2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-06-01 07:12:56
Today's challenges inevitably entail preparation for tomorrow's challenges. The future of the company, its flourishing or collapse depends on how effectively the problems facing the organization are solved, the ability to overcome obstacles invisible to the ordinary eye. According to the theory of Yitzhak Adizes, designated as corporate life cycle management, the functioning of any company is subject to the influence of the same factors on the development path.
The difficult role of a leader
All forms of organizational management of any firm, organization or enterprise are result-oriented. Therefore, all kinds of changes and their consequences have a direct impact on the development of the company.
Problem patterns are predictable and can be driven by the following indicative factors:
- Disintegration of the control system.
- Similar causes of problems.
- Predictable behavior when solving difficulties.
- The emergence of normal and abnormalproblems.
- Leadership requires a company to constantly change while maintaining the integrity and stability of the organization.

Corporate life cycle management can be objectively systematized and divided into several characteristic stages.
Mysterious PAEI
The duration of the organization's activities, its success in the near and future period of time is determined by a variety of properties and the ability to perform certain functions.
The book of management guru Itzhak Calderon Adizes "Corporate Life Cycle Management" defines PAEI as an approach or code that needs to be applied in the development of the activities of any organization. This system of measures has gained recognition in the business world.
The PAEI (Production, Administration, Entrepreneuership, Integration) model is made up of various functions that an organization needs to use to ensure life, and is conditionally divided into four main segments:
- P - a product or service that is produced to meet consumer demand. This function answers the question of what a company needs to do to create or develop.
- A - administration and effective management. The purpose of this stage lies in the ability to determine how to do it (release a product, service).
- E - entrepreneurship as the ability to constantly search for perspectives, the ability to set new goals in connection with market changes, and quick adaptation to changing conditions. Responsible forexpediency, explains when and why to do it.
- I - integration, or the ability to unite a team and achieve goals with common efforts. Determination function: who should do it?

The impact of PAEI on the development of the company
The functions of management have a significant impact on the management of the life cycle of a corporation, as each is aimed at solving a specific problem and achieving a precise goal. Successful completion of all the tasks of the PAEI code not only shapes the style of the company, but also ensures its profitability and comfort in the market. However, in his book Corporate Lifecycle Management, Yitzhak Adizes argues that most organizations are successful in only one or two of these functions.
What are companies overlooking, what opportunities are not being used from those offered by PAEI?
- P - the production cycle is aimed at creating functionality and results, has a short-term form, is not calculated as an indicator for the long term. In general, the product or service produced produces results in the short term and can be replaced at any time, depending on the requirements of the market.
- A - competent administration turns an organization into a well-functioning business system capable of effectively solving assigned tasks. In corporate lifecycle management, everything should be aimed at the short and long term.
- E is the most productive and creative featureactivities of management, always ready for proactive and anticipatory actions, is aimed at the long term in the activities of the organization.
- I is a function of the effectiveness of team efforts that are required yesterday, today, tomorrow; the successful use of this function always determines the long-term development of the company.

Scheduled development or general growing pains
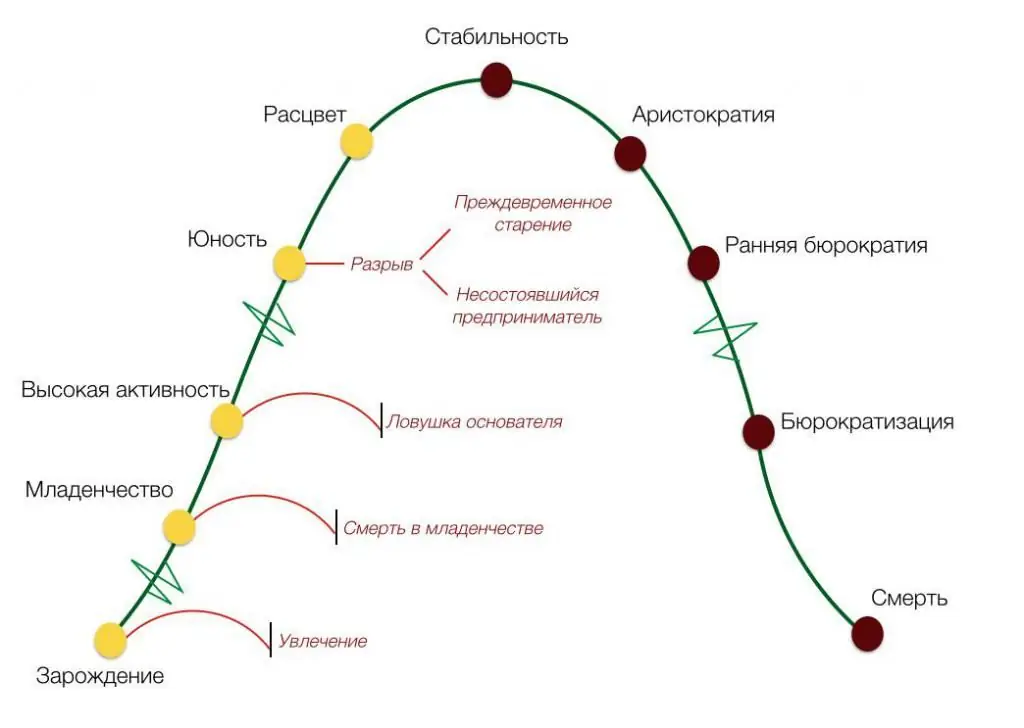
Based on the experience of many companies from different countries, we developed a methodology for recognizing organizational changes that are characteristic of business development. Its author is Yitzhak Calderon Adizes. Corporate life management is a study that radically changes ideas about how to improve the efficiency of a company. According to the model proposed by I. Adizes, the formation and development of a company goes through several stages, expressed in a graph.

Three stages at the beginning of the journey
The original grain in the methodology of management gurus is the identification of the birth of a business with the beginning and development of relationships between people. From the life cycle model graph, the first three stages of development are defined as:
- courtship - courtship;
- infancy - infancy;
- go-go or go-go.

In relation to the PEAI code, the first three stages can be characterized as follows:
- The PEAI model operates in the first stage of courtship, as the organization exists in the form of an idea or intentionorganize the type of business. Function E, or the entrepreneurial component of the code, is most pronounced. At this stage, two ways of development are possible, the emergence of an organization, or the idea remains an idea. “A company is born when there is a material manifestation of devotion to an idea, that is, when the founder of the company takes on the risk” (Iskak Adizes “corporate life management”.
- The second stage of the control cycle graph, or infancy, is characterized by the most pronounced P in the coordinate system. This is the stage of production, when the idea is realized, but the management of the company is still in its infancy and has not been worked out according to the procedures, budget or company policy. Behind the fuss and organizational issues, development prospects may be missed. During this period, the company is in need of raising working capital, is exposed to the pressure of short-term and minute-to-minute decisions, which can lead, according to the guru, to death in infancy.
- The next stage of development ("come on, come on") leads to the PaEi indicator. What does it mean to save the result (P) while seeing perspectives (E). The danger of the stage, according to the methodology of Adizes, lies in the excessive arrogance of the organizers and the intuitive approach to doing business, focused mainly on growth rates. If at the stage of the third stage of development, administration is not organized with the introduction of regular management, then the company will inevitably fall into the "founder's trap", when management is inherited.

According to market experts,the main share of companies in our country is going through this stage with a quick maturation in "Youth".
Where youth is, there blossoming is just around the corner
A few more stages, defined by the model proposed by Yitzhak Calderon Adiez, in managing the life cycle of a corporation. This is:
- Youth.
- Blossom.
- Stability, or late flowering.
A detailed study of the life cycles of the company again leads to the PAEI model and the corresponding “skews” in abbreviation preferences. In cycles it looks like this:
- Adolescence (or youth () is characterized by pAEi, or the transition from entrepreneurship (p) to professional management (A) with the delegation of authority of the head. There are changes in the company's production policy (E), the transition from the pursuit of production volumes to strengthening quality indicators. At this stage, conflict situations may arise between the "old" and "new" personnel of the company, corporate and individual goals, between the founders and collective interests. Only a clear distribution of responsibility, the introduction of information systems to evaluate the work of everyone will save the situation. Otherwise, " premature old age” (failed business) guaranteed.
- The Prime stage (flourishing) implies the development of three PAEi indicators. Orientation on efficiency and results (P) with advanced administration (A) and control of prospects (E) gives excellent growth rates and stability. At this stage, the focus is on customers and employees, the stage of creation and creativity with clear andcertain values. At this stage, it is possible to create new lines of business, which will significantly increase the life cycle of the company.
- Late Prime, or late flowering, it is also, according to the methodology of the guru, defined as stability with the PAeI code. At this stage, the organization is characterized by performance indicators (P), strengthening and streamlining management methods (A), as well as developed corporate friendships (I). However, the reluctance to be active in the market (e) leads to the loss of innovative ideas, to the emergence of a sense of routine, even in interesting and pleasant changes for employees in work and earnings. The danger is that the focus on current achievements deprives the company of a vision of development prospects.

How business aristocrats become bureaucrats
At the next stages, internal relations, the absence of conflicts and the minimization of all changes play a huge role in the development of the corporation. Adizes calls the last stages of aging:
- Aristocracy. At this stage, the most important role is played by the indicator A, I in the system of the pAeI model. Neither results nor entrepreneurship play a big role, risky decisions are not made, the influence of administration increases, this is the time of meetings and conference rooms, corporate clothes, cool-polite relations. Focus on past achievements.
- Early bureaucracy (pAei) develops in the next stage of obvious and disappointing organizational performance. Management is busy finding the culprit, managers are fightingwith each other in the desire to survive and stay in the corporation; “interest groups” are being created that are friends against the chosen “scapegoat” and the “witch hunt” conducted by the leadership.
- Bureaucratization - this stage systematically leads to the fact that the organization is isolated from external contacts, leaving one telephone channel - for the right customers. New procedures, rules, instructions are invented and used that do not matter to the organization, but create problems for customers. Potential clients are forced to leave because of the unwillingness to overcome all the new bureaucratic obstacles.
- Death is the stage at which an organization fails to demonstrate effective leadership, enterprise and innovation, and teamwork. She stops her activities.

Light at the end of the tunnel
The practical application of the Adizes model raises a logical question: is everyone doomed? Yes and no. Indeed, practical observations of enterprises at all stages of development show that organizations go through the same path of development. Nevertheless, some manage to avoid "death" with a timely determination of prospects.
There are many examples in the history of business when companies managed to avoid deadly management and bureaucratization. Nokia has been counting its history since 1865, and in those distant times it started the business of producing wood pulp. However, having managed to see the prospects and changes in the market in time, now it is one of the largest manufacturers of funds.ties.
Motorola started out by buying out a bankrupt communications business and then through innovation to launch the first radio receiver, the first commercial GPRS cell phone.
Examples can be given, but that's not the point. And that each stage of the development of the organization leads to a new starting point in business that cannot be missed.
Recommended:
Organization of enterprise management: functions, methods and goals

Business is influenced by many factors: competition in ongoing activities, the economic situation of the population, the quality of the goods and services offered, the location of the company and its remoteness from sales points, and so on. But, perhaps, the most important thing on which the success of the company depends is the organization of enterprise management
Tasks and goals of management accounting. Management Accounting and Budgeting Courses

Management accounting is always focused on determining the cost of products / services and company costs. At the same time, each enterprise independently determines how information will be processed within the framework of a particular production. If accounting is used correctly, then managers will be able to determine the break-even points and budget correctly
Classification of management functions: definition of the concept, essence and functions

Management is a complex and multifaceted process. Why is it needed and what is its essence? Let's talk about the concept and classification of control functions, consider approaches to this problem and characterize the main functions
Life and he alth insurance. Voluntary life and he alth insurance. Compulsory life and he alth insurance

To insure the life and he alth of citizens of the Russian Federation, the state allocates multi-billion sums. But far from all of this money is being used for its intended purpose. This is due to the fact that people are not aware of their rights in financial, pension and insurance matters
Corporate client. Sberbank for corporate clients. MTS for corporate clients

Each attracted large corporate client is considered an achievement for banks, insurance companies, telecom operators. For him, they offer preferential terms, special programs, bonuses for constant service, trying to attract and subsequently keep him with all his might