater launch (project 629, 641B "Tango", 658 and 877 Halibut).
"Underwater" confrontation between the two superpowers
DEPL actively participated in the confrontation between the USSR and the USA, at that time the two world superpowers, including in the "Caribbean" crisis, which almost threw the globe into the third world, but already a nuclear-atomic war. Fourth Insects, including the Chelyabinsk Komsomolets, took part in Operation Kama. When they attacked our merchant ships carrying missiles with nuclear warheads to Cuba, they had the task of attacking the American fleet. In the Atlantic, diesel submarines of the USSR fell into a storm they had never seen before, but the equipment and people survived. The second test, worse than the previous one, came with an exit to the place of possible hostilities: the heat in the boats was over 50 degrees Celsius. At the same time, water was given out in an extremely limited way - one glass per day per person. This project was designed for combat operations in the northern latitudes, andnot at the equator. The politicians managed to agree and the military conflict did not take place, and later many additions were made to the design of long-range diesel-electric submarines, including those of a radical nature.

During the Cold War, submarines operated covertly off the coast of a potential enemy, being in autonomous navigation for up to three months. There is a known case when, without entering the coastal waters of Italy, our submarine determined its location by casting anchor on the US aircraft carrier Nimitz. And the 705 nuclear submarine of the project followed the NATO warship for almost a day, despite all its attempts to “throw” it off its “tail”, and stopped the pursuit only after receiving the appropriate order.
Projects, the principle of operation of submarines and their types
Initially, submarines were built using different principles of their propulsion:
- using human power;
- electric batteries only;
- using gasoline;
- submarine diesel engine only;
- air motor only;
- on combined use of steam and electricity.

The dual scheme of using diesel and electric engines completely "dominated" the entire first half of the last century, showing its superiority over previous projects and the principles of operation of submarine propulsion.
Projects of diesel submarines with artillery mounts did not succeed due to the low efficiency of "work"artillery against ground targets and subsequently found their solution in "shock" diesel-electric submarines firing cruise missiles.
Further directions for the development of diesel-electric submarines
It consisted of the following:
- increased movement speed;
- noise reduction;
- improvement of systems for detecting and destroying underwater, surface; air and ground targets;
- increasing the time and range of autonomous navigation;
- Increased dive depth.
Pros and cons
It's a paradox, but the main advantage of diesel submarines - the ability to move both on the surface and underwater, which was provided by two fundamentally different types of engines (diesel and electric), was also their main drawback. This required large crews for servicing, which were “crowded” in the already not too spacious interior of the submarine.
The disadvantage of diesel submarines was the relatively low speed of movement in the underwater state, which was limited by the low power of the electric motors and the capacity of the batteries that store electricity.

Elimination of one of the shortcomings of diesel-electric submarines
The weak point of diesel-electric submarines in the first half of the last century was the inability to attack coastal fortifications and land in general. With the launch in 1953 of a cruise missile from the American submarine "Tunets", an era of rivalry between submarines and aviation began in terms of the threat of destroying strategic military facilities and cities on enemy territory,which reached its apogee with the advent of nuclear submarines (NPS).
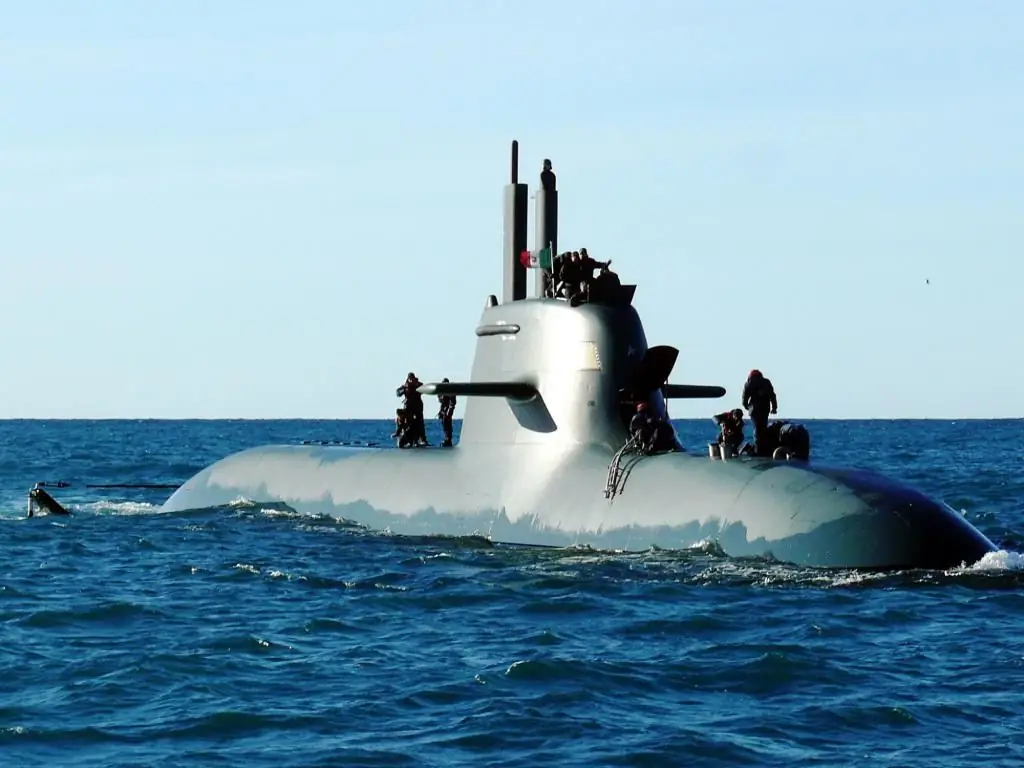
Varshavyanka diesel submarines
Project 877 "Halibut" was implemented in the last two decades of the last century. In the USSR, this submarine was also called "Varshavyanka" (project 636), as they were going to equip their allies under the Warsaw Pact with them, and in NATO they were called "Improved Kilo". The multi-purpose diesel-electric submarine (diesel-electric) had a double spindle-shaped hull (light 6-8 mm and “strong” 35 mm steel), six isolated compartments and was significantly faster and quieter.

Technical and tactical characteristics
The following are documented:
- crew - more than 50 people;
- displacement 2,325 tons (surface), 3,076 tons (submerged);
- length - up to 75 -;
- width - up to 10 -;
- draft - up to 7 -;
- power plant - one shaft, 2 diesel engines with a capacity of 3.65 thousand l / s and an electric motor - 5.9 thousand l / s, as well as 2 standby electric motors of 102 l / s;
- speed of movement - up to 10 knots on the surface and up to 19 - in the underwater position;
- cruising range - up to 7 thousand miles at a speed of 8 knots per hour under RPD (at periscope altitude) and up to 460 miles submerged at a speed of 3 knots per hour;
- autonomy of navigation - 45 days;
- diving depth - up to 0.33 km;
- armament - 6 vehicles loaded with eighteen torpedoes or 6 more by the number of mines, 4 CR (cruise missiles with a rangedefeat 0.5 thousand km.) and short-range air defense systems of the surface-to-air type (8 missiles). Various modern electronic equipment for detecting targets and maintaining their own ste alth.
Interesting! The guides for the main shaft are made… of wood! The truth is a special tree. This is a backout native to Central America. It is very hard (1.3 thousand kg/m), saturated with guaiac resin, very wear-resistant, with natural lubrication. These indicators make it possible for the shaft to serve for a couple of decades.

"Black hole" and its place in the modern world
Excellent acoustic ste alth and the possibility of a preemptive attack due to the long range of target detection, to date (taking into account the constant modernization of various systems) provide the priority of "Varshavyanka". No wonder it is also called the "Black Hole" for its secrecy, in the non-nuclear sector of the submarine. Last fall, one of these submarines launched a missile attack on terrorists in Syria.
Modern diesel submarines are third-generation boats, of which more than 50 have been built in total. The early series have already been decommissioned, and currently 6 submarines of this type are based in the Black Sea and 6 more should be built in the next 5 years for the Russian Pacific Fleet. "Varshavyanka" sold well for export. 10 pieces were delivered to India and China, 6 pieces to Vietnam and Iran, respectively. and 4, and two were even sold to Algeria. They are still in use today.
DPL of Russia
Now in Russia to replace those who have proven themselves and served the Fatherland,operating diesel-electric submarines should be boats of project 677 "Lada", a prototype is already undergoing appropriate tests. The construction of two diesel submarines of this type in Russia is in full swing, and the issue of concluding a contract for the construction of two more boats of the Lada project is being considered.

Cheaper and lighter than its prototype Halibut project, the three-tier Lada is stuffed with good modern "brains" (more than a hundred of the latest detection and ste alth systems in communication, due to which the crew was reduced by 1/3), has air-independent power plant, but is based on the energy of the "cold war" of the two superpowers. In this direction, this diesel-electric submarine is being finalized.
Perhaps in the next decade they will not finalize it, but will switch to Russian diesel submarines of the Kalina project, which, most likely, will solve all the tasks, including arming diesel-electric submarines with a Zircon-type hypersonic missile for implementation strategic tasks on non-nuclear deterrence.
Consequences of contemporary Western anti-Russian sanctions
In connection with Western anti-Russian sanctions, the Russian-Italian project of a small non-nuclear submarine of the S-1000 project has been frozen. Its length is just over 52 m, the crew is 16 people. plus a special team of up to 6 people, diving up to 250 m, with an "underwater" speed of 14 knots and armament of 14 units. torpedoes and/or cruise missiles. Therefore, Russia switched to the latest diesel submarines being developed for a long time - the Amur-950 project, similar to the S-1000, but surpassing it in speed (+6knots) and weapons (+2 units). And the main highlight of Amur-950 is the simultaneous launch of 10 vertical-launched missiles. This submarine has a great export potential, but so far there are no orders for its construction.

Conclusion
In the 21st century, the US and England build only nuclear submarines. The Russian Federation, France and China have both diesel-electric submarines and nuclear submarines, while the submarine fleet of all other states consists only of diesel submarines.
Russian designers are practically working on fifth-generation submarines with might and main. Whereas the contours of the sixth generation are already visible strategically. According to military experts, the main parameters of these submarines will be "unified underwater platforms" with completely unique parameters for today's submarines, which can be very easily changed by replacing any of the corresponding modules, like in transformer robots.
Recommended:
Continuous casting of steel: principle of operation, necessary equipment, advantages and disadvantages of the method
Today, a huge number of various things, parts, etc. are made of steel. Naturally, this requires a large amount of source material. Therefore, the plants have long been using the method of continuous casting of steel, characterized by the most important feature - high productivity
Electric locomotive 2ES6: history of creation, description with photo, main characteristics, principle of operation, features of operation and repair

Today, communication between different cities, passenger transportation, delivery of goods is carried out in a variety of ways. One of these ways was the railroad. Electric locomotive 2ES6 is one of the types of transport that is currently actively used
"Renault": manufacturer, history and date of creation, management, country, technical focus, development stages, introduction of modern technologies and car quality
The Renault manufacturer produces high-quality cars that are in demand in many countries of the world. The products were to the taste of Russian motorists. In 2015, the French concern produced the millionth car from the lines of the Russian plant
Letterpress is Letterpress printing technology, modern stages of development, necessary equipment, advantages and disadvantages of this type of printing

Letterpress is one of the typical methods of applying information using a relief matrix. The elements that protrude are covered with paint in the form of a paste, and then pressed against the paper. Thus, various mass periodicals, reference books, books and newspapers are replicated
Diesel operation principle: features, advantages and disadvantages

Diesel cars on our roads are by no means uncommon. In the countries of Western Europe, they are in the majority. Diesel engines have a number of advantages over gasoline engines. But at the same time, there are some drawbacks. What is this motor, what is the diesel device and the principle of operation? Consider in our today's article

