2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-06-01 07:12:56
In a market economy, prices for various goods that an enterprise can purchase for economic activity are constantly changing. The purchase price of an item of fixed assets in the current year may differ significantly from that for which this item was purchased. An enterprise can track changes in prices for those objects of property that it has, make a special recalculation of the cost for them and take into account the difference. This process is called property revaluation (hereinafter PI). Before proceeding to the description of the PI system, let's consider some concepts.
What are non-current assets?
Non-current assets (hereinafter referred to as VOA) are items of property of the company that are constantly used in its business activities. Any property that the society does not intend to commodify for an extended period,is a non-current asset. SAIs of the company include: deferred tax assets, intangible assets, land plots, nature management facilities, buildings, structures, transport, livestock, various equipment, office equipment, etc.

The main criteria for determining the HLW are the period of its use, which must be more than 12 months (or one operating cycle if it is more than 12 months), and its presence in the company as an object of property capable of generating income (as means of labor). Also, non-current assets include various financial investments that will bring income to the company for more than one year, or investments that will pay off in the future after the expiration of this period. It is worth noting that the item of property may, for some reason, not participate in the production activities of the company at a particular moment, but be considered as an SAI. When attributing an item of property to the SAI, the dominant role in this case is played not by the very fact of its use to generate income, but by the reason for its acquisition for this purpose. With PI, the main role is played by the replacement price of property, determined through the market value of a non-current asset.
What is the replacement and market price?
Replacement price is the cost of full restoration of an item of property in case of its breakage or loss. In other words, this is the money that the firm must pay for exactly the same item if the old one ceases to participate in the productionactivities. The market price is the price at which a newly purchased item can be sold. That is, this is the money that you can get if you decide to sell the property immediately after the purchase (at the time it is included in the accounting).
In fact, in our case, there is no difference between the recovery and the market price. In some situations, for example, when a company receives an item of property free of charge, it is included in accounting at the market price. Then we can say that the market value becomes the original. In our case, the market price becomes a recovery price.
What is the revaluation of non-current assets?
PI is a revision of the price for which a particular item of the company's property was purchased, by comparing this value with the replacement value. If the original purchase price differs significantly from the replacement price, then it is necessary to depreciate or revaluate the non-current asset. A significant difference between these indicators is not strictly defined by law, but the generally accepted limit is 5% of the difference. If the initial price of the property is less than 5% of the replacement price, then an additional assessment should be carried out. If the original cost is more than 5%, a markdown must be carried out. In the future, revaluation and markdown should be reflected. In the balance sheet, the revaluation of non-current assets is line 1340.

PI is not an obligatory factor both for the general taxation system and for the simplified one. The company may not conduct a revaluation of property at all untiluntil the need arises. However, this does not mean that the firm can carry out the PI at any time it wants. The decision to carry out this procedure should be fixed in the accounting policy.
It is worth mentioning that the PI can relate to both the entire property of the company, and part of it. That is, it is not necessary to overestimate everything that is. Under the PI, certain groups of homogeneous objects should be formed. At the same time, there is no strict classification of them by the legislature. Societies are allowed to define these groups themselves. Uniformity should not be understood as such things as, for example, the location of objects or their color. In this case, technical characteristics, purpose of use, and the like matter. Groups of homogeneous items should also be fixed in the accounting policy. There are two ways for PI: direct price recalculation and indexation.
Meaning of holding a PI?
As mentioned at the beginning of the article, the prices of various things that can become the SAI of a firm are constantly changing. The revaluation of non-current assets allows you to equalize the initial cost of these assets and make them the same as the prices on the market at a given time.
There are many reasons for PI. It is necessary to conduct it if it is necessary to sell part of the property or the entire society as a whole. If the firm decides to attract investments, it is also necessary to carry out a PI if the attraction is related to obtaining a loan. To do this, the price of the collateral must be reliably determined. And since the collateral is the property of the company, then one cannot do without PI. If aa decision was made to place (issue) securities, and a revaluation of property is also being carried out, since the authorities must know the real financial situation of the company (issuer) that will issue securities into circulation.

Just for the sake of improving the investment attractiveness for potential investors, a PI is also needed. If the company's net assets fall below its authorized capital, the company risks going bankrupt. Therefore, to clarify the value of assets, a revaluation of property is also needed. If a decision is made to insure property, an insurance base must be formed. PI is also needed here. Also, the reasons for the revaluation include the processes of mergers and acquisitions of firms, especially if these processes relate to foreign companies operating in accordance with the international financial reporting standard (IFRS). In such cases, the PI is mandatory. When an item of property becomes obsolete, when its market price falls sharply against the background of new developments, revaluation allows you to equalize the value of existing items with their market price for more accurate information about the financial situation of the company. There are other reasons for PI.
Revaluation periods
If a company once revalued non-current assets, then it must be periodically carried out throughout the life of the organization. The signal for IP is the significant change mentioned above between the price of the item of property accepted for accounting and its market value. Revaluation of the company should be carried out no more than once a year.year. It is possible to establish specific periods for this procedure in the accounting policy, but if there is a reservation about the possibility of making an unscheduled PI. In view of this factor, after the first revaluation, the company must annually find information on market prices for all items of property that it owns. And in case of a significant difference of 5%, it is necessary to carry out a markdown or reassessment based on the results.

In accordance with the current regulations, the PI should be carried out closer to December 31, that is, at the end of the year, and reflected in the accounting separately. In the new year, items of property are accepted for accounting at a new price. The question arises: what to do if it is necessary to conduct a PI in the middle of the year? Legislatively, this issue is not regulated anywhere, that is, the company can conduct a reassessment in the middle of the year, but if the data of its beginning are taken into account.
PI Methods
There are two ways to carry out revaluation - direct price recalculation and indexation. The conversion method is the most common. For its implementation, it is necessary to determine the market price of the items of property subjected to PI. To obtain information about this, you can use the websites of manufacturers, special literature, government statistics, the services of independent appraisers, etc. After that, you can re-evaluate using the calculations described in the next section.
The second PI method is practically not used. To implement it, you need to know the deflator indices - price indices (in our case, for the BOA). Until 2001, state statistical bodies regularly provided informationaccording to the BHA price index. Now, such a service can only be obtained for a fee from the same statistical bodies.
Formulas for conducting PI
Since the revaluation of non-current assets concerns not only items of property, but also the amounts of accumulated depreciation, then first you need to calculate depreciation (including accumulated) at the time of the PI. There are four depreciation methods, so we will skip this step.
Direct conversion method
After determining the market price of the revalued item, you need to use the formula:
O=PC / PS100 - 100, where
- O - price deviation in percent;
- RS - market value;
- PS - the original or current price of restoration, if the item has already been revalued.

After the calculation, you should get a percentage (positive or negative). If the positive percentage is more than 5%, then this is a signal for an increase in the value of a non-current asset, and it is necessary to reassess. If the negative percentage is less than 5%, a markdown should be made. The revaluation or markdown value is the difference between the original and replacement price.
Next, you need to recalculate depreciation:
PA=AO where
- PA - restated depreciation;
- A - depreciation (including accumulated);
- O - price deviation in percent.
Index method, or indexing method
In this case, the recovery (market) price is not determined byinformation from the outside, as in the case of direct recalculation, but is calculated using deflator indices:
BC=PSID1ID2ID3ID4, where
- VS - replacement price;
- PV - initial or current replacement cost if the item has already been revalued;
- ID1-ID4 are the deflator indices for the SAI for the four quarters of the reporting year.
After calculating the replacement price, the next steps are the same as when recalculating prices directly. After these calculations and accounting for PI in the accounts (more on this below), the revaluation of non-current assets is reflected in the balance sheet. This is the final step of this procedure.
PI system
If the item is revalued for the first time, then its revaluation is credited to account 83 “Additional capital”, and the markdown is debited to account 91.2 “Other income and expenses”. If the PI is carried out at the beginning of the year, then in the event of a markdown, the value is credited to the debit of account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)”. The depreciation calculated using the formula above should also be revalued. The same postings are made, only debits and credits are reversed, and depreciation accounts are used. There is nothing complicated here.

The most interesting thing begins if the item has already been re-evaluated before. If this happens, then the new revaluation is attributed to additional capital. If it is equal to the old markdown, then it is added to the credit of account 91.1. If the revaluation is greater than the previous markdown, then its residual value goes to additional capital.
If the item has already been revalued, the additional capital is reduced by the value of the markdown. If it is greater than the previous value, then first the additional capital is reduced by the value of the previous revaluation, and the residual value of the markdown goes to account 91.1 if the procedure is carried out at the end of the year (December 31), or to account 84 if the markdown occurs at the beginning (January 1).
If the item has already been marked down, the new value is credited to account 91.2 or to account 84 if the markdown occurs at the beginning of the year.
Wiring
Let's consider an example of a fixed asset UI.
Reassessment (first PI, or if there was also reassessment earlier):
- Dt 01 Ct 83 - revaluation reflection.
- Dt 83 Ct 02 - increase in depreciation.
Markdown (first PI or if there was a markdown earlier too):
- Dt 91.2 Ct 01 - markdown reflection.
- Dt 02 Ct 91.1 - decrease in depreciation.
Markdown (first PI at the beginning of the year or if there was a markdown earlier too):
- Dt 84 Ct 01 - markdown reflection.
- Dt 02 Ct 84 - decrease in depreciation.

Revaluation (previously there was a markdown):
- Dt 01 Ct 91.1 - revaluation reflection.
- Dt 91.2 Ct 02 - revaluation of depreciation.
- Dt 01 Ct 83 - revaluation residual value.
- Dt 83 Ct 02 - residual value of depreciation.
Markdown (previously reassessed):
- Dt 83 Ct 01 - markdown reflection.
- Dt 02 Ct 83 - depreciation markdown.
- Dt 91.2 Ct 01 - residual markdown value.
- Dt 02Kt 91.1 - the residual value of depreciation.
Depreciation (at the beginning of the year, there was a revaluation earlier):
- Dt 83 Ct 01 - markdown reflection.
- Dt 02 Ct 83 - depreciation markdown.
- Dt 84 Ct 01 - residual markdown value.
- Dt 02 Ct 84 - residual value of depreciation.
Reflecting PI in the balance sheet
The PI carried out at the end of the year should be reflected in the balance sheet separately in line 1340 “Revaluation of non-current assets”. At the same time, line 1130 "Fixed assets" should be reflected with the results of IP for fixed assets included in it, and line 1350 "Additional capital (without IP)" should reflect additional capital without taking into account the results of IP. The values from the credit balance on account 83 are used as information for filling in line 1340.
Recommended:
Net sales in the balance sheet: string. Sales volume in the balance sheet: how to calculate?

Annually, enterprises prepare financial statements. According to the data from the balance sheet and income statement, you can determine the effectiveness of the organization, as well as calculate the main planned indicators. Provided that the management and finance department understand the meaning of terms such as profit, revenue and sales in the balance sheet
General concepts of the balance sheet: assets, liabilities, balance sheet currency

The balance sheet contains important information for assessing the company's financial results. Each section of the asset, liability, as well as the balance sheet currency is necessary to calculate many financial indicators
Formula of net assets on the balance sheet. How to calculate net assets on a balance sheet: formula. Calculation of net assets of LLC: formula

Net assets are one of the key indicators of the financial and economic efficiency of a commercial firm. How is this calculation carried out?
Liquidation balance sheet is Definition of the concept, approval, form and sample of filling out the liquidation balance sheet
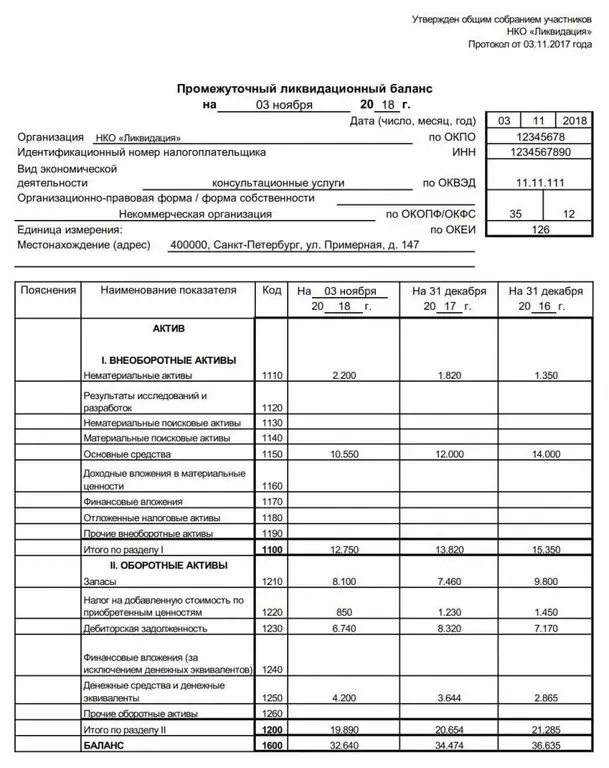
The liquidation balance sheet is an important financial act drawn up during the closing of an organization. It can be intermediate or final. The article tells what is the purpose of these documents, what information is entered into them, as well as how and when they are approved and submitted to the Federal Tax Service
The book value of the assets is the balance line 1600. The balance sheet

The assets of the company, or rather, their combined value, are the necessary resources that ensure the process of manufacturing new products, the possibility of expanding sales markets and modernizing existing facilities, searching for new partners and customers, that is, the financial and economic side of the company's life

