2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:29
Jewelers, motorists, manufacturers of facing materials often face the same question: how to make a beautiful, shiny surface of a product? The dagger comes to the rescue. What it is? This is a process in which the hard surface of a part is cleaned and machined.
The essence of the method
Tumbling is a mixture of abrasive material and workpieces in a container. The interaction of components occurs in two ways of movement:
- rotary (rotating);
- vibrating.
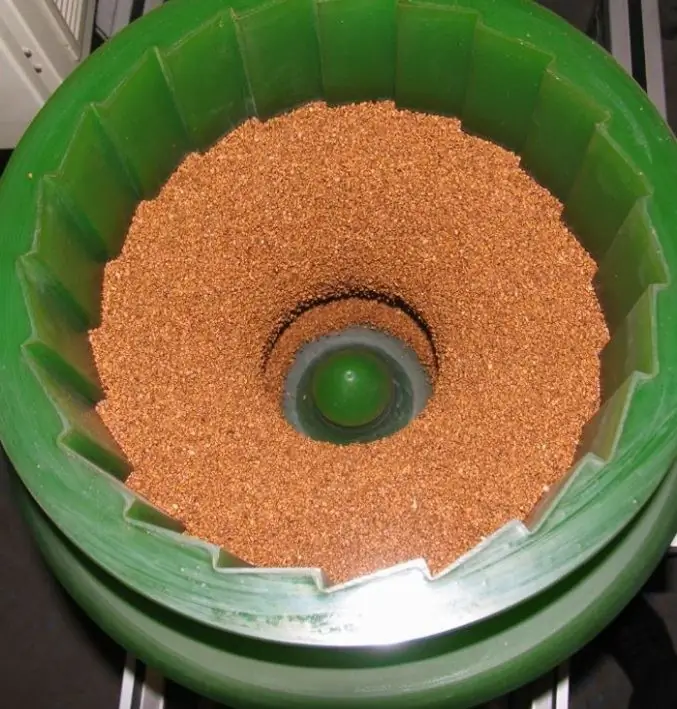

Solid tumbling bodies, due to friction, clean the surface to the desired gloss or roughness by removing microparticles from it. The process can take from 4 to 80 hours.
The advantage of the method is the possibility of processing surfaces with non-standard shapes and sizes. The disadvantages includethe impossibility of processing thin-walled parts.
It is worth noting that tumbling is a process of running-in parts, which can be done in two ways:
- dry;
- wet.
The dry method uses special pastes, powders and abrasive components. In the wet method, a working fluid, coagulants, and tumbling solutions are added to the drum. Wet tumbling is usually used before applying various types of coatings: galvanized, enameled, and so on.
Where applicable
Answering the question what is tumbling, it should be noted that in addition to polishing, it allows you to remove flash, burrs, rust, scale from parts. The selection of the desired abrasive material will allow you to give the desired roughness and specular surface. Applications:
- instrumentation;
- mechanical engineering;
- construction;
- jewellery.
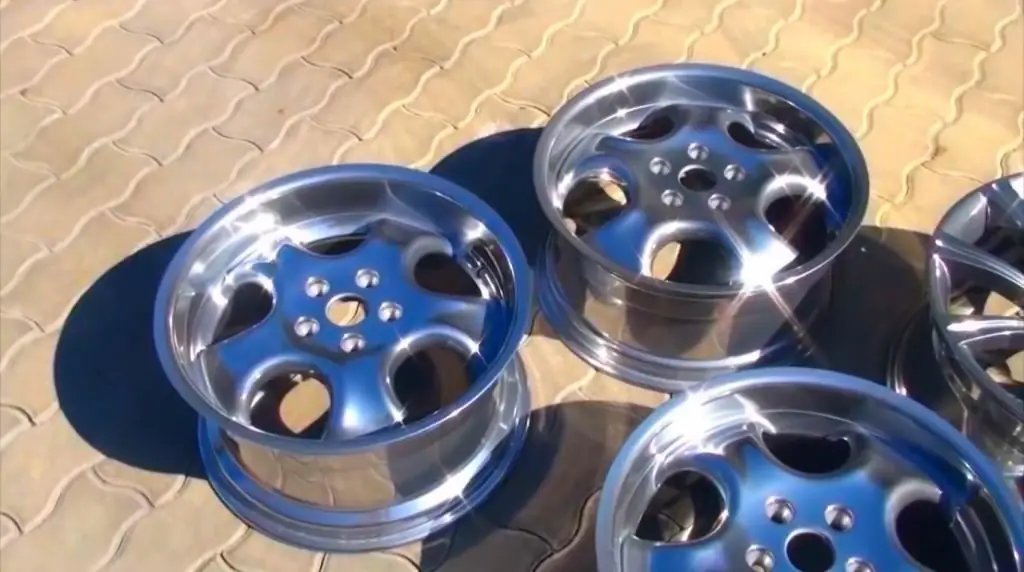
In addition, tumbling is used for household products (knives, blades, blades), car rims, natural materials (stones), plastic products.
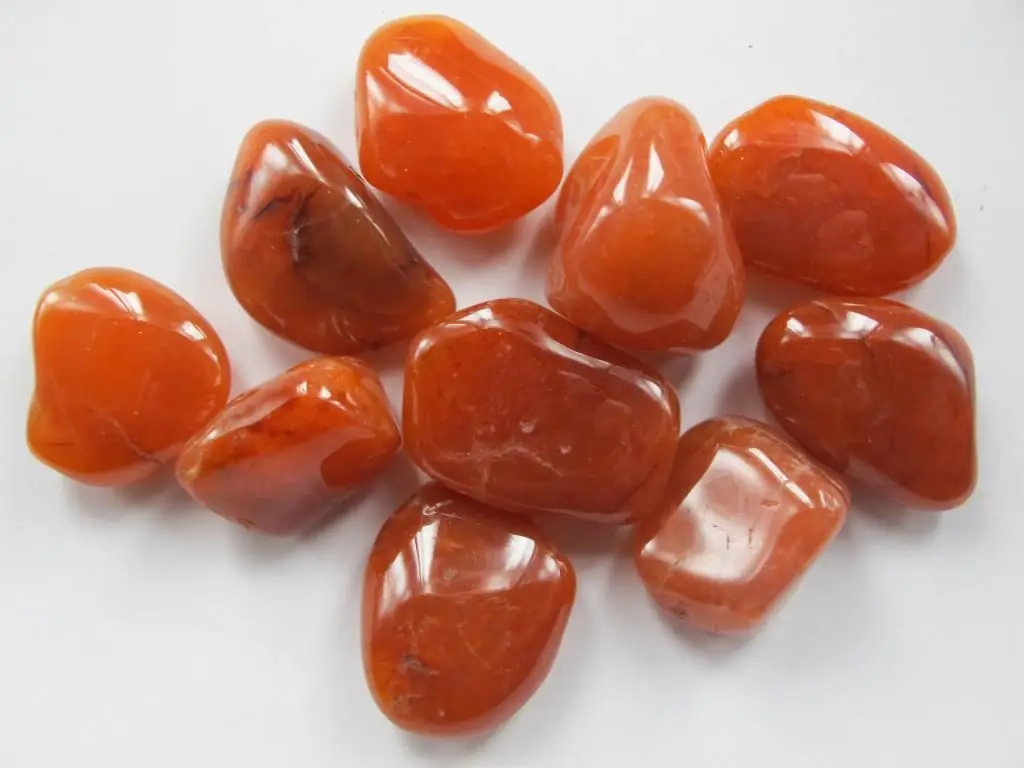
Mineral tumbling is done to give the stones a beautiful appearance, shine, grind sharp edges, create smooth lines, get rid of plaque and chips. Such products can later be cut or used as talismans, amulets. Tumbling is done for stones such as:
- citrine;
- aquamarine;
- amethyst;
- shungite;
- jasper;
- quartz;
- obsidian;
- malachite;
- agate;
- carnelian;
- rhinestone;
- hematite;
- aventurine.

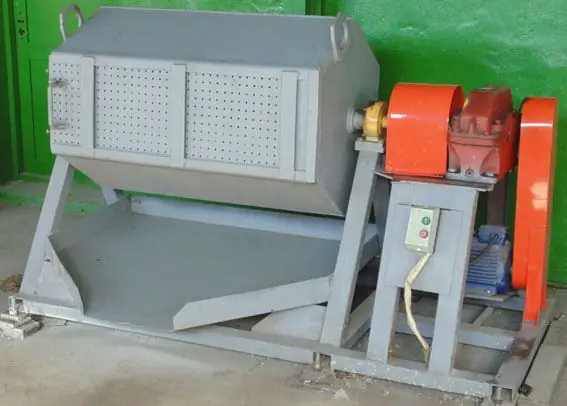
Equipment
For tumbling, special tumbling machines are used, which are standardized by GOST 10548-74. The working surface in cross section is a circle or a prism.
- The simplest type of equipment is a tumbling drum. Rotation is carried out by means of an electric motor, processing occurs due to the free mixing of the abrasive and parts. Used for simple products, has low processing speed and efficiency, visual control over the process is not available with this method.
- Vibration equipment - the most common today - is an open bath with an attached vibration drive, which gives it oscillatory movements. Abrasive bodies begin to apply micro-impacts on the surface, removing a thin top layer. Equipment of this type allows you to simultaneously process large batches of parts.
- Rotor equipment - is a fixed drum, in the lower part of which there are rotating blades. The disadvantages include rapid wear of the inner surface of the drum, the inability to process large products. The advantage of this method is the high productivity and quality of the resulting surface.
- Spindle equipment - the part is fixed in the spindle, lowered into the container with abrasive material and starts to rotate. Implementation of slow, unidirectional or any other specific actions is possible. Used in high-tech industries: aircraft construction, medical prosthetics.

Tumbling materials
It can be said that tumbling is such collisions, sliding and microcutting of the surfaces of parts with an abrasive filler, in which the final result will depend on the type and material of the lapping bodies. As a stripping tool use:
- pebbles;
- abrasive grain;
- granular abrasive;
- corn macerate;
- nutshell;
- steel polished spheres;
- ceramic and volcanic abrasive;
- quartz sand;
- limestone;
- wooden bodies.

Phase tumbling is often used, when there is a gradual decrease in the size of abrasive particles. The shape of the lapping bodies can also be different:
- tetrahedron;
- parallelepiped;
- cube;
- ball;
- cylinder;
- cone;
- prism.
Sometimes it can take more time and resources to finish processing than it does to make a part.
Recommended:
Hoskold method, Ring method, Inwood method - ways to recover investment capital
When a person invests his own money in an income-generating object, he expects not only to receive profit from the invested capital, but also to fully repay it. This can be done through resale or by obtaining such profits that not only bring interest, but also gradually return investments
How to open an auto parts store: rules and tips

How to open an auto parts store? Who should work in it? For successful trading, you will definitely need professional consultants who specialize in the sale of automotive parts. It's good if they understand how the car works
Abrasive powder: production, consumption. Where can abrasive powder be used?
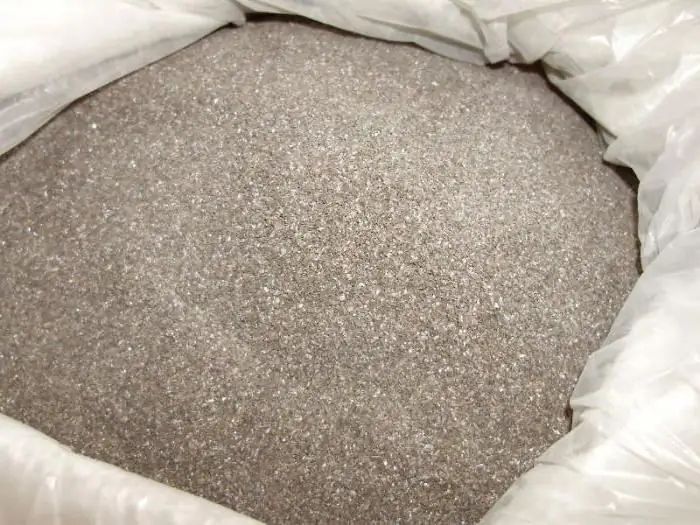

Abrasive powder is mainly used to clean metal surfaces from rust. Most often, for this purpose, its varieties such as cooper slag and nickel slag are used. Diamond powder is used to make abrasive pastes and grinding tools
Residential complex "Yaroslavsky" (Chelyabinsk): characteristics, finishing, developer, reviews

The residential complex "Yaroslavsky" in Chelyabinsk is a new modern quarter with business-class apartments. Convenient interchange, clean air and relatively low housing prices - that's what the developer offers
Chrome plating parts. Chrome parts in Moscow. Chrome parts in St. Petersburg
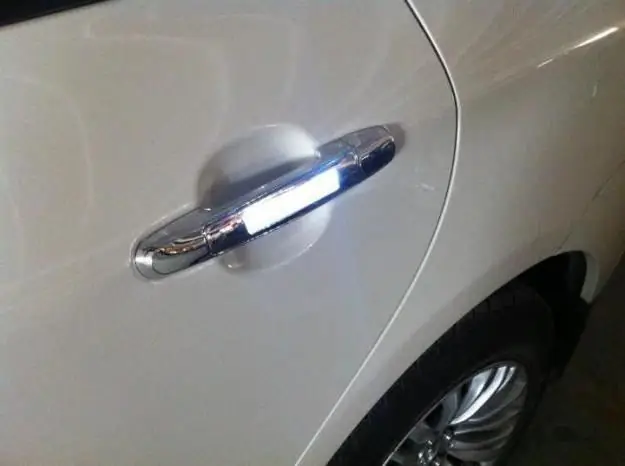

Chrome plating of parts is an opportunity to give them a new life and make them more reliable and of high quality in operation

