2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:36
Ultrasonic welding of metals is a process during which a permanent joint is obtained in the solid phase. The formation of juvenile areas (in which bonds are formed) and the contact between them occur under the influence of a special tool. It provides joint action of relative sign- alternating tangential displacements of small amplitude and compressive normal force on the blanks. Let's take a closer look at what ultrasonic welding technology is.

Connection mechanism
Low-amplitude displacements occur between parts with ultrasonic frequency. Due to them, microroughnesses on the surface of parts are subjected to plastic deformation. At the same time, contaminants are evacuated from the connection zone. Ultrasonic mechanical vibrations are transmitted to the welding site from the tool on the outside of the workpiece. The whole process is organized in such a way as to exclude slippage of the fixture and support alongdetail surfaces. During the passage of vibrations through the workpiece, energy is dissipated. This is provided by external friction between the surfaces at the initial stage of welding and internal friction in the material located between the support and the tool after the formation of the setting area. This raises the temperature in the joint, making it easier to deform.
Specific material behavior
Tangential displacements between the parts and the stresses that they cause and act together with the compression from the welding force provide localization of severe plastic deformation in small volumes in the near-surface layers. The whole process is accompanied by grinding and mechanical evacuation of oxide films and other contaminants. Ultrasonic welding reduces the yield strength, thereby facilitating plastic deformation.

Process Features
Ultrasonic welding contributes to the formation of the necessary conditions for the connection. This is ensured by the mechanical vibrations of the transducer. Vibration energy creates complex shear, compression, and strain stresses. Plastic deformation occurs when the elastic limits of materials are exceeded. Obtaining a strong connection is ensured by increasing the area of direct contact after the evacuation of surface oxides, organic and adsorbed films.
Using KM
Ultrasound is widely used in the scientific field. With its help, scientists investigate a number of physical propertiessubstances and phenomena. In industry, ultrasound is used for degreasing and cleaning products, working with difficult-to-machine materials. In addition, fluctuations favorably affect crystallizing melts. Ultrasound provides them with degassing and grain refinement, improving the mechanical properties of cast materials. Vibrations contribute to the removal of residual stresses. They are also widely used to increase the rate of slow chemical reactions. Ultrasonic welding can be used for various purposes. Vibrations can become a source of energy for the formation of seam and point joints. When the weld pool is exposed to ultrasound during crystallization, the mechanical properties of the joint are improved due to the refinement of the weld structure and the intensive removal of gases. Due to the fact that vibrations actively remove dirt, artificial and natural films, it is possible to connect parts with an oxidized, varnished, etc. surface. Ultrasound contributes to the reduction or elimination of self-stresses that appear during welding. Due to vibrations, it is possible to stabilize the components of the structure of the connection. This, in turn, makes it possible to prevent the possibility of spontaneous deformation of structures subsequently. Ultrasonic welding has recently become more and more widely used. This is due to the undoubted advantages of this connection method in comparison with cold and contact methods. Especially often ultrasonic vibrations are used in microelectronics.

Promising directionconsidered ultrasonic welding of polymeric materials. Some of them cannot be connected by any other method. At industrial enterprises, ultrasonic welding of thin-walled aluminum profiles, foil, wire is currently carried out. This method is especially effective for joining products from dissimilar raw materials. Ultrasonic welding of aluminum is used in the manufacture of household appliances. This method is effective when splicing sheet raw materials (nickel, copper, alloys). Ultrasonic welding of plastics has found application in the production of optics and fine mechanics devices. At present, machines have been created and introduced into production for connecting various elements of microcircuits. Devices are equipped with automatic devices, due to which productivity is significantly increased.
U. S. power
Ultrasonic welding of plastic provides a permanent connection due to the combined action of high-frequency mechanical vibrations and a relatively small compressive force. This method has much in common with the cold method. The ultrasonic power that can be transmitted through the medium will depend on the physical properties of the latter. If the strength limits in the compression zones are exceeded, the solid material will collapse. In similar situations, cavitation occurs in liquids, accompanied by the appearance of small bubbles and their subsequent collapse. Together with the latter process, local pressures arise. This phenomenon is used in the cleaning and processing of products.
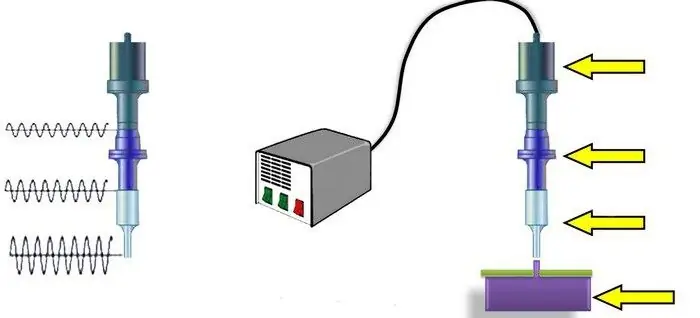
Device nodes
Ultrasonic welding of plastic is carried out usingspecial machines. They contain the following nodes:
- Power supply.
- Vibrational mechanical system.
- Control equipment.
- Pressure drive.
The oscillatory system is used to convert electricity into mechanical energy for its subsequent transmission to the connection section, concentrating it and obtaining the required value of the emitter speed. This node contains:
- Electromechanical transducer with windings. It is enclosed in a metal case and cooled by water.
- Elastic oscillation transformer.
- Welding tip.
- Support with pressure mechanism.
The system is fixed using a diaphragm. Ultrasonic radiation occurs only at the moment of welding. The process occurs under the influence of vibrations, pressure applied at right angles to the surface, and the thermal effect.

Method capabilities
Ultrasonic welding is most effective for plastic raw materials. Articles made of copper, nickel, gold, silver, etc. can be combined both with each other and with other low-plastic products. As the hardness increases, the ultrasonic weldability deteriorates. Refractory products made of tungsten, niobium, zirconium, tantalum, molybdenum are effectively connected with the help of ultrasound. Ultrasonic welding of polymers is considered a relatively new method. Such products can also be connected both to each other and to other solid parts. As for the metal, it can be combined withglass, semiconductors, ceramics. You can also tie the blanks through the layer. For example, steel products are welded to each other through aluminum plastic. Due to the short stay under elevated temperature, a high-quality connection of dissimilar products is obtained. The properties of raw materials are subject to minor changes. The absence of foreign impurities is one of the advantages that ultrasonic welding has. Harmful factors for humans are also absent. When connected, favorable hygienic conditions are created. The bonds of the products are chemically homogeneous.
Connection Features
Metal welding is carried out, as a rule, in an overlapping way. At the same time, various design elements are added. Welding can be carried out by points (one or more), a continuous seam or in a closed circle. In some cases, when pre-forming the end of the wire blank, it is tee-jointed with a plane. It is possible to carry out ultrasonic welding of several materials at the same time (package).

Part thickness
It is limited by the upper limit. With an increase in the thickness of the metal workpiece, it is necessary to apply oscillations with a larger amplitude. This will compensate for the loss of energy. An increase in amplitude, in turn, is possible up to a certain limit. Limitations are associated with the likelihood of fatigue cracks, large dents from the tool. In such cases, one should evaluate howultrasonic welding would be appropriate. In practice, the method is used for product thicknesses from 3…4 µm to 05…1 mm. Welding can also be used for parts with a diameter of 0.01 … 05 mm. The thickness of the second product may be significantly greater than the first.
Possible problems
When applying the ultrasonic welding method, it is necessary to take into account the probability of fatigue failure of existing joints in products. During the process, the blanks can turn relative to each other. As mentioned above, dents remain on the surface of the material from the tool. The device itself has a limited service life, due to the erosion of its working plane. At some points, the material of the product is welded to the tool. This leads to wear on the device. Repair of equipment is accompanied by a number of difficulties. They are related to the fact that the tool itself acts as an element of a non-separable single unit design, the configuration and dimensions of which are designed exactly for the operating frequency.
Product preparation and mode parameters
Before performing ultrasonic welding, it is not necessary to carry out any complex measures with the surface of the parts. If desired, you can increase the stability of the quality of the connection. To do this, it is advisable only to degrease the product with a solvent. For joining ductile metals, a cycle with a pulse delay relative to the start of ultrasound is considered optimal. With a relatively high hardness of the product, it is advisable to wait for a slight heating before turning on the ultrasound.

Welding patterns
There are several of them. Technological schemes of ultrasonic welding differ in the nature of tool oscillations. They can be torsional, bending, longitudinal. Also, schemes are distinguished depending on the spatial position of the device relative to the surface of the welded part, as well as on the method of transferring compressive forces to the products and the design features of the supporting element. For contour, seam and point connections, variants with bending and longitudinal vibrations are used. Ultrasonic action can be combined with local pulsed heating of parts from a separate heat source. In this case, a number of advantages can be achieved. First of all, you can reduce the amplitude of oscillations, as well as the strength and time of their transmission. The energy properties of the thermal pulse and the period of its superposition on ultrasound act as additional parameters of the process.
Thermal effect
Ultrasonic welding is accompanied by an increase in temperature at the joint. The appearance of heat is caused by the appearance of friction on the surfaces of the contacting products, as well as by plastic deformations. They, in fact, accompany the formation of a welded joint. The temperature at the contact area will depend on the strength parameters. The main one is the degree of hardness of the material. In addition, its thermophysical properties are of considerable importance: thermal conductivity and heat capacity. The selected welding mode also affects the temperature level. As practice shows, the emerging thermal effect does not act as a determining condition. itis due to the fact that the maximum strength of the joints in the products is achieved before the temperature rises to the limiting level. It is possible to reduce the duration of transmission of ultrasonic vibrations by preheating the parts. This will also increase the strength of the connection.

Conclusion
Ultrasonic welding is currently an indispensable method of joining parts in some industries. This method is especially common in microelectronics. Ultrasound allows you to connect a variety of plastic and hard materials. Today, scientific work is being actively carried out to improve welding tools and technologies.
Recommended:
How to cook cast iron by electric welding: work technology and necessary materials

The main composition and types of cast iron. Difficulties and features of welding cast iron products. Cast iron welding methods. Preparatory operations before welding. How to cook cast iron by electric welding in a cold and hot way, as well as gas equipment. Features of the electrodes used for welding cast iron. Safety measures during welding
Corrosion of aluminum and its alloys. Methods for combating and protecting aluminum from corrosion

Aluminium, unlike iron and steel, is quite resistant to corrosion. This metal is protected from rust by a dense oxide film formed on its surface. However, in the case of destruction of the latter, the chemical activity of aluminum greatly increases
Technology of electric arc welding of metals

The impact of an electric arc on the structure of a material is one of the oldest ways to obtain a strong connection between metal workpieces. The first technological approaches to this welding method had a lot of disadvantages associated with the porosity of the weld and the formation of cracks in the working area. To date, manufacturers of equipment and auxiliary devices have significantly optimized the method of electric arc welding, expanding the scope of its use
Welder's mask is a reliable means of protection against the most harmful factors of the welding process

Of course, metal welding is one of the most dangerous for humans, because all welding work is accompanied by a constant release of harmful substances and factors. Some of the most dangerous are: electric arc, bright glow, toxic gases, infrared and ultraviolet radiation
Welding in a shielding gas environment: work technology, process description, execution technique, necessary materials and tools, step-by-step work instructions and expert advice

Welding technologies are used in various branches of human activity. Versatility has made welding in a protective gas environment an integral element of any production. This variety makes it easy to connect metals with a thickness of 1 mm to several centimeters in any position in space. Welding in a protective environment is gradually replacing traditional electrode welding