2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:45
Rabbits are pets that, even with proper care, suffer from various pathologies. One of the common ailments is a wet muzzle, or stomatitis. This ailment is often referred to as biting midge. Pathology is difficult. If stomatitis in rabbits is not treated, then the entire livestock of animals can become infected, as a result, almost all rabbits die. To avoid this, it is necessary to carry out the prevention of the disease, and if a wet muzzle is found, immediately begin therapy
Features of pathology
Stomatitis is an infectious pathology caused by a filtering virus. When a rabbit is affected, inflammation of the salivary glands is observed, which is why the muzzle is constantly wet. The disease passes quickly from one individual to another, so it is important to start taking measures to treat stomatitis in rabbits as soon as possible. Incubation periodlasts 2-8 days. If urgent action is not taken, then the death can reach 50% of the total livestock.

The causative agent of the infection is a virus that is practically not resistant to conventional disinfectants. Most often, young animals under the age of three months suffer from stomatitis. Adults rarely get sick. Pathology manifests itself in the spring and autumn periods, when there is high dampness.
Causes of infection
Stomatitis refers to viral diseases. The causative agent of infection multiplies rapidly in the body of the animal and is excreted into the external environment with saliva and urine.
The spread of infection is:
- Close keeping of rabbits.
- Sudden temperature fluctuations.
- Presence of drafts.

Transmission of the disease can occur from the carrier mother to the rabbits with milk and blood. Because of this feature, all recovered animals are culled and not used as producers. After an infection, the animal develops immunity, but it remains a carrier of the virus for life.
Clinical manifestations
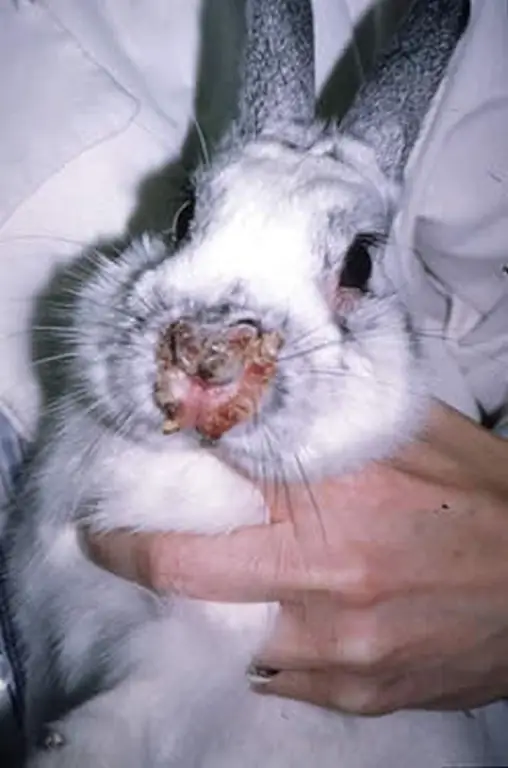
When symptoms of stomatitis appear in rabbits, treatment is started immediately. This ailment in the clinical picture is somewhat reminiscent of human stomatitis. Animals show the following signs:
- Salivation intensifies. Visually, the symptom is manifested by wetting the hair near the nose.
- On examination, hyperemia of the oral cavity is observed.
- The animal does not eat well or refuses to eat at all, loses weight.
- After a couple of days from the beginning of the manifestation of the disease, the tongue is covered with a white coating. On the fifth day, it changes color - turns yellow or turns brown.
- Tongue swollen.
- Small sores appear at the site of plaque formation.
- Due to profuse salivation, inflammation of the skin occurs, hair falls out.

Without treatment, infectious stomatitis in rabbits can go away on its own, but only with a mild degree of infection and in isolated cases. Usually the disease leads to the death of the entire livestock.
Forms of pathology
The outcome of the disease is influenced by its form. With mild pathology, animals retain their appetite, although they eat less food. The nature of the chair in this form does not change. If you start treating stomatitis in rabbits immediately at the first signs, then the prognosis for recovery is favorable - the animal recovers in two weeks.
With an atypical form, weight remains normal, as does appetite. However, on examination, there may be a slight inflammation of the oral mucosa, chin. With proper treatment, recovery occurs on the fifth or sixth day. In severe form, the digestive system is involved in the pathological process. Patients have severe diarrhea, a sharp decrease in weight, and symptoms of dehydration. On the fifth or seventh day, the animal dies.
Treatment methods
Treatment of stomatitis in rabbits is urgent. To get started, you needisolate a sick animal from he althy ones, disinfect the cage, inventory, feeders. All animals near the patient are subject to daily inspection.
There are many methods of therapy, among them there are traditional and non-traditional. The most common method is the treatment of stomatitis in rabbits with antibiotics, local therapy in the form of irrigation of the oral cavity with a solution of potassium permanganate. You can apply streptocide ointment, copper sulfate to the oral mucosa, use antibiotics in the form of injections, or give the drug inside, after crushing the tablets. With proper treatment, the animal will feel better on the third day, it will begin to eat.

Streptocide is used to treat stomatitis in rabbits. Small animals are poured into the mouth twice a day, 0.1-0.2 g of powder. Instead, penicillin can be used to treat stomatitis in rabbits. It can also be used intramuscularly at a dosage of 40 thousand units per kilogram of animal weight. The drugs are used for three days. A positive effect is given by intramuscular injection of penicillin diluted with novocaine. Injections are carried out twice a day.
Stomatitis therapy
Treatment of stomatitis in rabbits with copper sulfate is carried out in the form of irrigation of the oral cavity. A 2% solution is preliminarily prepared from this substance. For ease of use, the composition is poured into a bottle of nasal drops or a syringe. You can use a solution of potassium permanganate (1: 1000) instead of copper sulfate. Local treatment is carried out for three days twice a day.day. If stomatitis therapy is started at the initial stages of the disease, then in a week the animal recovers completely.
Ointment of 30 g of lanolin helps well, 200,000 units. penicillin, 2 g sulfamide and 200 g vaseline. Everything is thoroughly mixed until a homogeneous mass. The ointment lubricates the oral cavity.

Treatment of stomatitis in rabbits with "Biseptol". And how to give this drug to rabbits? For treatment, the tablet is diluted with water and poured into the mouth. The best way to do this is with a syringe. Dosage - 1/4 tablet per rabbit. The drug is used twice a day.
To enhance the treatment, experienced rabbit breeders recommend sprinkling food with an antibiotic, mixing streptocide into feed. During treatment, it should be borne in mind that it is difficult for the animal to swallow, chew rough food. Because of this feature of the course of the disease, only soft food is introduced into the diet. In case of refusal to eat, rabbits are fed with liquid top dressing from a syringe. It can be decoctions of herbs, liquid cereals, mixtures for babies, animals.
Other treatments
Some rabbit breeders use "Apidermin" in their farms. This is a natural remedy used to treat burns, sores. It helps to cope with stomatitis. Apidermin contains honey, propolis and pollen. The remedy relieves inflammation, accelerates cell regeneration, reduces pain, improves immunity.
There are folk methods of treating the disease, these include:
- Decoction of chamomile, oak.
- Infusion of sage, calendula.

Herbal formulations are used in conjunction with antibiotics. They treat the oral cavity, use for watering animals. Herbal decoctions and infusions help relieve inflammation, reduce pain, boost immunity, and normalize digestion. If the pathology caused diarrhea, then herbs will help get rid of it by normalizing the stool.
Prevention
Any disease is easier to prevent than to cure. To avoid the occurrence of infection, it is necessary to monitor the quality of feed, the conditions in which animals are kept. Cages should always be dry and clean. Animals should not be allowed to crowd. Be sure to conduct a daily inspection of all individuals, the cells are periodically disinfected with sodium hydroxide or bleach. Be sure to clean the feeders, drinkers with their simultaneous disinfection.
In the rabbitry, all tools are subjected to periodic processing. At the entrance to the premises where animals are kept, a disinfecting barrier will be organized. To do this, a small depression is made into which lime is poured. It serves as an excellent barrier to the processing of shoes, and therefore will prevent the transmission of infection by service personnel.

Prophylaxis of stomatitis is the proper feeding of the animal. Rabbits are given only high-quality, nutritious feed. For prevention, a few drops of iodine are added to the water every few days.
If an animal becomes ill, it will be immediately isolated. The rabbitry is being disinfected. All individuals that were kept together with a sick rabbit,are treated, even if there is no clinical manifestation of the disease. To prevent stomatitis, rabbits are given injections. Usually such procedures are carried out in veterinary clinics. At home, pets are rarely vaccinated on their own.
Conclusion
Activation of a viral infection in the household occurs at those moments when young rabbits appear, due to stress, when the immune system weakens. The state of he alth is affected by heat, drought, rainy weather, stuffiness, cold, stressful situations (they arise due to the location of the road next to the rabbitry, because of loud sounds, visiting the rabbitry by cats, dogs, etc.). To reduce the likelihood of infection of rabbits, it is imperative that cages, feeders, drinkers are treated, properly fed and only high-quality feed, and preventive examinations are carried out. As a preventive measure, some rabbit breeders periodically mix streptocide into the feed, give medicinal herbs, and prepare decoctions from them. All this helps to prevent the appearance of not only stomatitis, but also other ailments that can lead to the death of the entire livestock.
Recommended:
Can rabbits eat wheat? Features of the care and feeding of rabbits, diet, tips and tricks

Experienced rabbit breeders know that if rabbits are properly cared for, almost all diseases can be avoided. One of the keys to good he alth is good nutrition. Before you start rabbit breeding, you should carefully study what can be given to rabbits and what is strictly prohibited
Diseases of rabbits: symptoms and their treatment. Disease prevention in rabbits
Rabbit diseases can destroy most of the livestock in a matter of days. In order to provide assistance to animals in time, it is necessary to be able to determine the disease, as well as vaccinate in time, follow the rules of care
Fruit rot: causes, first signs and symptoms of infection, methods of treatment and improvement of the garden

It happens that the gardener does not have time to collect the fruits - they rot right on the branches and fall off. At the same time, in appearance, apples and pears look quite he althy, but from the inside, an insidious enemy of all stone fruit and pome crops lurks - fruit rot. Despite the fact that this dangerous adversary is well studied and can be defeated, amateur gardeners often do not notice signs of infection in the early stages of the disease
Eimeriosis of rabbits: causes, symptoms, treatment methods

Eimeriosis, or coccidiosis, is the most common invasive disease of young rabbits that damages the digestive organs. Mortality among young animals reaches almost one hundred percent. Most often, rabbits are exposed to the disease from one to five months. Due to eimeriosis, many farms are closed and the number of animals is significantly reduced
Breeds of rabbits with photos and names. Giant rabbits. Meat breeds of rabbits

The rabbit was tamed by man a long time ago. This is mentioned in the written sources of ancient Roman history. From that time to the present, many new breeds have been created by rabbit breeders. Rabbits are bred to obtain dietary meat, fur, fluff. Fur products are highly durable, and the quality of the down prevails over the wool of the merino and angora goats. This article will present rabbit breeds with names and photos

