2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:39
Automotive equipment is mainly equipped with standardized internal combustion engines (ICEs), the design of which is focused on placement in the engine compartment. However, there is a strong demand for power units of this kind in the garden equipment segments, from manufacturers of snowplows, snowmobiles, etc. Moreover, the requirements for integration and performance parameters in such cases differ sharply from automotive standards. In this regard, a whole segment of general-purpose engines was formed with an optimized design, but different technical characteristics.
Assignment of aggregates

Like other types of internal combustion engines, general-purpose power plants are used to generate and convert thermal energy into mechanical energy. By optimizing thisprocess in technical and structural terms, the developers were able to offer this product to a wide range of consumers. Among them are manufacturers of garden, construction, road, cleaning, boating and sports equipment and machinery. For example, in the construction segment, a general purpose engine may be used to support the compressor equipment function. At the same time, the unit itself does not necessarily have to be integrated into the design of the compressor. Connection is carried out in a separate order, and the internal combustion engine operates as an autonomous generator powered by gasoline or diesel fuel. Garden equipment manufacturers are more likely to use small engines in lawn mowers, motor cultivators, pumping stations, watering machines, etc. The largest and most powerful units of this type are used in power plants, special equipment and snowmobiles.
Design of general purpose engines

The principle of operation is the same as that of standard internal combustion engines. Accordingly, the device provides a similar set of structural elements with a group of cylinders, bearings, a crank mechanism and a shaft. The differences are only in the dimensions, the configuration of the arrangement of parts and additional equipment. As for the dimensions, to a greater extent these are compact units. On the one hand, size optimization is determined by the limitations of the technical and operational process (small dimensions of the target equipment), and on the other hand, by increased environmental requirements (especially forgarden equipment).
In terms of layout configuration, general purpose engines are more diverse than conventional motors for road vehicles. Versatility is manifested in the fact that the unit of one form factor can suit several groups of target equipment from various segments at once. Auxiliary equipment is used for more ergonomic operation and expansion of the possibilities for integrating this type of internal combustion engine. These can be frame platforms, devices with handles, frames and load-bearing platforms with a chassis.
Varieties of general purpose internal combustion engines

The layout configuration of functional elements is one of the key features of the separation of models. So, according to the location of the crankshaft, general-purpose internal combustion engines are classified as follows:
- With horizontal shaft. Such devices are often used in the production of construction equipment. For example, this group includes internal combustion engines that power vibrating plates, cutters, and some waterjet machines.
- With vertical shaft. The optimal solution for small-sized equipment, which is often controlled by the operator on weight. General purpose vertical shaft engines include power units for lawn mowers and garden trimmers. In such designs, the cutting blades are fixed to the crankshaft without intermediate mechanisms, which just makes it possible to reduce the size and weight of the equipment.
The design of the shaft itself also differs. It may be tapered orcylindrical shape. The first option is preferable in terms of placement ergonomics, but the second one is distinguished by its versatility in principle.

Specifications
Mostly we are talking about small-sized light units, but in this segment there are differences in the ranges of indicators in technical and operational parameters. For example, there is a popular segment of engines from 8 to 13 hp. With. Such units are just more often used in garden equipment. Within a cylinder volume of up to 1 liter, the power potential can reach 25 liters. With. These are air-cooled diesel units that can be used in construction and transport equipment. The same general purpose diesel engine with a spindle speed of about 1500 rpm is well spread in the niche of industrial and commercial equipment. Household units are mainly equipped with high-frequency four-stroke units running on gasoline fuel. However, the use of various general-purpose internal combustion engines, depending on the consumption resource, should be discussed separately.

Application of gasoline engines
An extensive group of power plants that find their place in the household, industry and even energy. For example, gas generators can be used for autonomous power plants, at a remote construction site as a backup power source, or in the power supply of a private house. To the most famousmanufacturers of such internal combustion engines include Robin-Subaru, Kipor, Green Field and Honda. They also produce decent drive mechanisms for walk-behind tractors, snowmobiles, construction and agricultural machinery. A typical representative of the segment is a single-cylinder general-purpose Honda engine in the CV 530 modification. The unit is characterized by an overhead valve arrangement, air cooling and a vertical shaft. A significant difference between this unit and diesel analogues can be called a high degree of environmental friendliness.
Diesel engine applications

Diesel technology traditionally wins in terms of power, which allows it to be used in equipping professional road and boat equipment. It is also an attractive solution for autonomous power supply, and, unlike gasoline units, such internal combustion engines have a longer working life with similar maintenance costs. The standard arrangement of general purpose diesel engines is demonstrated by the German three-cylinder Deutz TD226B-3D unit, which is also considered one of the most economical and environmentally friendly in its class. These characteristics just became possible due to the presence of a full power take-off system (45-60 hp) from the flywheel for radial or axial drive. Added to this is water cooling with direct fuel injection.
Application of electric motors
General-purpose electric motors also have their advantages, which is expressed in their environmental friendliness, low noiseand small sizes. Of course, they also have the lowest performance indicator, but this nuance does not prevent the full use of this technique in motorcycles, the same lawn mowers, electric shears and chain saws. Innovative solutions in the segment of general purpose engines are regularly demonstrated by Siemens, releasing models with power from 0.06 to 1000 kW. In the assortment of the company you can find aluminum and cast iron structures that are suitable for a variety of operating conditions.
Conclusion

The concept of a general purpose internal combustion engine is driven by the need for technological progress that expands the scope of power equipment. Against this background, the tasks of unifying such equipment are logically exacerbated. But the versatility of engines has its negative sides. They are expressed in high cost, low power and maintenance problems. On the other hand, the Chinese Lifan general-purpose engines, for all their shortcomings, which appear in the context of comparison with the same German units, show an example of combining versatility and worthy consumer properties. And this is not to mention the low cost of this product, which is initially included in the budget segment. Domestic general-purpose internal combustion engines from the VTZ, YaMZ and Altai-diesel enterprises are famous for partly the same advantages.
Recommended:
Classification of engines. Types of engines, their purpose, device and principle of operation
Nowadays, most vehicles are powered by an engine. The classification of this device is huge and includes a large number of different types of engines
Driver controller: purpose, device and principle of operation
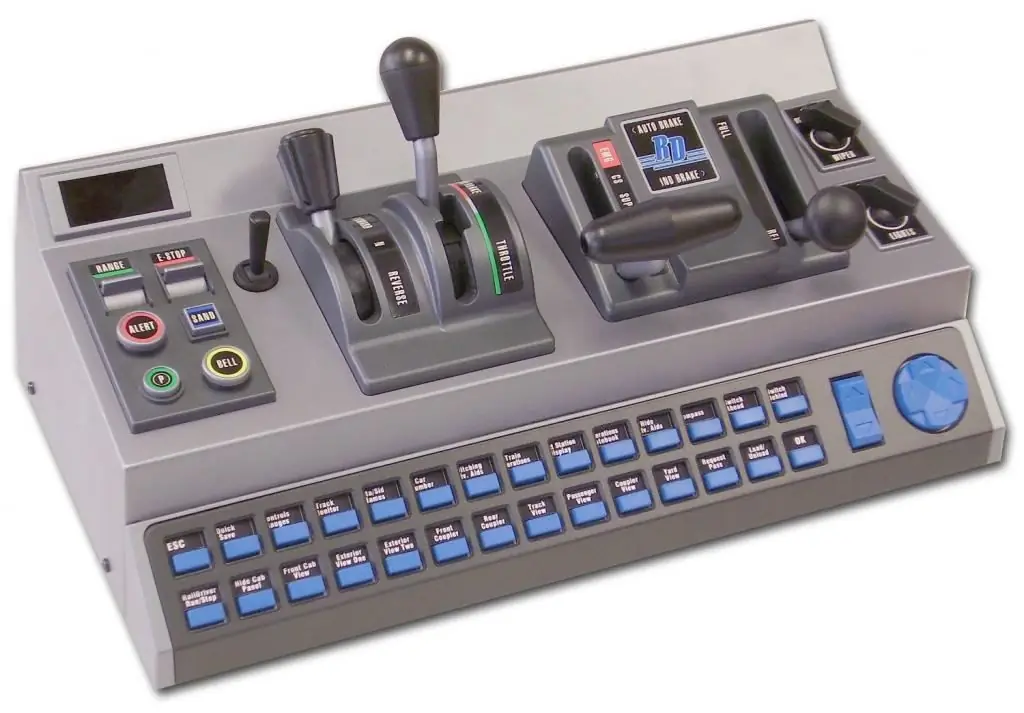

The use of a variety of vehicles today is very active. They all have in common that they need to be managed. The driver's controller is also designed for control. With it, you can remotely control the traction motor in braking or traction mode
Turboprop engine: device, scheme, principle of operation. Production of turboprop engines in Russia

A turboprop engine is similar to a piston engine: both have a propeller. But in every other way they are different. Consider what this unit is, how it works, what are its pros and cons
Reservoir breathing valve: purpose, device, principle of operation, verification

Oil refineries and technological complexes using oil and gas products contain a system of pipelines for servicing fuel materials in their working infrastructure. Maintaining sufficient performance in the circulation circuits of the same oil requires the use of special plumbing fittings. Its key element is the reservoir breather valve, through which the pressure is regulated
Cylinders "Rockwool" (Rockwool): description, device, principle of operation, application, photo
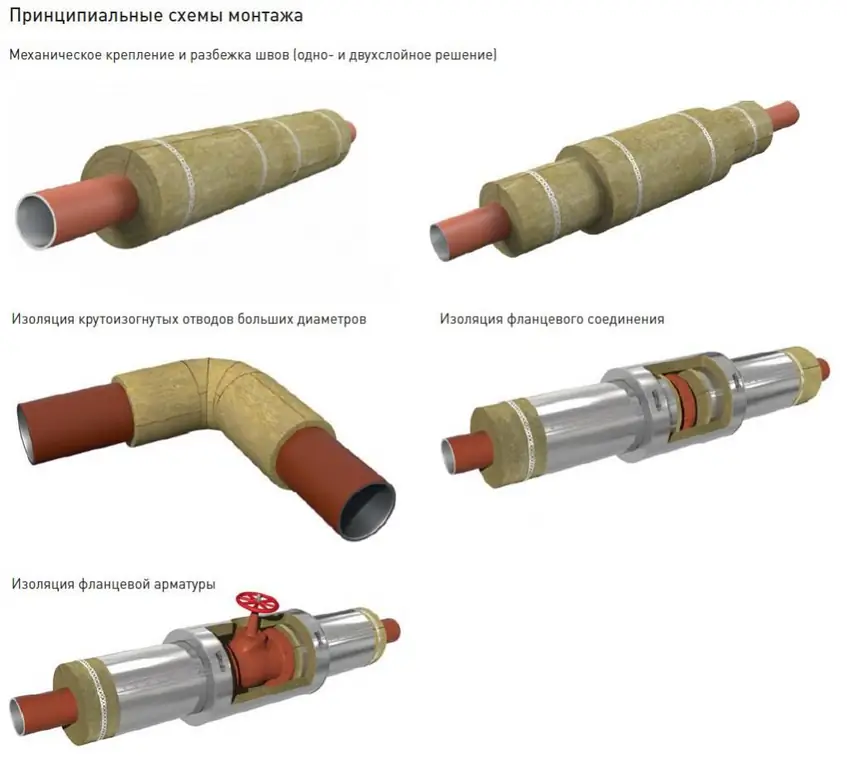

The service life of pipes is reduced due to their use in conditions of low temperatures and high humidity. This problem, however, can be solved by using modern protective materials made of mineral wool. Among the huge variety of proposals on the market, Rockwool cylinders are not the last. The company started its activity more than a century ago in Denmark. During its existence, it has achieved consumer recognition

