2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:37
Oil refineries and technological complexes using oil and gas products contain a system of pipelines for servicing fuel materials in their working infrastructure. Maintaining sufficient performance in the circulation circuits of the same oil requires the use of special plumbing fittings. Its key element is the reservoir breather valve, due to which pressure is regulated in conditions of depressurization and vacuum of the operated vessel.
Device assignment
The range of applications for such valves is extensive and covers almost all niches where oil and gas product storage processes are organized. The use of special control valves for tanks containing fuel is due to the requirements for the safe operation of such facilities. Oil products -combustible, fire and explosive raw materials, which leads to high requirements for its content. And this is not to mention the special rules for long-term storage of oil, which preserves its optimal working properties.
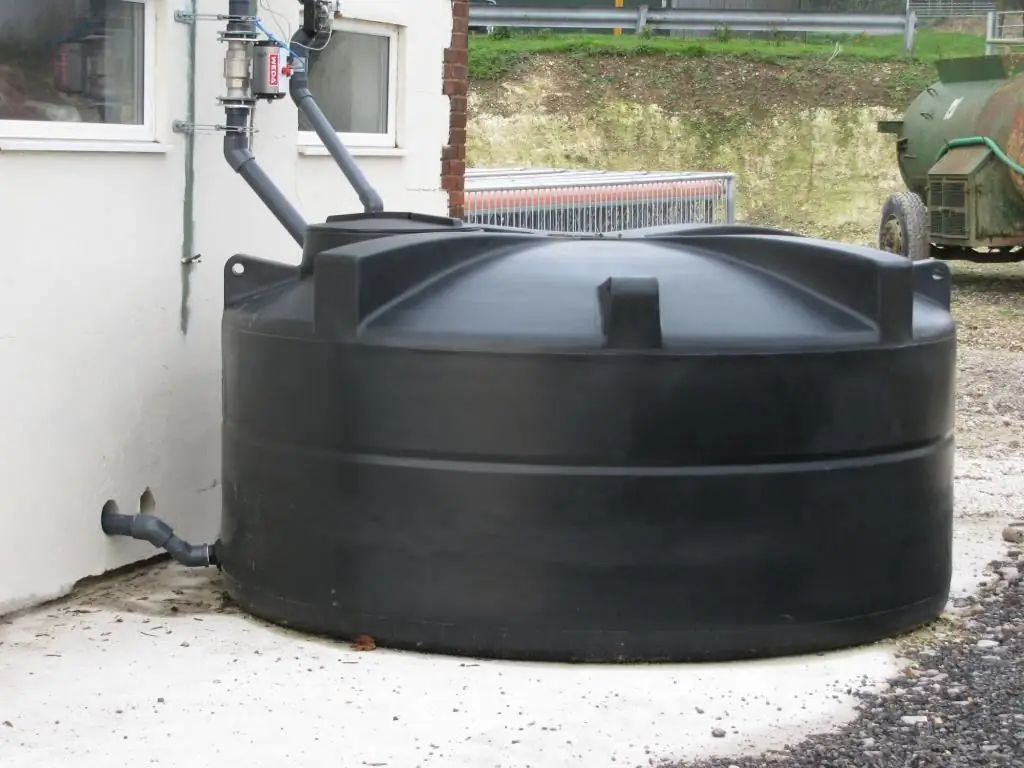

How can a reservoir breather valve help in this context? The purpose of such devices in a broad view can be reduced to ensuring the sealing of the capacitive space, which contains the target storage products. As a rule, we are talking about tanks with a gaseous medium, which must be protected from the penetration of a flame. The internal pressure regulation function is also basic and determines the degree of safety in the maintenance of oil storage facilities.
Design
The most common group of control valves in this class is the breather valve of the SMDK tank, that is, a combined mechanical regulator, the device of which provides for a standard pressure plate and a pressure plate with weights. On the back side, the body is provided with a refractory screen that prevents the flame from passing into the container with fuel products. This option is activated when gas mixtures and vapors leave the tank together with air. Vacuum and pressure plates can change their position by adjusting the volume of the buffer zone.
The working mechanical bodies of the structure include a device for handling the load (removal and installation), clamp brackets, flywheel, flange mounts, etc. However, in the foreground inWhen choosing a design, the type of form factor often comes out, on which the direction of the gas-air flow will depend. For example, the reservoir breather valve design is designed to orient this flow downwards vertically, which makes it difficult to remove heat while stabilizing combustion. Accordingly, the fire resistance of the fuse itself is reduced. This configuration is typical for non-freezing regulators that have horizontal valve surfaces. But one should not completely rely on the frost resistance of such fittings - in particular, it is on the outer surfaces that the frozen condensate can be up to 50 mm thick, which cannot but affect the performance of the fuse as a whole.
The principle of operation of tank breathing valves
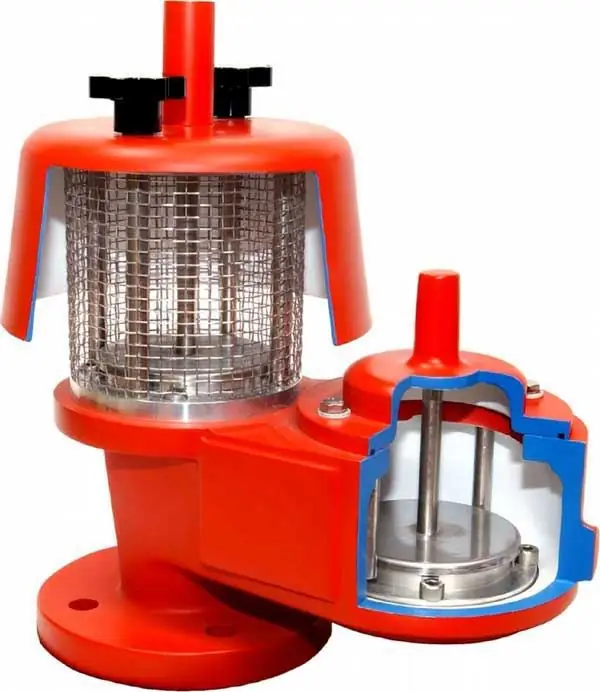

The simplest schemes of industrial breathing valves can be compared with the function of air vents, which are widely used to remove excess air from domestic pipes. In this case, the same principle of formation of a buffer zone with two levels of regulation of the passage of excess steam and air operates. In the normal state, both valves are closed, and the change in capacity begins from the moment the pressure in the circuit is exceeded, which naturally causes the valve to rise from the seat. The specific pressure at which the reservoir breather valve begins releasing excess gas-air mixtures is set individually in accordance with the requirements forserviced area. Moreover, the conditional activation point of the valves can be not only a high pressure value, but also sharp temperature fluctuations, as well as an excessive underestimation of pressure with the formation of a vacuum. In conclusion of the above, it can be summarized that when fixing the excess pressure, the pressure control valve comes into operation, and when the vacuum is excessive, the system of vacuum valves. The regulation process itself provides for either the release of excess steam and air, or an increase in sealing under conditions of artificial injection of technical gas mixtures.
Mechanical shutter valves
The oldest and most common form of breather valve designed to maintain sufficient pressure in horizontal oil and gas containers. But this group also has its differences. So, closed-type models are used to capture vapors of volatile products, and a combined mechanical breathing valve is used for gas station tanks (gas stations), where it is necessary to ensure the safety of the operational properties of the resource. What is the difference between the design with a mechanical shutter in principle? Mainly - ways of fastening the plates on the body. For example, fixation can be provided by rigid guide rods or peripheral hangers of the plate using collars. The difference between the two different approaches to installing a valve is the same as when attaching conventional pipelines. Rigid fastening ensures the stability of the field connection and the immobility of the circuit, which is beneficial whenoperation of communications of small capacities. However, even slight vibrations during maintenance of a large tank can deform or completely rip off the hard fastener mounting assembly. Therefore, in such systems, it is customary to use a "floating" mechanical fixation with clamps that provide a small range of oscillation.

Wet Seal Valves
Hydraulic seals work on the principle of regulation of internal pressure created by a low-viscosity, low-evaporating and non-freezing liquid filled into the regulator structure. It can be a solution of glycerin, diesel oil, diesel, ethylene glycol and other mixtures that are capable of generating sufficient force for the operation of a hydraulic seal. The valve itself is mounted strictly horizontally, since its operation is calculated on the creation of a reduced vacuum and pressure regulation as a result of a decrease in the mass of liquid relative to the standard value. Tank breather hydraulics are replacing mechanical valves to better control pressure in highly volatile product stores. The hydraulic valves have a membrane that separates the vapor-gas space of the tank from the atmosphere, if necessary, also extinguishing the flame inside the circuit due to the built-in fire fuse.
Valve design
The main design data used in the process of designing industrial breathing valves includethroughput rates. These data are directly dependent on the performance of the circuit and the ability to regulate the flow. Moreover, in the calculations of breathing valves for tanks, two indicators of throughput are used - by internal pressure, and by vacuum. In both cases, the output is given as a specific measure of fluid passage per hour. For direct calculation, the performance parameter for filling and draining the product from the tank is used. It affects the amount of throughput and the characteristics of the serviced environment. Depending on the properties of the same oil product, the performance accounting factor may change. For example, the gas content of crude oil has a significant impact.
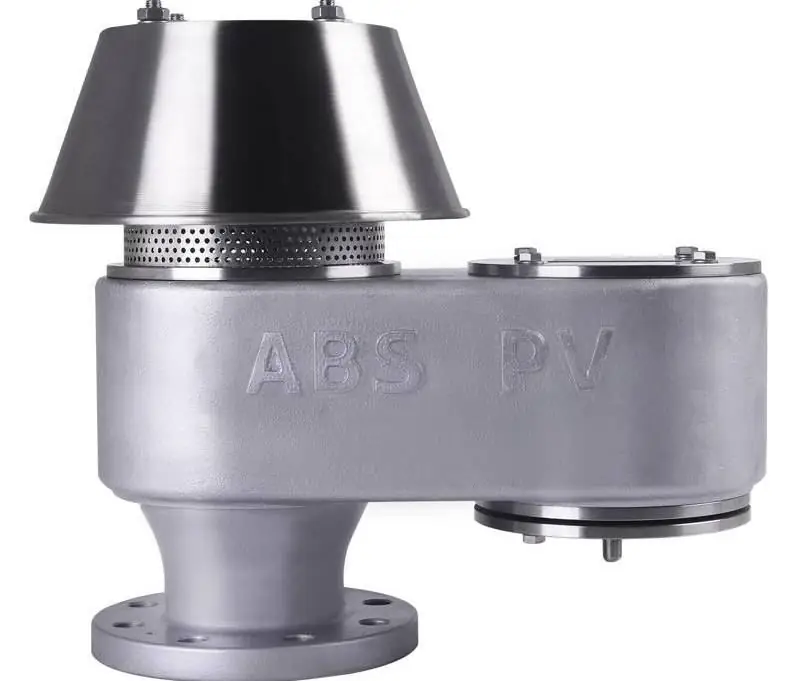

Valve accessories
After determining the parameters of the valve and the characteristics of its design, you can begin to select the elements through which the device will interact with the tank's communications. First of all, this applies to the pipe for connecting to the tank. Two parameters will be important - the diameter of the nozzle and performance. The actual throughput will be limited by the valve itself, and the connection pipe diameter will determine the flow rate, which is not regulated by the technical documentation. However, there are general regulations for tank vent valves that state that, in principle, joints less than 350 mm thick should not be used. There is also an upper limit of 1500-1700 mm, withwhich has a high center of gravity and a large windage, which ultimately gives a significant load on the nozzle. When choosing a communication link valve-pipe, it is optimal to adhere to a format of 400-600 mm, also taking into account external influences during operation.
If necessary, the regulation unit is also supplied with stretch marks. They are generally recommended for use as an auxiliary element in valve installations where the greatest hydraulic loads are expected. Guy wires are fixed on the roof of the tank, which provides additional insurance for the working infrastructure.
Another important component of control valves is the reflector disc. It is used to reduce the loss of oil products and gas mixtures during the evaporation process. The baffle disc works in combination with the tank breather valve to reduce salable material emissions by 3-5%. This device forms a kind of filter umbrella over the ejection channel, diverting part of the useful product flows into the horizontal plane. At the next stages of technological processing, these mixtures are received by special collectors and transported to the main circulation channel of the oil and gas product without deterioration in performance.
Valve application

Immediately before installation work, lift the valve bracket with covers, and then remove the plates and shipping sleeves. Next, the housing structure must be blown out with compressed air and reassembled in the reverse order. Installationvalve on the tank communication is carried out through a special flange of a suitable format. Also, a gasket is used when connecting. Mechanical fastening is carried out with bolts and nuts that are suitable in design for a particular unit of the installation. In the future, during operation, periodic maintenance of the breathing valve of the tank is carried out, which may include repair measures. For example, as a result of a technical inspection or during normal operation of the circuit, the following problems are often detected:
- Uncharacteristic change in pressure indicators. As a rule, it is associated with contamination of the fire fuse cassette. This unit needs to be flushed with kerosene and then purged with air.
- Depressurization at the junction of the tank branch pipe with the breathing and safety valve. It is recommended to check the photoplastic coating or rubber gasket. Sometimes these problems occur due to icing of the valve neck.
- Depressurization at the place where the bolt was attached. More likely there are violations in the clamp fastening design. It is not necessary that the clamp itself be damaged - it is possible that the clamp free position range was incorrectly adjusted during its adjustment.
Checking tank breathers

The above problems are far from always detected during the general maintenance of tanks with petroleum products, and even more so they are noticed in normal modeoperation. At the same time, the slightest deviation in the performance of the pressure regulator can lead to a fire at the manned station, not to mention other negative factors associated with the uncontrolled release of flammable vapors and liquids to the outside. Accordingly, a special check of the breathing valves of the tanks should be carried out in a separate order, during which the current state of the pipeline, the roof of the tank and the working environment is analyzed. As part of this kind of activities, the following is carried out:
- Test valve capacity under pressurized conditions to optimum performance.
- Checking the capacity of the regulator under vacuum conditions.
- Checking the mechanics of the valves at the moments of closing and opening of plates with shutters.
- If necessary, commissioning with regulation of the valve operating parameters.
Each application of this valve has its own schedule for diagnostic operations. On average, the frequency of checking the breathing valves of tanks is 1-2 times a month. Usually in the summer such events are held more often than in the winter. In this case, the tank during operation must be subjected to a general inspection on a daily basis. Based on the results of all examinations, a protocol is drawn up with the data recorded during the verification.
Conclusion

The concept of using auxiliary fittings with valves and other structuralmeans of regulation are gradually becoming a thing of the past. Manufacturers of pipeline systems are trying to shift the regulatory and safety functions to integrated oil storage control stations. However, the complete withdrawal of respiratory valves from the practice of using speech is not yet discussed. Moreover, there are promising directions for their technological development. In particular, the common format of the breather valve for the gas station tank in recent years has acquired a removable flame arrester and received a stamped welded body. The first innovation made it possible to use the device in regions with extremely low temperatures in winter, and the second one reduced the weight of the structure by 2 times. The fourth generation valves also have fewer moving parts, which improves their operational reliability.
Some manufacturers are also focusing on optimizing valve maintenance processes. So, a very convenient solution, from the point of view of operation, was the introduction of fixed casings with a special placement configuration, which does not require the dismantling of entire groups of parts for internal inspection of the valve structure.
Recommended:
Classification of engines. Types of engines, their purpose, device and principle of operation
Nowadays, most vehicles are powered by an engine. The classification of this device is huge and includes a large number of different types of engines
Driver controller: purpose, device and principle of operation

The use of a variety of vehicles today is very active. They all have in common that they need to be managed. The driver's controller is also designed for control. With it, you can remotely control the traction motor in braking or traction mode
Reservoir parks: device, principle of operation, volume

The extraction of oil products is quite well developed today. To create a main oil pipeline, there are several mandatory conditions, among which is the creation of a tank farm. But what is it? In itself, such a park is a group of several separate tanks used to store oil, combined into one unit
Thermal expansion valve: principle of operation, device and characteristics

Today, expansion valves are used in many devices. With their help, you can easily adjust the temperature in a living room, they can be added to the design of a tap, used in car air conditioners, etc
General purpose engines: device, principle of operation, application, photo

Automotive equipment is mainly equipped with standardized internal combustion engines (ICEs), the design of which is focused on placement in the engine compartment. However, there is a great demand for power units of this kind in the garden equipment segments, from manufacturers of snowplows, snowmobiles, etc. Moreover, the requirements for integration and operational parameters in such cases differ sharply from automotive standards

