2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:38
A zener diode is a semiconductor diode with unique properties. If an ordinary semiconductor is an insulator when switched back on, then it performs this function until a certain increase in the applied voltage, after which an avalanche-like reversible breakdown occurs. With a further increase in the reverse current flowing through the zener diode, the voltage continues to remain constant due to a proportional decrease in resistance. In this way, it is possible to achieve stabilization mode.

In the closed state, a small leakage current first passes through the zener diode. The element behaves like a resistor, the resistance value of which is large. During breakdown, the resistance of the zener diode becomes negligible. If we continue to increase the voltage at the input, the element begins to heat up and when the current exceeds the permissible value, an irreversiblethermal breakdown. If the matter is not brought to it, when the voltage changes from zero to the upper limit of the working area, the properties of the zener diode are preserved.
When a zener diode is directly turned on, the characteristics are the same as a diode. When the plus is connected to the p-region, and the minus is connected to the n-region, the transition resistance is small and the current flows freely through it. It rises as the input voltage increases.

A zener diode is a special diode connected mostly in the opposite direction. The element is first in the closed state. In the event of an electrical breakdown, the voltage zener diode maintains it constant over a wide current range.

A minus is applied to the anode, and a plus to the cathode. Beyond stabilization (below point 2), overheating occurs and the probability of element failure increases.
Features
Zener parameters are as follows:
- Ust - stabilization voltage at rated current Ist;
- Ist min - minimum electrical breakdown start current;
- Ist max - maximum allowable current;
- TKN - temperature coefficient.
Unlike a conventional diode, a zener diode is a semiconductor device in which the electrical and thermal breakdown regions are quite far apart on the current-voltage characteristic.
Associated with the maximum allowable current is a parameter often specified intables - power dissipation:
Pmax=Ist max∙ Ust.
The temperature dependence of the zener diode can be either positive or negative. By connecting elements in series with coefficients of different signs, precision zener diodes are created that do not depend on heating or cooling.

Inclusion schemes
Typical circuit of a simple stabilizer, consists of a ballast resistance Rb and a zener diode that shunts the load.
In some cases, there is a violation of stabilization.
- Submission to the stabilizer of a large voltage from the power source in the presence of a filtering capacitor at the output. Current surges when charging it can cause failure of the zener diode or destruction of the resistor Rb.
- Load shutdown. When the maximum voltage is applied to the input, the current of the zener diode may exceed the allowable one, which will lead to its heating and destruction. Here it is important to observe the safe work passport area.
- Resistance Rb is selected small so that at the minimum possible supply voltage and the maximum allowable current at the load, the zener diode is in the working regulation zone.
Thyristor protection circuits or fuses are used to protect the stabilizer.
Resistor Rb is calculated by the formula:
Rb=(Upit - Unom)(I st + In).
Currentzener diode Ist is selected between the allowable maximum and minimum values, depending on the input voltage Upit and load current In.
Zener Selection
Elements have a large spread in stabilization voltage. To get the exact value of Un, zener diodes are selected from the same batch. There are types with a narrower range of parameters. With high power dissipation, the elements are installed on radiators.
To calculate the parameters of the zener diode, initial data are required, for example, these:
- Upit=12-15 V - input voltage;
- Ust=9 V - stabilized voltage;
- Rn=50-100 mA - load.
The parameters are typical for devices with low power consumption.
For a minimum input voltage of 12 V, the current on the load is selected to the maximum - 100 mA. According to Ohm's law, you can find the total load of the circuit:
R∑=12 V / 0.1 A=120 Ohm.
At the zener diode, the voltage drop is 9 V. For a current of 0.1 A, the equivalent load will be:
Req=9 V / 0.1 A=90 Ohm.
Now you can determine the resistance of the ballast:
Rb=120 Ohm - 90 Ohm=30 Ohm.
It is selected from the standard row, where the value is the same as the calculated one.
The maximum current through the zener diode is determined taking into account the disconnection of the load so that it does not fail if any wire is unsoldered. The voltage drop across the resistor will be:
UR=15 - 9=6 B.
Then the current through the resistor is determined:
IR=6/30=0, 2 A.
Since the zener diode is connected in series with it, Ic=IR=0.2 A.
Power dissipation will be P=0.2∙9=1.8 W.
According to the parameters obtained, a suitable Zener diode D815V is selected.
Symmetrical zener diode
Symmetrical diode thyristor is a switching device that conducts alternating current. A feature of its work is a voltage drop of up to several volts when turned on in the range of 30-50 V. It can be replaced by two counter-connected conventional zener diodes. Devices are used as switching elements.
Analogue of a zener diode
When it is not possible to find a suitable element, they use an analogue of a zener diode on transistors. Their advantage is the possibility of voltage regulation. Multi-stage DC amplifiers can be used for this.

A voltage divider with a trimming resistor R1 is installed at the input. If the input voltage increases, on the basis of transistor VT1 it also increases. At the same time, the current through the transistor VT2 increases, which compensates for the increase in voltage, thereby maintaining it stable at the output.
Marking of zener diodes
Glass zener diodes and zener diodes in plastic cases are produced. In the first case, 2 numbers are applied to them, between which the letter V is located. The inscription 9V1 means thatUst=9, 1 V.

On the plastic case, the inscriptions are deciphered using a datasheet, where you can also find out other parameters.
The dark ring on the case indicates the cathode to which the plus is connected.
Conclusion
A zener diode is a diode with special properties. The advantage of zener diodes is a high level of voltage stabilization with a wide range of operating current changes, as well as simple connection schemes. To stabilize a small voltage, the devices are switched on in the forward direction, and they begin to work like ordinary diodes.
Recommended:
Shelf life of water meters: period of service and operation, verification periods, operating rules and time of use of hot and cold water meters

The shelf life of water meters varies. It depends on its quality, the condition of the pipes, the connection to cold or hot water, the manufacturer. On average, manufacturers claim about 8-10 years of operation of devices. In this case, the owner is obliged to carry out their verification within the time limits established by law. We will tell you more about this and some other points in the article
Silicate industry - and the house, and the roof, and dishes

Like mushrooms after the rain, grandiose skyscrapers began to grow in many cities of the world, which are bright design solutions that organically combine concrete and glass. It is the building materials that are so in demand at the present time that the silicate industry produces
Planning and economic department: its functions and tasks. Regulations on the planning and economic department

Planning and economic departments (hereinafter PEO) are created for the effective organization of the economy of organizations and enterprises. Although often the work of such departments is not clearly regulated. How should they be organized, what structure should they have and what functions should they perform?
Device, principle of operation and diagram of the rectifier diode bridge
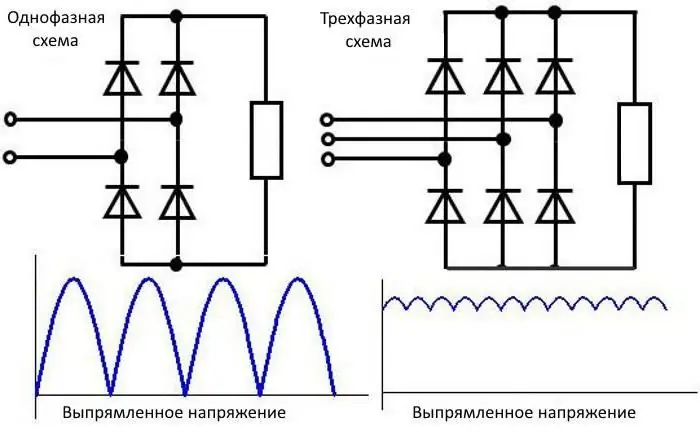
Alternating electric current is converted into a constant pulsating through the use of special electronic circuits - diode bridges. The rectifier diode bridge circuit is divided into 2 versions: single-phase and three-phase
What you need to work in a taxi: necessary documents and requirements, regulations and legal aspects. Feedback and advice from taxi drivers, customers and dispatchers

According to many passengers, the job of a taxi driver is the easiest. You sit, listen to pleasant music and drive back and forth. And they give you money for it. But this is only the outer side of the coin. The reverse is much less rosy. We will talk about it in this article. And we will also highlight what you need to work in a taxi

