2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-06-01 07:12:56
Plasma cutting is used in the processing of conductive metals. The processed material receives energy from a current source by means of ionized gas. The standard system includes a power source, ignition circuit, and torch that provide the power, ionization, and control needed for quality, high-performance cutting on a variety of metals.
DC power output sets the material thickness and cutting speed and maintains the arc.
The ignition circuit is made in the form of a high-frequency alternating voltage generator of 5-10 thousand V with a frequency of 2 MHz, which creates a high-intensity arc that ionizes the gas to a plasma state.
The torch is a holder for consumables - nozzle and electrode - and provides cooling of these parts with gas or water. The nozzle and electrode are compressed and support the ionized jet.
Manual and mechanized systems serve different purposes and require different equipment. Only the user can determine which one is best for their needs.
Metal cutting with plasma is a thermala process in which a beam of ionized gas heats an electrically conductive metal to a temperature above its melting point and removes the molten metal through a drilled hole. An electric arc occurs between the electrode in the burner, to which a negative potential is applied, and the workpiece with a positive potential, and the material is cut by an ionized gas flow under pressure at a temperature of 770 to 1400 °C. A jet of plasma (ionized gas) is concentrated and directed through a nozzle, where it condenses and becomes capable of melting and cutting a wide variety of metals. This is the basic process for both manual and mechanized plasma cutting.
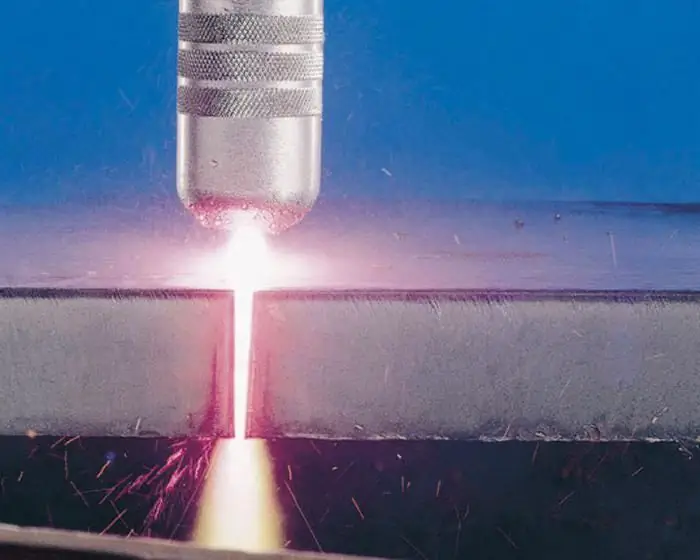
Hand cut
Manual cutting of metal with plasma is done using fairly small devices with a plasma torch. They are maneuverable, versatile and can be used to perform various tasks. Their capabilities depend on the current strength of the cutting system. Manual cutting settings range from 7-25 A to 30-100 A. Some devices, however, can produce up to 200 amps, but these are not widely used. In manual systems, process air is usually used as the plasma and shield gas. They are designed in such a way that they can be used with various input voltages, which can vary from 120 to 600 V, and can also be used in single- or three-phase networks.
Hand-held metal cutting plasma is commonly used in workshops processing thinmaterials, factory maintenance services, repair shops, scrap metal collection points, in construction and installation works, in shipbuilding, car repair shops and art workshops. As a rule, it is used to trim the excess. A typical 12 amp plasma machine cuts a maximum of 5 mm of metal at a rate of about 40 mm per minute. 100 amp cuts 70 mm layer at up to 500 mm/min.
As a rule, the manual system is selected depending on the thickness of the material and the desired processing speed. A device that delivers high current is faster. However, when cutting with high current, it becomes more difficult to control the quality of the work.
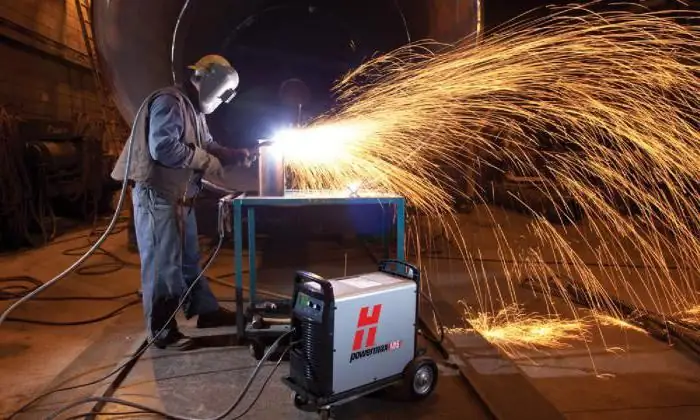

Machining
Mechanized metal cutting with plasma is performed on installations, which, as a rule, are much larger than manual ones, and is used in combination with cutting tables, including those with a water bath or with a platform equipped with various drives and motors. In addition, mechanized systems are equipped with CNC and cutting head jet height control, which can include torch height presetting and voltage control. Mechanized plasma cutting systems can be installed on other metalworking equipment such as stamping presses, laser cutters or robotic systems. The size of the mechanized configuration depends on the size of the table and the platform used. The cutting machine can be smaller than 1200x2400 mm and larger than 1400x3600mm. Such systems are not very mobile, so before installation, you should consider all their components, as well as their location.
Power Requirements
Standard power supplies have a maximum current range of 100 to 400 A for oxyfuel cutting and 100 to 600 A for nitrogen cutting. Many systems operate in the lower range, such as 15 to 50 amps. There are nitrogen cutting systems with currents of 1000 amps and above, but they are rare. The input voltage for mechanized plasma systems is 200-600 V three-phase.

Gas requirements
Compressed air, oxygen, nitrogen, and argon/hydrogen mixtures are commonly used to cut mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and various exotic materials. Their combinations serve as plasma and auxiliary gases. For example, when cutting mild steel, the starting gas is often nitrogen, the plasma is oxygen, and compressed air is used as an auxiliary.
Oxygen is used for mild carbon steel because it produces high quality cuts in material up to 70mm thick. Oxygen can also act as a plasma gas for stainless steel and aluminum, but the result is not entirely accurate. Nitrogen serves as the plasma and assist gas as it provides excellent cutting performance on virtually any type of metal. It is used at high currents and allows processing sheet metal up to 75 mm thick and as an auxiliary gas for nitrogen and argon-hydrogen plasma.
Compressed air is the most common gas for both plasma and auxiliary gases. When low-current cutting of sheet metal up to 25 mm thick is performed, it leaves an oxidized surface. When cutting with air, nitrogen or oxygen is the auxiliary gas.
Argon/hydrogen mixture is typically used for machining stainless steel and aluminium. Provides a high quality cut and is essential for mechanized cutting of sheets over 75mm thick. Carbon dioxide can also be used as an assist gas when cutting metal with nitrogen plasma, as it can handle most materials and guarantee good quality.
Nitrogen-hydrogen mixture and methane are also sometimes used in the plasma cutting process.
What else do you need?
The choice of plasma and auxiliary gases are just two of the most important decisions to be taken into account when installing or using a mechanized plasma system. Gas tanks can be purchased or rented, they are available in various sizes and storage conditions must be provided. Installing the system requires a significant amount of electrical wiring and piping for gas and coolant. In addition to the most mechanized plasma system, you need to pick up a table, a saw, CNC and THC. OEMs typically offer a variety of hardware options to suit any device configuration.

Is mechanization necessary?
Because ofthe difficulty of choosing a mechanized plasma cutting process, a lot of time must be devoted to researching various configurations and system criteria. Please note:
- types of parts to be cut;
- number of industrial items per lot;
- desired cutting speed and quality;
- cost of consumables.
- total cost of operating the configuration, including electricity, gas and labor.
The size, shape and number of parts to be produced can determine the required industrial manufacturing equipment - the type of CNC, table and platform. For example, the production of small parts may require a platform with a specialized drive. The rack and pinion drives, servo drives, drive amplifiers and sensors used on the platforms determine the quality of the cut and the maximum speed of the system.
Quality and speed also depends on what metalworking equipment, CNC and gases are used. A mechanized system with adjustable current and gas flow at the beginning and end of the cut will reduce material consumption. In addition, with a CNC with a large memory capacity and a choice of possible settings (for example, the height of the flame at the end of the cut) and fast data processing (input / output communications) will reduce downtime and increase the speed and accuracy of work.
Ultimately, the decision to buy or upgrade a mechanized plasma cutting system or use a manual one must be a sound one.
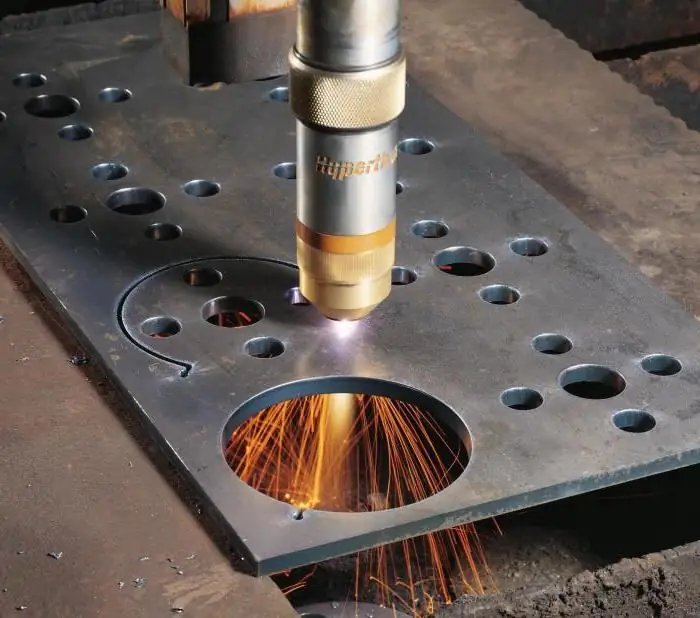

Plasma metal cutting equipment
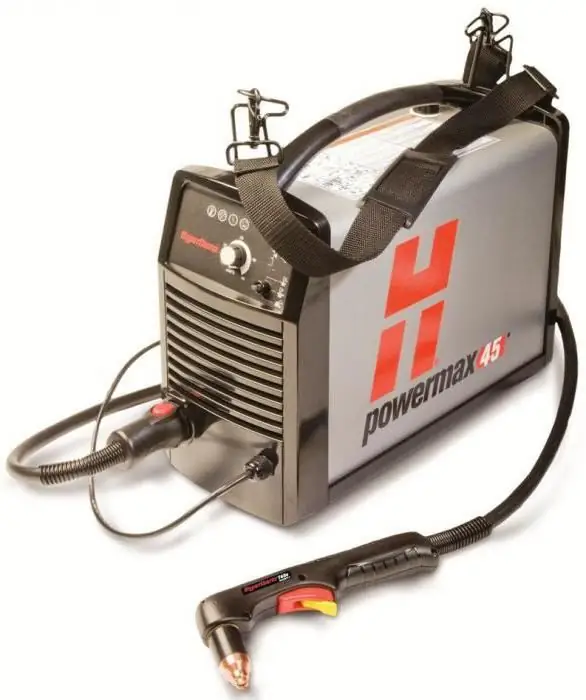
Hypertherm Powermax45 is a portable device with a large number of standard components based on an inverter, i.e. an insulated gate bipolar transistor. It is very easy to work with, whether it is cutting thin steel or 12 mm thick plates at 500 mm/min or 25 mm at 125 mm/min. The device is capable of generating high power for cutting various kinds of conductive materials such as steel, stainless steel and aluminum.
The power system has an advantage over analogues. Input voltage - 200-240 V single-phase current with a power of 34/28 A at a power of 5.95 kW. Variations in mains input voltage are compensated for by Boost Conditioner technology, which provides the torch with improved performance at low voltages, fluctuating input power, and when powered by a generator. Internal components are efficiently cooled with PowerCool for improved performance, runtime and reliability. Another important feature of this product is the FastConnect torch connection, which facilitates mechanized use and increases versatility.
The Powermax45 torch features a dual angle design that extends nozzle life and reduces operating costs. It is equipped with the Conical Flow function, which increases the energy density of the arc, which significantly reduces dross and produces high-quality plasma cutting. Powermax45 price is $1800.
Hobart AirForce 700i
Hobart AirForce 700i has the mostcutting capacity of this line: nominal cutting thickness - 16 mm at a speed of 224 mm / min, and maximum - 22 mm. Compared with analogues, the operating current of the device is 30% less. The plasma cutter is suitable for service stations, repair shops and small building construction.
Features a lightweight yet powerful inverter, ergonomic start fuse, efficient air consumption and low cost torch consumables to produce safe, high quality and affordable plasma cutting. The AirForce 700i is priced at $1,500.
Comes with ergonomic hand torch, cable, 2 replacement tips and 2 electrodes. The gas consumption is 136 l/min at a pressure of 621-827 kPa. The weight of the device is 14.2 kg.
40-amp output provides exceptional sheet metal cutting performance - faster than other manufacturers' mechanical, gas and plasma devices.

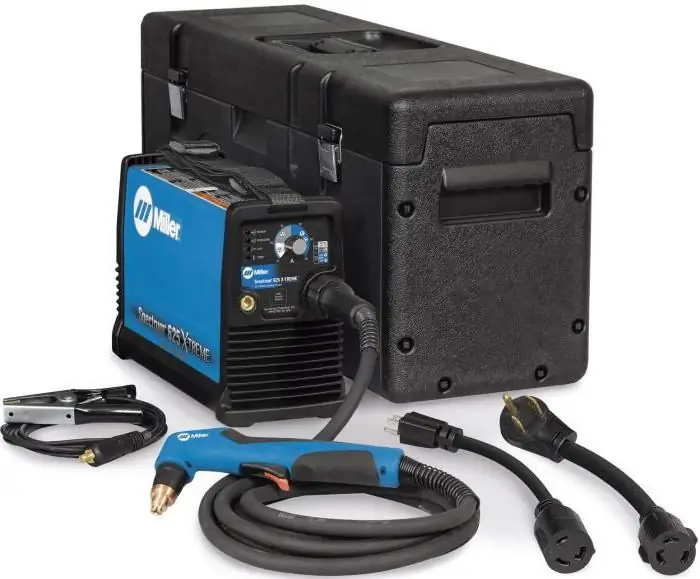
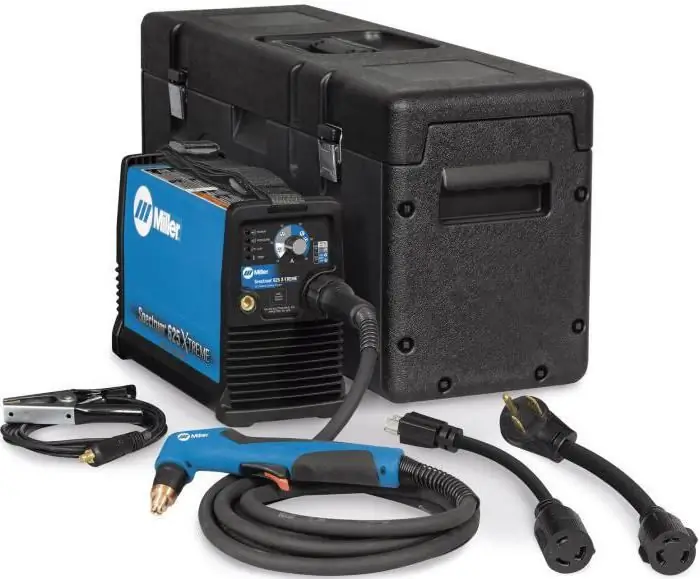
Miller Spectrum 625 X-treme
Miller Spectrum 625 X-treme is a small machine powerful enough to cut various types of steel, aluminum and other conductive metals.
Powered by 120-240 V AC, automatically adjusting to the applied voltage. Lightweight and compact design makes it highly portable.
With Auto-Refire technology, the arc is controlled automatically, eliminating the need to constantly press the button. The nominal cutting thickness at 40 A is 16mm at a speed of 330 mm/min, and the maximum is 22.2 mm at 130 mm/min. Power consumption - 6, 3 kW. The weight of the device in manual execution is 10.5 kg, and with a machine cutter - 10.7 kg. Air or nitrogen is used as plasma gas.
The reliability of the Miller 625 comes from Wind Tunnel technology. Thanks to the built-in high-speed fan, dust and debris do not get inside the device. LED indicators inform about pressure, temperature and power. The price of the device is $1800.

Lotos LTP5000D
Lotos LTP5000D is a portable and compact plasma machine. With a weight of 10.2 kg, there will be no problems with its movement. The 50 amp current generated by the digital converter and the powerful MOSFET provide efficient cutting of 16 mm mild steel and 12 mm stainless steel or aluminium.
The device automatically adjusts to the mains voltage and frequency. Hose length - 2.9 m. The pilot arc does not come into contact with metal, which allows the machine to be used for cutting rusty, raw and painted materials. The device is safe to use. Compressed air used for cutting is not harmful to humans. And the strong shock-resistant case reliably protects the device from hit of dust and debris. The price of Lotos LTP5000D is $350.
When buying a plasma cutter, you should always prioritize quality. Beware of the temptation to buy a cheap low-quality device, as its rapid wear and tear in the long run will lead tomuch higher costs. Of course, it's also not worth overpaying, there are enough decent budget options without accessories and high capacities that you may never need.
Recommended:
Oxyfuel cutting of metal: technology, necessary equipment, safety precautions

Oxy-fuel cutting of metals (in the literature you can find the term "oxy-fuel cutting") is actively used in industry for cutting sheet material from steel and other alloys into workpieces of the required length. The article contains information about the technology itself, about the necessary equipment and basic safety precautions for oxygen cutting of metals and other materials
Types of metal cutting: an overview of modern technologies and equipment

One of the most common metalworking operations is cutting. It is a technological process during which a sheet or billet is divided into parts of the desired format. Modern types of metal cutting allow this operation to be performed with high accuracy and a minimum amount of scrap
Metal cutting: methods, equipment and tools
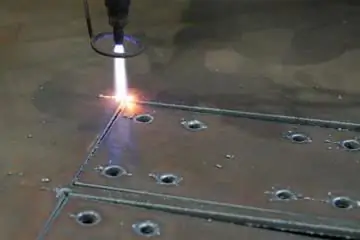
Metal cutting is performed in order for the workpiece to acquire the desired shape. To this end, it is necessary to remove the excess. Such manipulation is carried out through the use of different cutting tools on special machines. In mechanical engineering, metal cutting is very important. Indeed, without this process, neither ordinary machines nor other devices can be made
Metal plasma cutting

The article is devoted to plasma cutting of metal. Features of technology, tools, scopes and advantages are considered
Metal cutting machine. Plasma metal cutting machine
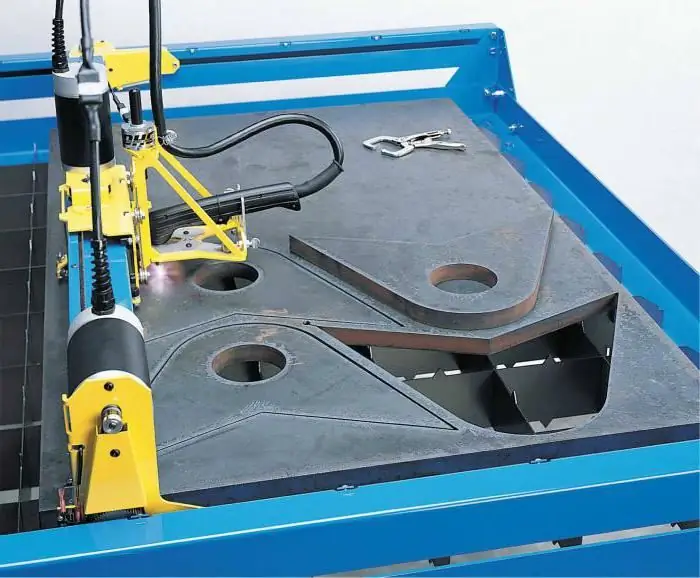
The article is devoted to the apparatus for cutting metal. The technology of plasma cutting, as well as the device and features of the equipment are considered

