2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:43
Sources of electrical energy in each locality differ in the way it is received. So, in the steppes it is more expedient to use the power of the wind or convert heat after burning fuel, gas. In the mountains, where there are rivers, dams are built and the water drives giant turbines. The electromotive force is obtained almost everywhere at the expense of other natural energies.
Where consumer food comes from
Electrical energy sources receive voltage after the transformation of wind force, kinetic movement, water flow, the result of a nuclear reaction, heat from the combustion of gas, fuel or coal. Thermal power plants and hydroelectric power plants are widespread. The number of nuclear power plants is gradually decreasing as they are not entirely safe for people living nearby.

Chemical reactions can be used, we see these phenomena in car batteries and household appliances. Batteries for phones work on the same principle. Wind deflectors are used in places with constant wind, where electrical energy sources contain a conventional high power generator in their design.
Sometimes one station is not enough to power the whole city,and electrical energy sources are combined. So, solar panels are installed on the roofs of houses in warm countries, which feed individual rooms. Gradually, environmentally friendly sources will replace stations that pollute the atmosphere.
In cars
The battery in transport is not the only source of electrical energy. The circuits of the car are designed in such a way that when driving, the process of converting kinetic energy into electrical energy begins. This is due to the generator, in which the rotation of the coils inside the magnetic field generates the appearance of an electromotive force (EMF).

A current begins to flow in the network, charging the battery, the duration of which depends on its capacity. Charging starts immediately after starting the engine. That is, energy is generated by burning fuel. Recent developments in the automotive industry have made it possible to use the EMF of a source of electrical energy for traffic.
In electric vehicles, powerful chemical batteries generate current in a closed circuit and serve as a power source. Here the reverse process is observed: EMF is generated in the coils of the drive system, which causes the wheels to spin. The currents in the secondary circuit are huge, proportional to the speed of acceleration and the weight of the car.
The principle of the coil with a magnet
The flowing current through the coil causes an alternating magnetic flux. He, in turn, exerts a buoyant force on the magnets, which forces the frame with tworotate with opposite polarity magnets. Thus, the sources of electrical energy serve as a node for the movement of cars.

The reverse process, when the frame with the magnet rotates inside the windings, due to kinetic energy, allows you to convert the alternating magnetic flux into the EMF of the coils. Further, voltage stabilizers are installed in the circuit, providing the required performance of the supply network. According to this principle, electricity is generated in hydroelectric power plants, thermal power plants.
EMF in the circuit also appears in an ordinary closed circuit. It exists as long as a potential difference is applied to the conductor. Electromotive force is needed to describe the characteristics of an energy source. The physical definition of the term sounds like this: EMF in a closed circuit is proportional to the work of external forces that move a single positive charge through the entire body of the conductor.
Formula E=IR - total resistance is taken into account, consisting of the internal resistance of the power source and the results of adding the resistance of the fed section of the circuit.
Restrictions on installation of substations
Any conductor through which current flows generates an electric field. The energy source is an emitter of electromagnetic waves. Around powerful installations, in substations or near generator sets, human he alth is affected. Therefore, measures have been taken to limit construction projects near residential buildings.

OnAt the legislative level, fixed distances to electrical objects are established, beyond which a living organism is safe. It is forbidden to build powerful substations near houses and on the route of people. Powerful installations must have fences and closed entrances.
High-voltage lines are mounted high above the buildings and taken out of the settlements. To eliminate the influence of electromagnetic waves in the residential area, energy sources are closed with grounded metal screens. In the simplest case, a wire mesh is used.
Units of measure
Each value of the energy source and circuit is described by quantitative values. This facilitates the task of designing and calculating the load for a specific power supply. Units of measurement are interconnected by physical laws.
The units for power supplies are as follows:
- Resistance: R - Ohm.
- EMF: E - Volt.
- Reactive and impedance: X and Z - Ohm.
- Current: I - Amp.
- Voltage: U - Volt.
- Power: P - Watt.
Building Serial and Parallel Power Circuits
Chain calculation becomes more complicated if several types of electrical energy sources are connected. The internal resistance of each branch and the direction of the current through the conductors are taken into account. To measure the EMF of each source separately, you will need to open the circuit and measure the potential directly at the terminals of the supply battery with a device - a voltmeter.

When the circuit is closed, the device will show a voltage drop, which has a smaller value. Multiple sources are often required to obtain the necessary nutrition. Depending on the task, several types of connections can be used:
- Sequential. The EMF of the circuit of each source is added. So, when using two batteries with a nominal value of 2 volts, they get 4 V as a result of connecting.
- Parallel. This type is used to increase the capacity of the source, respectively, there is a longer battery life. The EMF of the circuit with this connection does not change with equal battery ratings. It is important to observe the polarity of the connection.
- Combined connections are rarely used, but they do occur in practice. The calculation of the resulting EMF is made for each individual closed section. The polarity and direction of the current of the branches are taken into account.
Power supply ohms
The internal resistance of the source of electrical energy is taken into account to determine the resulting EMF. In general, the electromotive force is calculated by the formula E=IR + Ir. Here R is the consumer resistance and r is the internal resistance. The voltage drop is calculated according to the following relationship: U=E - Ir.

The current flowing in the circuit is calculated according to Ohm's law of the complete circuit: I=E/(R + r). Internal resistance can affect the current strength. To prevent this from happening, the source is selected for the load according tofollowing rule: the internal resistance of the source must be much less than the total total resistance of the consumers. Then it is not necessary to take into account its value because of the small error.
How to measure power supply ohms?
Since sources and receivers of electrical energy must be matched, the question immediately arises: how to measure the internal resistance of the source? After all, you can’t connect with an ohmmeter to contacts with the potentials available on them. To resolve the issue, an indirect method of taking indicators is used - the values \u200b\u200bof additional quantities are required: current and voltage. The calculation is made according to the formula r=U/I, where U is the voltage drop across the internal resistance, and I is the current in the circuit under load.

Voltage drop is measured directly across the power supply terminals. A resistor of known value R is connected to the circuit. Before taking measurements, it is necessary to fix the EMF of the source with an open circuit - E with a voltmeter. Next, connect the load and record the readings - U load. and current I.
Desired voltage drop across the internal resistance U=E − U load. As a result, we calculate the required value r=(E − U load)/I.
Recommended:
Thermal imaging control of electrical equipment: concept, principle of operation, types and classification of thermal imagers, features of application and verification
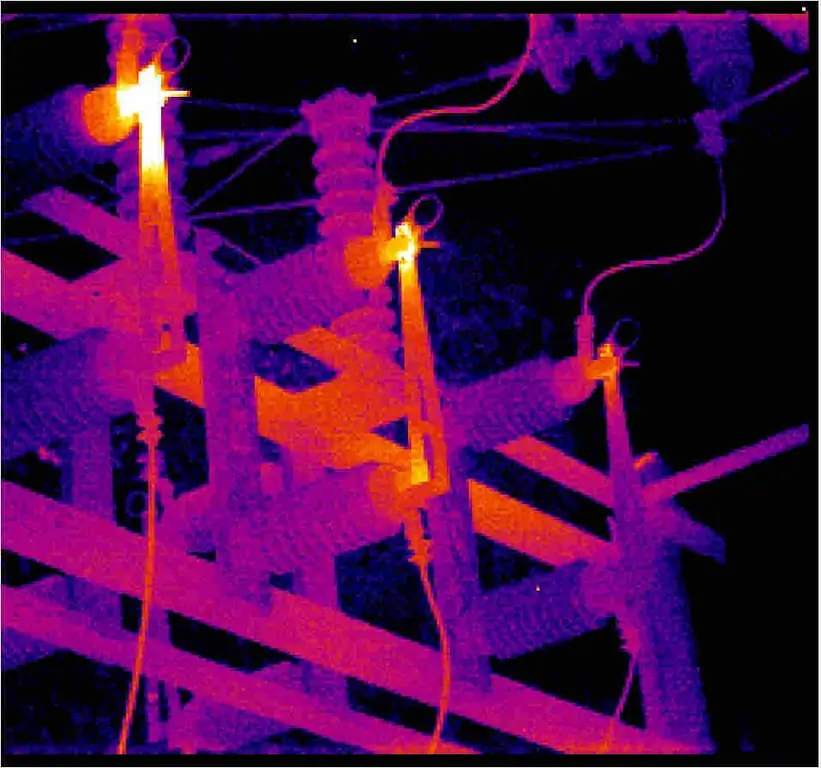
Thermal imaging control of electrical equipment is an effective way to identify defects in power equipment that are detected without shutting down the electrical installation. In places of poor contact, the temperature rises, which is the basis of the methodology
Conversion of thermal energy into electrical energy with high efficiency: methods and equipment

There is growing concern around the world about the catastrophic decline in the levels of natural energy resources needed for modern life, such as oil, natural gas and coal. Nevertheless, this fact contributes to the development of new technologies based on the use of alternative natural resources: solar energy, hydropower, wind energy, bioenergy, geothermal energy. This is popular in the article
Types of energy: traditional and alternative. Energy of the future

All existing areas of energy can be conditionally divided into mature, developing and being in the stage of theoretical study. Some technologies are available for implementation even in a private economy, while others can only be used as part of industrial support
What is an electrical substation? Electrical substations and switchgear

Trams and trolleybuses require voltage not alternating, but constant. This means that a separate very powerful substation is needed. Electrical energy is converted on it, that is, it is rectified
Alternative energy sources in Belarus. Fuel and energy resources of Belarus

The problem of the growing shortage of energy resources is now reaching the level of the problem of climate change, and, as you know, the history of mankind is the history of the struggle for energy resources. A similar situation is observed in the 21st century (for example, wars in the Middle East for oil)

