2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:43
A database administrator is a person who is responsible for developing the requirements for the various databases of an organization. He is responsible for the design, effective use, maintenance of the integrity and maintenance of the repository. The administrator manages accounting type records and organizes a system of protection against unauthorized use of the information in the database. A detailed description of this speci alty is established in the professional standard "Database Administrator", approved by order of the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation No. 647n of September 2014. Speci alty code 40064.
Administrator tasks
The flow of transmitted information plays an important role in the modern world. All data is systematized in certain groups - databases. An administrator is a person who provides qualified management of these databases, including their comprehensive protection. Due to the connection of any processes taking place in organizations, this profession is in great demand in the market.
The main task of a database administrator is to ensure the smooth operation ofoperation of all equipment located in the organization (networks, servers and other electronics). The activity of a specialist includes the implementation of certain algorithms for processing and distributing the entire amount of information in the enterprise (its maintenance and dispatching), which will allow you to continuously retrieve and use the necessary information if necessary.
A database administrator is a specialist who spends most of his working time maintaining the finished information system. But in some cases, it is assigned other tasks as part of the workflow:

- design and development of flowcharts and databases;
- development of necessary requirements;
- Data warehouse performance rationing;
- formulation of access rights and basic regulations;
- copying databases in backup mode and restoring them;
- determining the format of user accounts;
- research of use cases for protecting databases from unauthorized intrusions into the system;
- developing options to prevent hardware-type errors and software failures in order to maintain the integrity of the data volume;
- ensuring the ability to quickly migrate to an updated version of the database management system.
General administrator duties
The job description for a database administrator provides for the implementation of a large number of activities related to the information system in the organization. Anythe instruction includes several general points that are characteristic of any variety of information managers.
- Carrying out continuous copying of databases in backup mode. In the case of permanent data saving in case of problems with servers or networks, all data from the infobase can be easily restored (or most of them).
- Regular software updates. Information arrays are often processed not by one program, but by a whole complex of maintenance software. Therefore, with constant software updates, the database administrator is required to have knowledge about the features of various software services, protocols (network), as well as programming skills in different computer languages. In addition, each administrator should be able to independently write a utility that is required in his activity.
Special duty groups
Working as an administrator involves performing, in addition to general duties, one of five groups of specific functions:
- ensure the smooth functioning of data systems;
- optimization of infobases;
- prevent data loss damage;
- providing databases with various security measures;
- expansion management and infobase development.
Work to ensure the functioning of the database (databases) includes the following responsibilities.
- Copying information from the database in backup mode.
- Restoring information from the database.
- Managing infobase access options.
- Installation, configuration of database management software.
- Analysis of events that occur during database operation.
- Logging and fixing events that occur during the processing of information in databases.
Optimizing the work of infobases includes the following responsibilities:

- analysis of database operation, collection of statistical information about the operation of information bases;
- optimization of the redistribution of computational data that interact with databases;
- rationing the performance of infobases;
- optimization of elements of computer networks that interact with databases;
- optimization of queries to infobases;
- optimizing lifecycle controls stored in information systems.
Prevention of data corruption and loss includes the following responsibilities.
- Development of regulations on copying infobases in backup mode.
- Enforcement of backup provisions.
- Develop plans for backing up infobases.
- Development of procedures for creating information copies of data in automatic backup mode.
- Implementation of procedures for data recovery after "collapses" of information.
- Analysis of failures occurring in the system, identificationreasons for violations.
- Development of instructions and guidelines for database maintenance.
- Research on the functioning of database hardware and software support.
- Configuring the functioning and he alth of infobases.
- Develop proposals for upgrading supporting firmware.
- Assessment and analysis of the risks of failures in the activity of infobases.
- Developing ways to automatically reserve infobases.
- Development of procedures for the introduction of hot data replacement modes.
- Database reporting.
- Consultation for users in the operation of infobases.
- Development of proposals in the field of professional development of employees.
Providing databases with various security measures includes the following responsibilities:

- development of a database information security strategy;
- monitoring compliance with information security measures at a basic level;
- optimization of the functioning of the system in the field of security at the database level;
- audit of the information system and protection of databases from external threats;
- drawing up regulations that contribute to the security of data information systems;
- improvement of the security system to reduce the burden on the functioning of information systems;
- preparation of performance and status reports and reportssecurity systems in information media and storages.
Managing the expansion and development of data bases includes the following responsibilities.
- Analysis of problems in the system for processing information in databases and the development of proposals for the development of prospects in the work of databases.
- Drafting regulations for updating system software in databases, infobases into new software options and their combination with new platforms.
- Studying and putting into practice new options and ways of working with infobases.
- Tracking updates of infobase options.
- Track information store adoption and compatibility with new platforms and new software releases.
- Development and creation of the structure of departments, development of the personnel reserve.
Problem Oriented Administrator
A problem-oriented database administrator is a specialist who solves problems that arise during the operation of an infobase system. The sources of such problems can be different. This may be inaccurate data, lack of demand, unreliable production processes, etc.

The problem-oriented administrator is concerned with identifying and structuring internal and external problems. The identified problems are analyzed, after which options for their solution are put forward.
Most often the administrator,focused on solving problems, is involved in work in the presence of emergency situations, when a quick qualified analysis of the situation and the search for its solution is necessary.
In most cases, the problem-oriented administrator performs the duties of a network administrator during non-crisis times and deals with database management and connecting network users in the organization.
When a crisis occurs, the administrator first of all analyzes the organization's resources to solve the problem from the inside, checks the possibility of using new technologies to overcome the crisis, and predicts how long the organization will need to solve the problem.
The activity algorithm of a problem-oriented network manager is as follows:
- analysis of the current situation;
- identifying specific problems that arose at the time of the crisis;
- determining the entity authorized to solve such problems;
- analysis of options for solving the problem with the calculation of financial costs;
- determination of the forecasted terms for the restoration of the pre-crisis situation;
- actual problem solving if all the above actions and calculations are approved by management.
Performance Analyst
The role of a database administrator in performance analytics is to analyze the performance of the database and develop new methods for solving problems identified in the analysis. The responsibilities of a performance analyst are as follows:
- analysis of errors in the structure of the system and its constituent parts;
- searching for weaknesses in program reliability and performance at every level, including hardware problems in networking and system logic;
- development of scripts that process various heterogeneous data about the operation of programs and computers (a stream of search requests, information on debugging equipment, network traffic, etc.);
- selection of the most important information, presentation of data in a form suitable for analysis;
- developing new approaches to collect and classify system performance data;
- increasing the degree of automation, autonomy and reliability of analytical tools, their improvement;
- creating readable and development-friendly code;
- create new ways to solve performance problems, develop architectural concepts, participate in improving the reliability of data systems;
- programming network applications.
System Data Store Administrator
The data warehouse administrator does more practical work, which is related to setting up database systems and debugging breakdowns that occur when using it.
The duties of a data warehouse administrator are as follows:

- Administration of automatic telephone exchange;
- serving remote and local servers, networks and storages;
- setting up local servers,Internet restrictions, servers with remote access, creating a network common to all users;
- server management;
- maintaining equipment in working condition;
- configuring terminal access for users (if necessary);
- organization of network booting of computers;
- Setting up a workplace for employees;
- assistance in installation of low current systems;
- small repair of office equipment and computers;
- technical and software user support.
Administrator requirements
The general requirements of the professional standard under the code 40064 include the presence of a technical higher education. Some employers also require a cybernetic education. This is due to the fact that the work of an administrator includes the construction of a structured database model, as well as the writing of appropriate programs.
In addition to having the appropriate education, the following are important requirements:
- ability to analyze the information management needs of various departments in the organization;
- skills in testing new products of the program, which are developed by departments and divisions of the organization;
- the ability to take the initiative in the development of new algorithms and methods of data storage, in the development of technologies for using information to increase the productivity and performance of the predicted result;
- experience in developing methodologies to interact with the userinformation databases.
Learning Outcomes
Despite the average salary, there are serious requirements for a DBA when graduating. These include the following:

- understanding the nature and purpose of different types of infobase architectures;
- the ability not only to design, but also to optimize the structure of information systems;
- high level of expertise in the application of algorithms that ensure the security inside the system and its protection from external threats;
- knowledge of programming, modeling and markup languages, the ability to apply them;
- ability to use infobase query languages.
Further education courses
For people who are knowledge base administrators, there are many types of advanced training courses in this area. Such courses are held on the basis of scientific or educational institutions, which provide a large amount of additional knowledge and skills in the field of database administration.
Speci alties in which you can improve the skills of a database administrator are:
- development of models of information arrays;
- architect of information network bases;
- database administrator for the 1C program in various areas;
- network administration;
- Microsoft SQL database administrator;
- management of information storage processes.
Administrator salary
The work of an infobase administrator does not imply part-time employment due to the specifics of the job. The complete computerization of society has led to the fact that even during the crisis, the demand for qualified personnel in the field of network administration did not fall. Most administrators are required in capital cities.
According to the analysis of the situation, the average salary level of specialists in the field of information administration was revealed in the country.
According to the results of 2017, it was found that the salary of a database administrator is expressed in the following figures:

- Moscow - from one hundred and ten to one hundred and sixty thousand rubles;
- St. Petersburg - from seventy-seven to one hundred thousand rubles;
- in the regions - from forty to seventy-five thousand rubles.
In some regions, wages are set below the average, but after the employee raises the skill level, it rises. The administrative profession is different in that any increase in the level of knowledge and the acquisition of new skills most often has a positive effect on wages.
Being a database operator has many benefits. First of all, the informatization of society provokes a constant increase in demand for specialists in the information sphere. In addition, network work provides an opportunity for continuous self-development without the involvement of outsiders.
Recommended:
Profession surgeon: description, pros and cons. Profession of a plastic surgeon

Have you ever wondered what role a doctor plays in the life of each of us? After all, when we turn to medical institutions, we hand over our lives to the people who work there. There are times when it is simply impossible to save a person's life without the surgical intervention of a surgeon. The profession of a surgeon gives people a second life. But despite this, there are also a considerable number of shortcomings of this activity
System administrator - who is this? System administrator courses

In this article, we will take a closer look at who a system administrator is, as well as the duties that he must perform
Translator (profession). Description of the profession. Who is a translator

Translator is a profession that has been very prestigious and in demand since ancient times. Mentions of the very first representatives of this speci alty date back to Ancient Egypt. Even then, translators were its honorary residents. Their services were especially in demand in Ancient Greece, which was in close contact with the states of the East
Administrator - who is this? Professional duties of an administrator

Administrator is an employee of the company, on whose shoulders lies a lot of responsibilities. You can learn more about his work in this article
Job description, rights, responsibilities and functional duties of a database administrator
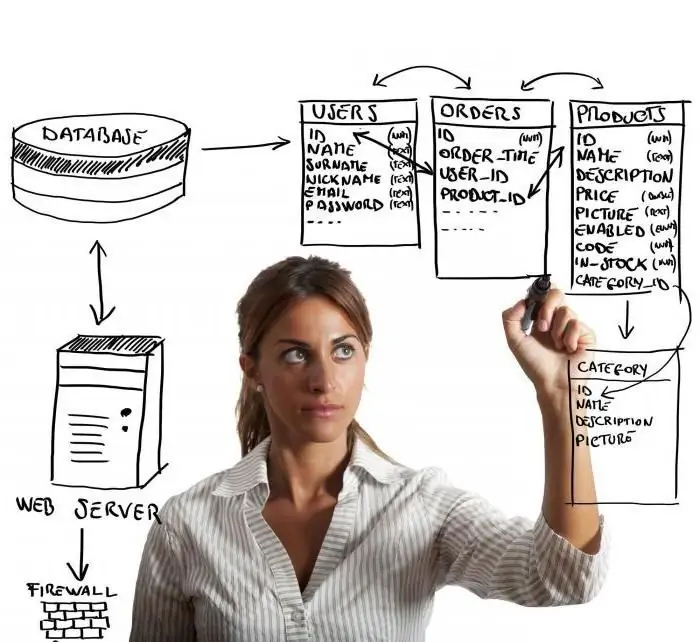
The employee hired for this position is a specialist who can be hired or fired only by the head of the company. Usually, the applicant is required to have a higher education in the profession, namely, that it relates to the mathematical, engineering or technical direction

