2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-06-01 07:12:56
When filling out a payment order for tax payment, you should indicate the status of the payer. A complete list is presented in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and some orders of the President of the Russian Federation. Let's take a closer look at how to determine the status of a taxpayer.
Responsibilities
Taxpayers are legal entities and individuals who pay fees. By law, they have the following duties:
- register with the Federal Tax Service;
- keep records of income (expenses) of objects of taxation;
- submit declarations and financial statements to the Federal Tax Service;
- submit documents for which the calculation of the amount of taxes was carried out;
- to comply with the requirements to eliminate identified violations, not to interfere with officials of the Federal Tax Service in the performance of their duties;
- for 4 years, keep accounting documents on the calculation and payment of taxes, income and expenses incurred.

Taxpayers must also notify the Federal Tax Service in writing of:
- opening\closing an account - within 10days;
- participation in organizations - within a month;
- separate subdivisions in the Russian Federation - within a month;
- declaration of bankruptcy, liquidation or reorganization - within 3 days;
- change of location (residence) - within 10 days.
Rights
In turn, the taxpayer has the right to receive from the Federal Tax Service:
- information on applicable taxes, clarifications on the application of legislation;
- use benefits in due course;
- get deferment and tax credit;
- be present at the field inspection.
Finding Information
As mentioned above, one of the duties of taxpayers is to pay taxes. In this case, the status of the taxpayer in the payment order is indicated. Otherwise, there is a possibility that the funds will not reach the addressee.

Taxpayer status is a required information. This information is used to identify the organization. The status of the taxpayer consists of a two-digit number and is entered in the payment in field 101. The table shows all existing statuses.
| Code | Deciphering the taxpayer |
| 01 | Enterprise |
| 02 | Tax agent |
| 06 | Foreign trader |
| 08 | IP, lawyer, notary who transfers contributions to the budget |
| 09 | IP |
| 10 | Private Notary Public |
| 11 | The lawyer who founded his own office |
| 12 | Head of Farm |
| 13 | Bank account holder |
| 14 | Taxpayer paying income to individuals |
| 16 | FEA participant - natural person |
| 17 | FEA participant - IP |
| 18 |
Payer of customs duties, not declarant |
| 19 | Enterprises transferring funds withheld from salaries |
| 22 (21) | Member (responsible) of the consolidated group |
| 24 | Individual transferring insurance premiums |
Division by taxes
The status of an active taxpayer depends on the type of tax paid. For example, if an enterprise transfers personal income tax from the salary of employees, then “02” must be put down in the payment. If we are talking about the payment of insurance premiums - "08". The detailed fee statuses are listed in the table below.
| Tax | Status |
| NDFL | 02 |
| Contributions to the PRF, FSS, FFOMS | 08 |
| Income tax, property tax, transport | 01 |
| VAT | |
| UTII, STS, ESHN |
Online verification
You can check the status of a personal income taxpayer through the website of the Federal Tax Service. In order not to waste time on manually entering the TIN, KPP, 1C developers have implemented this feature in the updated 1C: Accounting program. The results of the check are reflected in the list of clients in the card, in the invoice register, the purchase (sales) book, and primary documents. To check the entire list of clients, you need to generate a universal report on the register "State of counterparties" by periods. Verification options are regulated by the "Regular operations" register of the "Administration" subsystem in the "Support" menu.

After processing the information, the program returns the following results:
- "The organization is listed in the database" means that the counterparty is registered and has the status of an active one.
- “Ceased activity” means that the taxpayer is registered in the USRN, but did not have the status of an active taxpayer. Two options are possible here: the counterparty has ceased operations or the checkpoint has been changed.
- "The checkpoint does not match the one specified in the database" means that the entered combination of TIN, checkpoint has never been in the registry.
- "Missingcounterparty in the database" means that the taxpayer does not have the status of an active taxpayer; no one was registered with the specified TIN.
- "Not subject to verification" - such a message is displayed if the data of a foreign organization is entered.
All reflected verification results are valid for ±6 days from the date of request.

1С
The service for finding problem customers in 1C was introduced in 2015. The updates were caused by changes in Federal Law No. 134, according to which it was necessary to enter data on all invoices in the VAT return. Online status checks directly from 1C allow you to avoid errors when filling out the declaration. If, in response to a request, a notification is received that the taxpayer is registered, but did not have the status of an active one, then the line with the counterparty is painted over in gray, if the client is not found at all in the register - in red. These clients are reflected in the same way in the "Counterparty" line when entering primary documents.
In the book of purchases (sales), the journal of invoices, the results of the check are displayed on a separate panel. If the report includes inactive documents, they are highlighted in red and a button appears in the panel to select such lines. In the built-in VAT declaration, checks are carried out based on information from sections 8-12 of the Federal Law, its results are displayed on the panel of counterparties.
By default, verification is performed once a week in the background and is carried out by TIN. To avoid errors when entering data into the database, it is necessary to control the correctness bydischarge. If the information is entered incorrectly, it will be highlighted in red in the "Counterparties" directory. All documents for such clients will be reflected in the same way. Only during the audit it will be possible to avoid the situation when the taxpayer is registered in the USRN, but did not have the status of the current one and was included in the report.

NDFL
The status of the taxpayer, but in a different form, must be checked when calculating personal income tax. Depending on the source and whether an individual is a resident or not, different tax rates are set. A Russian can pay personal income tax at rates of 9, 13 and 35%. A non-resident must transfer to the budget 15% of the amount of dividends received and 30% of all other income. In addition to Russian legislation, there are also international treaties regarding the avoidance of double taxation. Tax rates for residents from allied countries are determined by these acts.
Terminology
According to Art. 207 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a resident is an individual who is in the territory of the Russian Federation for at least 183 days in 12 consecutive months. The countdown starts from the moment a person arrives on the territory of the Russian Federation, which is recorded in customs documents.
The status is fixed on the date of payment of income and specified:
- for non-residents without permanent residence - on the date of completion of their stay on the territory of the Russian Federation;
- for Russians with permanent residence - on the date of departure outside the Russian Federation.
Recalculation of the base is carried out at the end of the tax period. Consider an example of calculationthe number of days a citizen stays on the territory of the Russian Federation.

Example
The Russian has received income from Russian and foreign enterprises for the year. During this period, he repeatedly traveled outside the Russian Federation on business trips:
- 01.03-20.04 - to Germany;
- 15.08.-14.09 - in the USA;
- 20.12-20.01 - to Turkey.
The status of a personal income tax payer is determined according to the calculation of the number of days of stay in the territory of the Russian Federation. Border crossing days (01.03, 15.08 and 20.12) are not included in this calculation. That is, the taxpayer spent 90 days outside the country for a year, and 275 days in the Russian Federation. He is recognized as a tax resident and transfers fees to the budget at the rates prescribed in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Exceptions
For some categories of payers, the status and number of days of stay in the Russian Federation does not matter. Military personnel, employees of state authorities and local self-government, seconded outside the Russian Federation, are always recognized as tax residents.

Documents
The period of stay and absence on the territory of the Russian Federation must be supported by documents. This can be a certificate from the place of work, issued according to the data from timesheets, a migration card, a passport with border crossing marks, etc.
Persons who are not officially employed, do not leave the Russian Federation, can provide an identity document to confirm their tax resident status. It must indicatedata on citizenship and place of residence. In extreme cases, you can provide a certificate from the housing and communal services.
Recommended:
Courier documents: individual order, invoice, order form, document delivery rules and courier working conditions

Working in the delivery service is very popular today, especially among ambitious young people. A courier is not just a person delivering parcels, but a trained specialist who has certain skills and can bring a parcel or correspondence to the specified address with high quality and promptly
Payment order: filling order, purpose

The payment order is mentioned in the Regulation of the Central Bank No. 383-P of 2012. This settlement document is created in a banking institution to make a partial transfer of funds
Samples of filling out payment orders. Payment order: sample
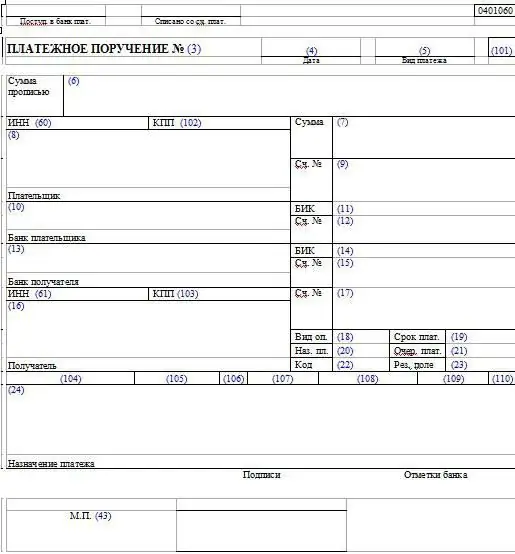
Most enterprises pay various taxes and fees to the budget. Most often this is done with the help of payment orders. How to compose them correctly?
Trading fee: payment details. How to fill out a payment order?

In the cities of regional significance, a sales tax has been introduced since 2015. You need to pay it in case of registration for the use of the object of trade in one of the types of activities. Next, we’ll talk about when and how to transfer the trading fee, payment details will also be indicated
UIP - what is it in a payment order? Unique payment identifier

Since 2014, the UIP is an important requisite that must be filled in if it is provided by the seller, and also if this identifier should be considered as a UIN when it is indicated in payment documents for paying fines, pen alties for taxes and fees . This code is indicated in the field of the payment order at number 22. It can be filled in both manually and using special software tools, the main of which is "1C: Enterprise"

