2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-06-01 07:12:56
Accounting is a complex system in which everything is interconnected, some calculations follow from others, and the whole process is strictly regulated at the state level. There are a lot of terms and concepts in it that are not always clear to people without specialized education, but it is necessary to understand them in certain situations. This article discusses such a phenomenon as the reflection of deferred tax liabilities in the balance sheet, what kind of phenomenon it is, which requires other nuances of the issue.
Balance sheet
The concept of the balance sheet is necessary in order to proceed to the main issue of the article - deferred tax liabilities in the balance sheet. This is one of the main elements of financial statements containing information about the property and funds of the organization, as well as its obligations to other counterparties and institutions.
Balance sheet, aka First form of accounting. reporting, presented in the form of a table, which reflects the property and debts of the organization. Each individual element is reflected in its own cell with an assigned code. The assignment of codes is carried outthrough a special document called the Chart of Accounts. It is officially approved by the Ministry of Finance and is used by all organizations operating in the territory of the Russian Federation. The users of the information contained in Form No. 1 are both the organization itself and third-party interested parties, including the tax service, counterparties, banking structures and others.

Asset and liability
The balance sheet is divided into two columns: asset and liability. Each contains lines with a certain property or its source of formation. How do you know if the deferred tax liability on the balance sheet is an asset or a liability?
There are two groups in the asset balance: current and non-current assets, that is, which are used in production for less than one year and more, respectively. All this - buildings, equipment, intangible assets, materials, long-term and short-term receivables.
The liability reflects the sources of formation of funds listed in the asset: capital, reserves, accounts payable.

Deferred tax liability on the balance sheet - what is it?
In accounting, there are two concepts that are similar in name, and therefore can mislead an ignorant person. The first is a deferred tax asset (abbreviated as IT), the second is a deferred tax liability (abbreviated as IT). At the same time, the goals and the result of applying these accounting phenomena are opposite. The first phenomenon reduces the amount of taxes that the organization must pay in the following reporting periods. At the same time, the amount of the final profit in the reporting period will be reduced, since the tax payment will be higher.
Deferred tax liability in the balance sheet is a phenomenon that causes an increase in net income in this reporting period. This happens due to the fact that in the following periods the amount of taxes paid will be greater than in the current one. From this, the conclusion is that deferred tax liabilities in the balance sheet are a liability, since the company uses these funds at a given point in time as profit, undertaking to pay them in the reporting periods that follow this one.

How phenomena such as IT and SHE are formed
The organization simultaneously maintains several types of accounting, namely accounting, tax and management. The emergence of deferred tax assets and liabilities is due to temporary differences in the maintenance of these accounting areas. That is, if in the accounting type of accounting expenses are recognized later than in tax accounting, and income is recognized earlier, temporary differences in the calculations appear. It turns out that a deferred tax asset is the result of the difference between the amount of tax paid at the moment and calculated with a positive result. The obligation, accordingly, is the difference with a negative result. That is, the company must pay additional taxes.

Reasons for temporary differences in settlements
There are several situations in which there is a time gap in the calculations of accounting and tax accounting. You can represent them in the following list:
- Getting an organization the ability to defer tax payments or installment payments.
- An enterprise with a cash method of work accrued pen alties to the counterparty, but the money was not received on time. The same option is possible with sales proceeds.
- The financial statements indicate a lower amount of expenses than the tax one.
- In buch. accounting and tax uses different methods of depreciation, resulting in a difference in the calculations.
Reflection in Shape 1
Since liabilities are sources of formation of funds and property of the organization, they are related to the liability of the balance sheet. In the balance sheet, deferred tax liabilities are current assets. Accordingly, in the table they are reflected in the right column. This indicator refers to the fourth section - "Long-term liabilities". This section contains several amounts related to different sources. Each of them is assigned its own individual code, which is also called the line number. Deferred tax liability in the balance sheet is line 515.

Calculation and adjustments
IT are taken into account strictly in the period in which they were identified. In order to calculate the amountliabilities, you need to multiply the tax rate by the temporary taxable difference.
IT are gradually repaid with decreasing temporary differences. Information on the amount of the obligation is adjusted on the analytical accounts of the relevant item. If the object on which the obligation has arisen is withdrawn from circulation, in the future these amounts will not affect income tax. Then they need to be written off. Deferred tax liabilities in the balance sheet are account 77. That is, the entry for which liabilities for retired taxable objects are written off will look like this: DT 99 CT 77. Liabilities are written off to the profit and loss account.

Calculation of net income and current tax
Current income tax - the amount of the actual payment made to the state budget. The amount of tax is determined based on the difference between income and expenses, adjustments to this amount, deferred liabilities and assets, as well as permanent tax liabilities (TLT) and assets (TLT). All these components add up to the following calculation formula:
TN=UD(UR) + PNO - PNA + SHE - IT, where:
- TN - current income tax.
- UD(UR) - specific income (specific expense).
This formula uses not only deferred but also permanent tax assets and liabilities. The difference between them is that in the case of constants there are no temporary differences. These amounts are always present in the account throughout the entire process of economic activity.organizations.
Calculation of net profit is made according to the formula:
PE=BP + SHE - IT - TN, where:
BP - profit recorded in accounting

Stages of calculation and reflection in accounting
To reflect all the above phenomena and procedures in accounting, certain postings are used based on the approved accounting chart of accounts. At the first stage of generating postings and making calculations, it is necessary to reflect the following operations:
- DT 99.02.3 KT 68.04.2 - the transaction reflects the product of the debit turnover of the account by the tax rate - these are permanent tax liabilities.
- ДТ 68.04.2 KT 99.02.3 - reflects the product of the loan turnover and the tax rate - these are permanent tax assets.
Permanent tax assets are formed in the balance sheet if the profit according to accounting data is higher than according to tax data. And accordingly, vice versa, if the profit is less, tax liabilities are formed.
At the second stage of calculations, losses of the current period are reflected. It is calculated by the difference between the product of the final balance on the debit of account 99.01 times the tax rate in tax accounting and the final balance on the debit of account 09 of accounting. Based on the above, we form the postings:
- DT 68.04.2 CT 09 - if the amount is negative.
- DT 09 CT 68.04.2 - if the amount is positive.
At the third stage of calculations, the amounts of deferred taxliabilities and assets, taking into account temporary differences. To do this, it is necessary to determine the balance of taxable differences in general, calculate the balance at the end of the month, which should be reflected in accounts 09 and 77, determine the total amounts for the accounts, and then adjust them according to the calculations.
Recommended:
Net sales in the balance sheet: string. Sales volume in the balance sheet: how to calculate?

Annually, enterprises prepare financial statements. According to the data from the balance sheet and income statement, you can determine the effectiveness of the organization, as well as calculate the main planned indicators. Provided that the management and finance department understand the meaning of terms such as profit, revenue and sales in the balance sheet
General concepts of the balance sheet: assets, liabilities, balance sheet currency

The balance sheet contains important information for assessing the company's financial results. Each section of the asset, liability, as well as the balance sheet currency is necessary to calculate many financial indicators
Formula of net assets on the balance sheet. How to calculate net assets on a balance sheet: formula. Calculation of net assets of LLC: formula

Net assets are one of the key indicators of the financial and economic efficiency of a commercial firm. How is this calculation carried out?
Liquidation balance sheet is Definition of the concept, approval, form and sample of filling out the liquidation balance sheet
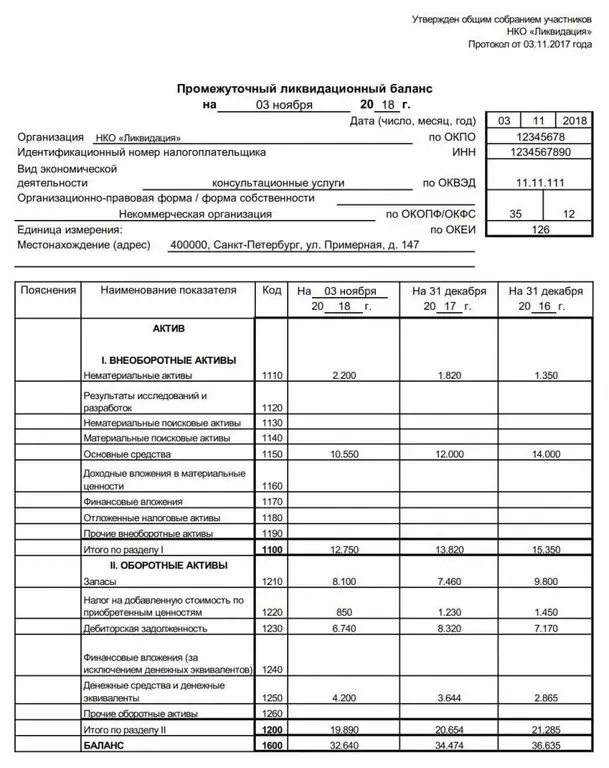
The liquidation balance sheet is an important financial act drawn up during the closing of an organization. It can be intermediate or final. The article tells what is the purpose of these documents, what information is entered into them, as well as how and when they are approved and submitted to the Federal Tax Service
Balance: types of balance. Types of balance sheet
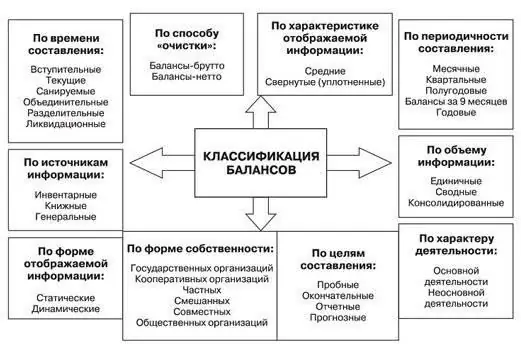
The balance sheet is the most important accounting document of an institution. What is it, what are the rules for filling it out, types and classification

