2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:47
Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) is the main raw material for the production of various types of rubber with optimal durability. It is a synthetic polymeric material obtained by copolymerization of butadiene with acrylonitrile (NAC). It can be called nitrile, divinyl-nitrile, butadiene-acrylonitrile rubber or butacryl. In the international designation, this material is labeled NBR (nitrile-butadienerubber), in the domestic designation - SKN (nitrile synthetic rubber).

Where applicable
This type of rubber is most often used in those industries where optimal resistance of rubber products to chemically aggressive environments is important. Of great importance are such properties of butadiene-nitrile rubber as high elasticity and small permanent deformation. This material is widelyused in the production of rubber elements that have direct contact with chemically active materials - these can be all kinds of seals, oil seals, rubber compensators, fuel and oil hoses, drive belts, fuel tanks for cars, aviation and oil industries, printing offset plates and other products.
Products based on this rubber do not swell in oily liquids, antifreeze and water. From some types of such material, the sheath of electrical wiring and rubber gloves are made, which have special strength and wear resistance. It is used in the production of various adhesives, sealants and polyurethane foam. Rubber is the basis in the production of adhesives.

When and where did this rubber come from?
Obtaining butadiene-nitrile rubber was recorded in 1934 in Germany. At that time, German scientists created a material unique in its properties and patented it under the name Buna-N. During the Second World War, the new material became extremely popular in the military industries.
Due to the lack of natural raw materials, the US top leadership launched a special program involving the active development of the production of butadiene-nitrile rubber and other types of synthetic raw materials for rubber goods. The material produced under this program was called GR-N. To date, BNR has become one of the most sought-after special-purpose rubbers. It is made in more than 20 countries around the world.

NBR production
This type of material is obtained by constructive polymerization in an aqueous emulsion. The process is carried out both at high and at low temperatures. The main monomers for their production are butadiene-1, 3 and acrylic acid nitrile (NAC), mixed in a certain proportion. These substances do not depend on temperature. Taking into account the laws of random copolymerization, it should be noted that this tandem of monomers should have the properties of an azeotropic composition containing about 40% acrylonitrile in a mixture of monomers.
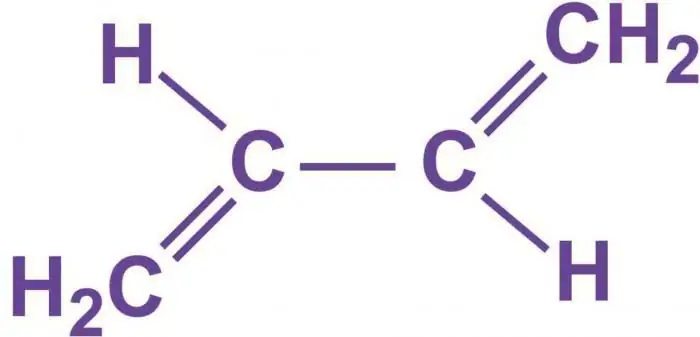
In the production of this type of rubber, there is a need for a more complete purification during coagulation of the emulsifiers used for polymerization. In the manufactured rubbers, a small amount of ash, mineral and volatile impurities (not more than 1%) is allowed. They can be loaded with stainable or non-stainable antioxidants.
What is BNK
In our country, rubbers of such types as nitrile rubber-18 (SKN-18), nitrile-butadiene rubber-26 (SKN-26) and nitrile butadiene rubber-40 (SKN-40) are produced. The numerical indicator in grades shows the number of acrylonitrile units in polymers. They can contain 18%, 26% or 40% Acrylonitrile, respectively.
Changing the number of constituent ingredients, you can achieve different properties of the resulting material. Depending on the percentage of acrylonitrile, the propertiesrubbers can vary in hardness, viscosity, oil - and petrol resistance. The percentage of NAC affects the intermolecular effect of structural units. It is this factor that affects the use of nitrile butadiene rubber in certain areas of the national economy. Nevertheless, it is used as a raw material for the manufacture of a huge range of industrial rubber products.

Material imperfections
Despite the fact that rubber products made with the addition of BNR have a whole range of excellent performance (high tensile strength and ductility, relative elongation, tear and abrasion resistance, excellent oil and gasoline resistance), this material and some flaws.
Tougher operating conditions associated with an increase in the speed of mechanisms and a lack of cooling oil, leads to the fact that rubber elements can only work at temperatures up to +150 degrees. When the operating temperature rises above this value, structuring occurs, and then the destruction of rubbers created on the basis of NBR. In other words, heated rubber becomes hard and brittle.
Exposure to low temperatures also has a negative effect on rubber products, which were used in the production of nitrile rubber. The optimum operating temperature for them is considered to be not lower than -35˚С.
Modern rubber modifications
To create rubber products witha unique set of properties, more modern modifications of rubbers are used. Hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubbers are considered one of the promising developments in modification. They have excellent processing properties in various types of rubber production.
Rubber made on the basis of polyvinylchloride-modified rubbers gives more stable performance in weather wear resistance (up to -50 degrees) and extreme operating temperature up to +160 degrees. It is significantly superior to products made on the basis of nitrile rubbers in terms of tear resistance and wear resistance. Has excellent resistance to active influence of chemically aggressive environments. However, this rubber is not so strong and elastic. Therefore, in order to improve the processing properties of the material, it is most often used in combination with conventional types of nitrile rubbers.

Vulcanization
The process of vulcanization of butadiene-nitrile rubbers is carried out using sulfur, as well as thiuram, organic peroxides, alkylphenol-formaldehyde resins and organochlorine compounds. The temperature can vary from 140˚ to 190˚ Celsius. During this process, a large plateau of vulcanization is observed. The increased content of NAC contributes to an increase in the rate of vulcanization. The quality of the resulting rubbers is evaluated by the inherent characteristics of the vulcanizers.

Properties
BNC properties are determinedacrylonitrile content. This type of rubber is highly soluble in ketones, some hydrocarbon solutions and esters. Aliphatic hydrocarbons and alcohol have practically no effect on the dissolution of nitrile butadiene rubbers. An increase in the composition of the material acrylonitrile contributes to the intermolecular action between the polymer chains: the more NAA in the composition of the material, the higher the density and temperature of the glass transition increase. An increased content of NAA reduces the dielectric properties, reduces the degree of solubility in aromatic solvents and increases the resistance to swelling in aliphatic hydrocarbons.
Depending on the course of rubber polymerization, it can be produced with different plastoelastic properties. They can be:
- Very hard (Defoe hardness 21.5 - 27.5 N). When marking such rubber, the letter “T” is added to its name.
- Solid (Defoe hardness 17.5 - 21.5 N).
- Soft (Defoe hardness 7.5 - 11.5 N). When marking such rubber, the letter “M” is added to its name.
For NBRs manufactured with alkylsulfonates as emulsifiers, the letter "C" is added to the marking. For example, SKN-26MS is a soft rubber that contains 26% bound NAC, and a biodegradable alkyl sulfonate emulsifier was used in the preparation.
Recommended:
Ceramic material: properties, production technology, application

The first pottery appeared long before people learned how to smelt metal. Ancient pots and jugs that archaeologists find to this day are proof of this. It is worth noting that the ceramic material has unique properties that make it simply indispensable in some areas
Alcohol-rosin flux: properties, application, self-production

Today, soldering is not the most common connection method, but it is still used quite often. Flux is always used for this operation. It can be not only purely rosin, but also a solution based on it. It's about alcohol-rosin flux
Methyl bromide: properties, production, purpose and application
Methyl bromide is a fumigant used against a wide range of pests including spiders, mites, fungi, plants, insects and rodents. Introduced as a pesticide in 1932. Methyl bromide fumigation is used to fumigate agricultural commodities, grain silos, mills, ships, clothing, furniture, and greenhouses
Ferrous sulfate: physical and chemical properties, production, application

Ferrous sulfate is a chemical compound that is extremely common in nature and widely used in various fields of economic activity. There are divalent and trivalent modifications of this substance. The first variety, also called ferrous sulfate, is an inorganic binary non-volatile compound having the formula FeSO4
Tung oil: production, application, properties, reviews

Tung oil has long been used to coat wood products. For several centuries, it has established itself as an excellent preservative, antiseptic with high decorative qualities

