2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:35
Boiler water heating equipment is widely used in industry, where the high performance of generator sets is valued. Such units are mainly used for technological operations - for example, to generate steam by evaporating water. But the possibility of household operation is not excluded, if it is necessary to organize hot water supply for several large consumers. Among the most optimized steam generator designs, one can note the water-tube design. A boiler of this type is not inferior to many analogues in terms of output per unit of time, but its design causes many restrictions on operation in cramped conditions.
Unit device
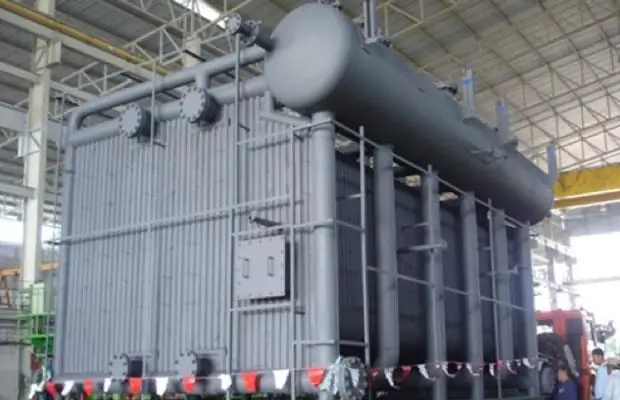

The most common design with two drums (collectors) at the base. These are metal tanks that are interconnected by pipes of differentdiameters. Also a mandatory component is a combustion chamber or a furnace that generates thermal energy. Other design elements include:
- Fuel supply pipe (usually liquid).
- Circulation communications for water.
- Inlets and outlets for water.
- Outlet for draining water.
- Partitions (if we are talking about a closed boiler system in a protective case).
- Chimney.
- Steam separator.
Most of the structural elements of the water tube boiler are made of heat-resistant steel alloy. There are also cast-iron models, but they can be used if the operating conditions allow the installation of heavy units. Tubular and fitting elements can also be partially made on the basis of fire-resistant ceramics, which is more practical than metal. The firebox window and a number of other areas of possible observation are made of heat-resistant tempered glass.
Auxiliary structural elements
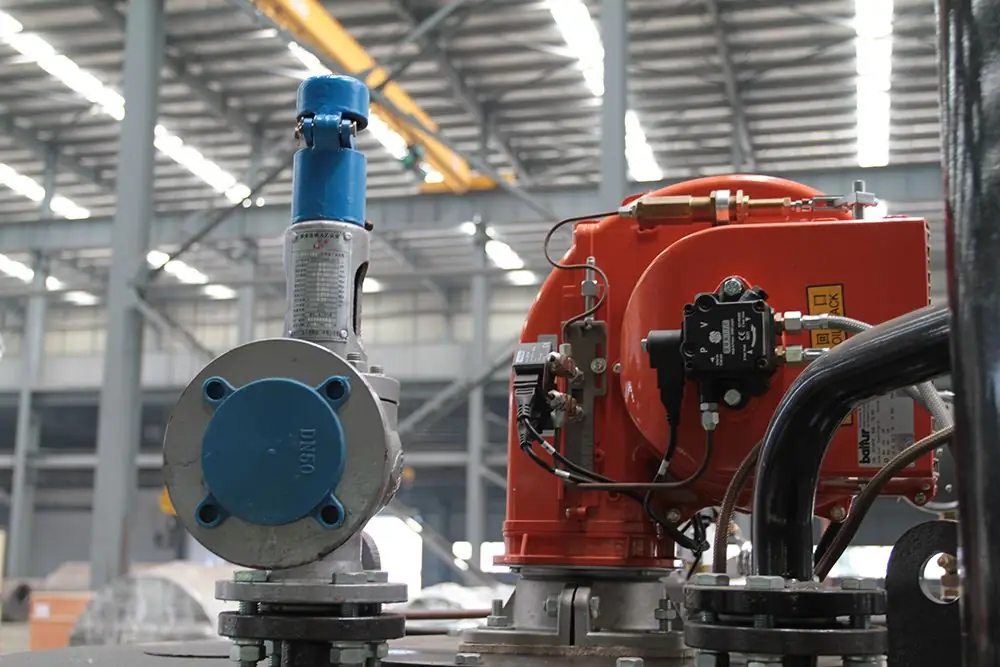

Optionally, the boiler may include additional devices that expand the capabilities and ease of use of the equipment. Among them, the following devices can be noted:
- Superheater. Designed to increase the steam temperature up to 100 °C and above. By itself, the design of water-tube units does not aim to bring the temperature regime of steam to certain values. As a rule, the target point of work is precisely the effect of evaporation. On the other hand, convectionsuperheaters, depending on the model, are capable of bringing the temperature of the outlet mixture up to 500 °C, which may be required in some technological operations in production.
- Dehumidifier. Also a steam preparation that dries it out by removing excess moisture.
- Steam accumulator. If the water-tube boiler cannot cope with the loads or, on the contrary, fills the steam chamber in minimal volumes, this device will help to balance the operating mode. The accumulator takes or pumps steam flows into the system when necessary.
- Device for water treatment. Water, as a source of generation, also needs appropriate treatment. For example, a special filter system reduces the volume of dissolved oxygen, removes s alts and unwanted chemicals.
- Today, more and more often without automatic controls, but they are also supplied as standard with equipment. You can only purchase an extended set of instrumentation that will allow you to comprehensively monitor the parameters of pressure, temperature, humidity, etc.
Operation principle
In the initial position, two drums are filled with water - one completely (water), and the second (steam) half. In the second collector, a separating membrane is provided inside, separating water from steam. This boundary is called the evaporation mirror. The working process begins from the moment the firebox is ignited, which is connected to a heat exchanger in the form of a tubular system with circulating water. Hot water enters the first drum,maintaining sufficient volume.
At the same time, the process of liquid evaporation begins in the steam header of the water-tube boiler. The principle of operation of the unit is based on convective heat exchange, which can be carried out in a natural non-stop mode. Cold water from the central water supply system passes the basic level of filtration, then enters the heat exchange system and is directed to the heating drum. Further, depending on the rate of evaporation, the liquid gradually replenishes the filling level of the steam collector. Steam, in turn, is either released through the chimney, or enters the process zone for further use.
Differences from fire tube boiler
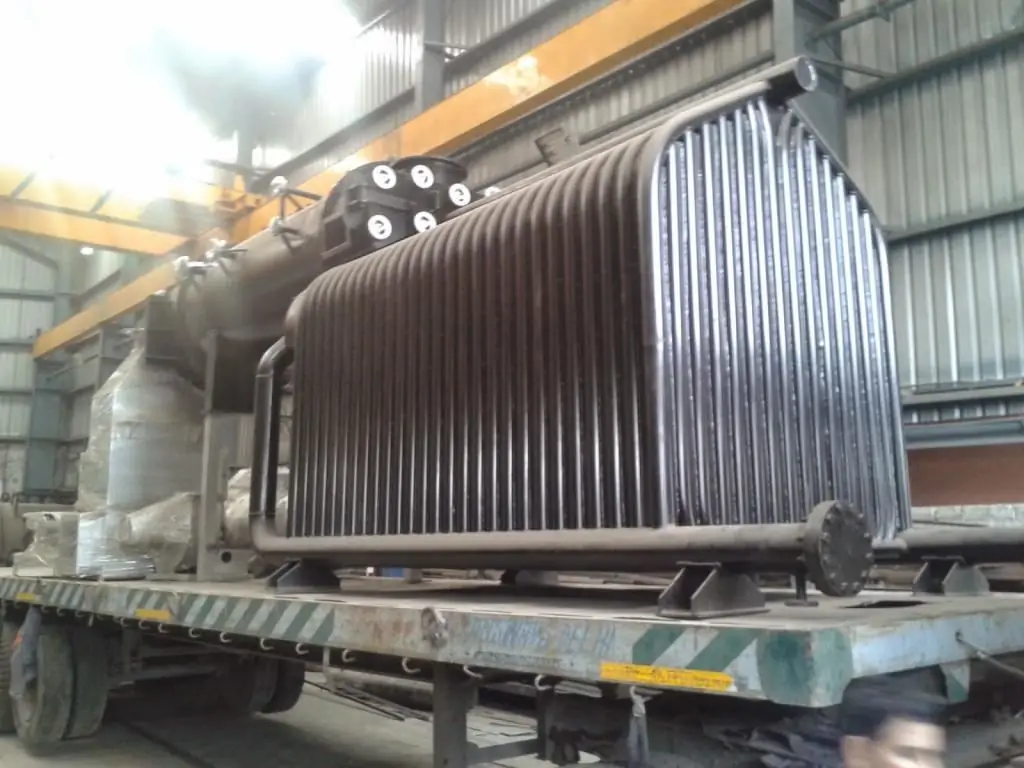

The difference between these units lies in the configuration of the placement of the combustion chamber or, in principle, the source of thermal energy relative to the heat exchanger and the water tank. Firstly, steam generation is not required at all. The fire tube boiler mainly works for heating with water, providing the function of the DHW system. Secondly, in such boilers, the furnace is located in the center of the structure, and the containers with water circulation circuits are of an applied nature. They are in contact with the heat exchanger on the outer surface of the structure.
But this is not the only difference between fire-tube and water-tube boilers. The difference also goes through the means of regulating the heat exchange process. The design of the water-tube unit provides for an economizer, due to which initially cold water is preheated. Accordingly, furtherheat transfer reactions are more intense and with less energy consumption. On the other hand, the advantages of fire-tube equipment include structural simplicity and a minimum amount of maintenance measures during operation.
Differences from gas-pipe equipment
In water-tube units, the direct translator of thermal energy is hot water, which fills the circulation pipes of the heat exchanger. It turns out an efficient and safe generator that contributes to the production of steam. As for gas-tube boilers, the technical design, even outwardly, may partly correspond to water-tube structures. The only difference is that the carrier of thermal energy will be the exhaust gases in the combustion chamber. How does this affect the operational process? If the principle of operation of a water-tube boiler allows the complete consumption of waste products without residues until the moment of evaporation and further use of steam, then a gas-tube boiler will have to release the working gas medium already in the heat exchanger system. Moreover, thick nozzles are provided for this to ensure the safety of the process.
Varieties of water tube boiler
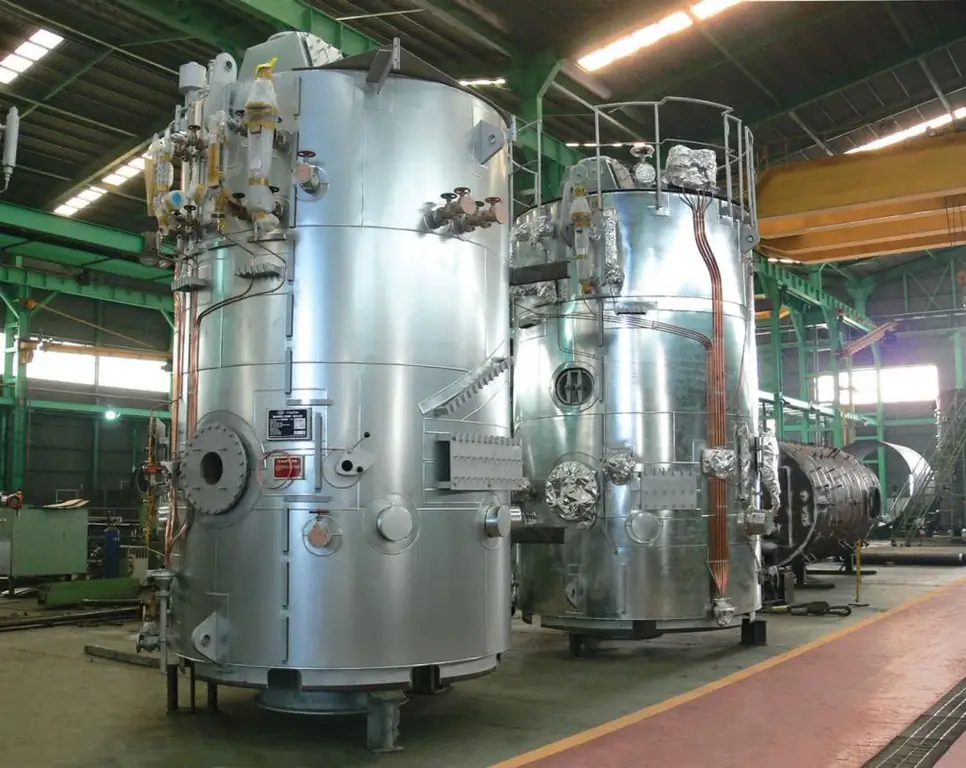

The main classification feature is the location of the collectors. Traditionally, structures are equipped with horizontal drums, which are conveniently connected to circulating water supply circuits. Two collectors are installed on the platform in parallel, and a firebox with outlet channels can be placed between them. If in the technical roomthere is not enough space, then vertical water-tube boilers on a special communication substrate are used. Cylindrical drums rush upward, and a working fluid with different temperatures is supplied from below. Process steam is output at the top.
Ship Water Tube Boiler
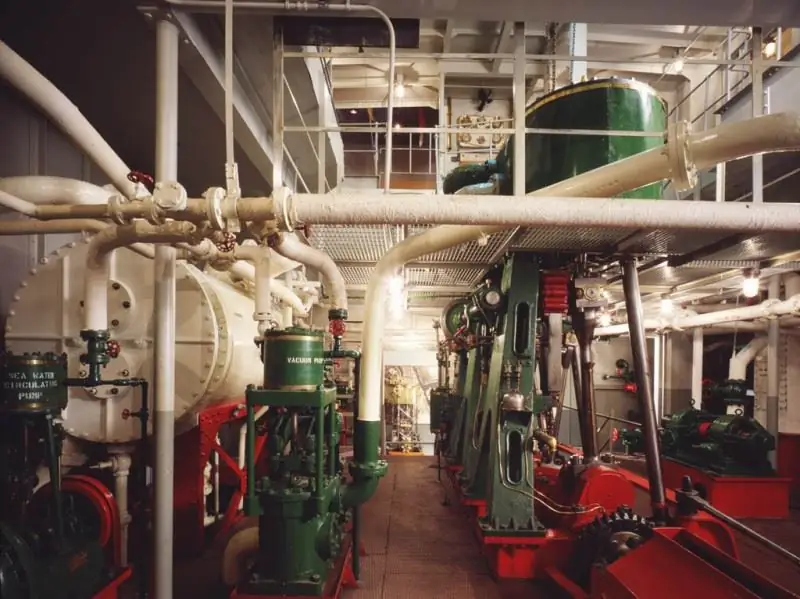

The design of such units is optimally suited for use as part of maritime transport. But even in this case, special modifications of boilers are used - radiation. Their distinguishing feature is the use of radiative thermal energy, which is also released during the combustion of fuel (usually diesel). A mandatory structural condition is the top location of the furnace nozzles. Another feature of the design of a water-tube boiler for marine vessels is the combination with steam turbine plants that provide intermediate heating of steam.
Equipment maintenance
Communication infrastructure with piping elements is quite complicated for water-tube units, which leads to an extensive list of technical measures for diagnostics and repair. Maintenance personnel must periodically check the condition of the pipes for tightness, carry out flaw detection of functional units and automatic controls, and also maintain the reliability of connections with fasteners. Particular attention is paid to the piping of the heat exchanger and collectors - the slightest pressure drop can damage the structure, which will create conditions for depressurization of the circuit.
Prosdesigns
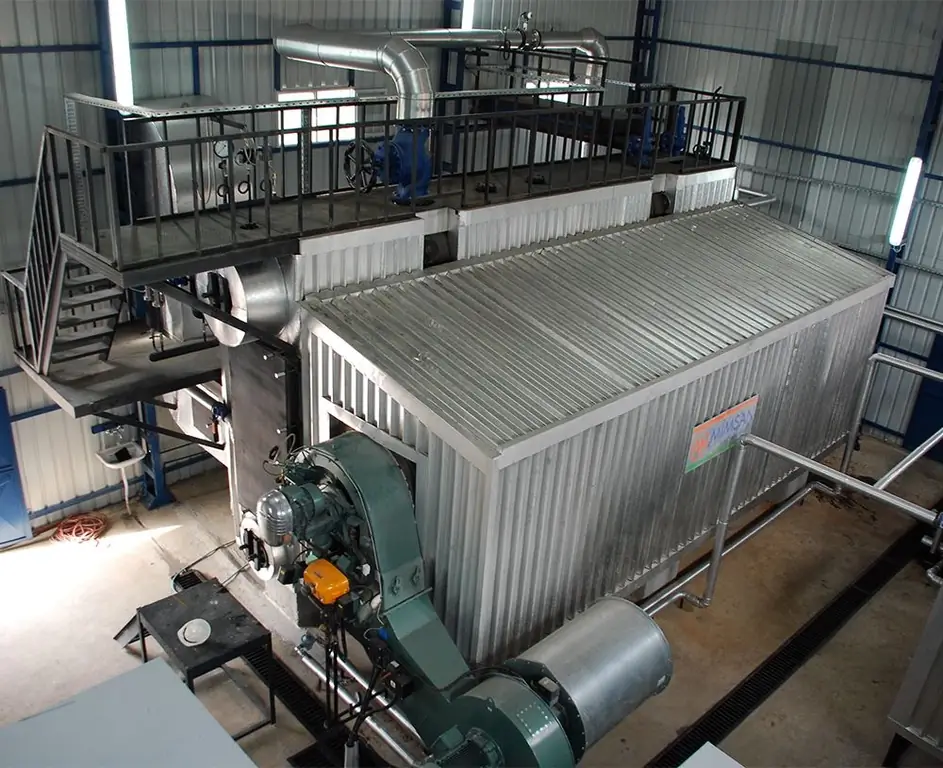

The most important advantage of such boilers in the general family of steam units is safety. Maintaining an optimal temperature balance, you can count on long-term operation of the equipment without accidents and damage to the working parts. Wide regulatory capabilities of the water pipe cat are also noted, which is confirmed by the integration of the economizer with automatic shut-off valves. The devices operate without the participation of the operator, based on the data of the installed thermostat algorithms. This makes it possible to program the system for several days ahead.
Design cons
The principle of operation of such boilers is focused on high performance, regardless of the conditions of use. Recently, this nuance is playing an increasingly important role against the backdrop of optimization and rationalization of production capacities. The massive body and multi-level communication interchanges of steam water-tube boilers force us to look for alternative solutions to steam generation problems. However, the concept of minimizing the device of this boiler is not excluded. But in this case, high efficiency will be lost, not to mention the possibilities of working in cogeneration mode with parallel provision of DHW operation. In other words, the equipment is optimally suited for large industries that need large volumes of process steam, but is hardly useful for supplying consumers with low demand for targeted energy.
Conclusion

The fundamental difference between the concept itselfwater tube boilers belong to the class of once-through equipment. Such installations have a significant advantage over autonomous systems, which lies in the possibility of a continuous generation process. Even at peak operating conditions, water tube boilers are able to operate for a long time maintaining the same quality of steam production. Another thing is that safety requirements still exclude long sessions of operation at high powers. As for autonomy, in relation to such boilers it is expressed in the elimination of the need for energy supply. Of course, the shut-off valves will need at least battery power, but the process of water circulation and subsequent evaporation is quite manageable without electricity.
Recommended:
The rate of water consumption and sanitation. The principle of rationing water consumption

Economical use of all natural resources is the task of each of us. It is no secret that in cities there is a norm of water consumption for each inhabitant, such norms have been developed for industrial enterprises. Moreover, water disposal is also normalized, i.e. sewage
UV water disinfection: principle of operation, installation. Drinking water - GOST valid
Technologies in the field of water treatment do not stand still. Today, many methods are used to ensure the required quality of drinking liquids that meets the requirements of GOST. One of them is ultraviolet disinfection of water. It will be discussed in the article
Water valves: overview, types, principle of operation and characteristics

Despite its apparent simplicity, the water valve is a relatively complex design, the build quality and reliability of which directly affect the workflow when supplying water
Water tower: principle of operation, purpose, characteristics

Water tower is the simplest design designed for autonomous regulation of water flow and pressure in the plumbing system. The simple principle of operation of the water tower determined its widespread use
Industrial flotation machines for wastewater treatment: types, device, principle of operation
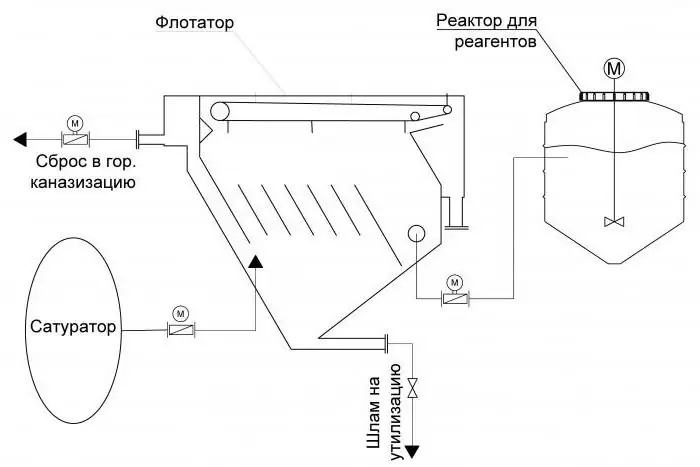
2017 has been declared the year of environmental protection in Russia, and therefore environmental education is one of the tasks for this year. Wastewater generated during the economic activities of enterprises contains a large amount of pollutants in concentrations exceeding the permissible and normative ones. As a rule, we are talking about heavy metals (iron, nickel, copper, lead, mercury, cadmium, etc.), oil products, suspended solids, aluminum, and surfactants. These substances, getting into water bodies, violate the norms

