2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-01-24 13:10:36
In the 1950s, the USSR was intensively developing various remote regions of the country. Existing wheeled vehicles, despite continuous improvement, were not very suitable for movement in difficult climatic and road conditions. The country and the army needed a passable vehicle capable of withstanding operation at ambient temperatures from minus 45 degrees to plus 45.
Building a machine
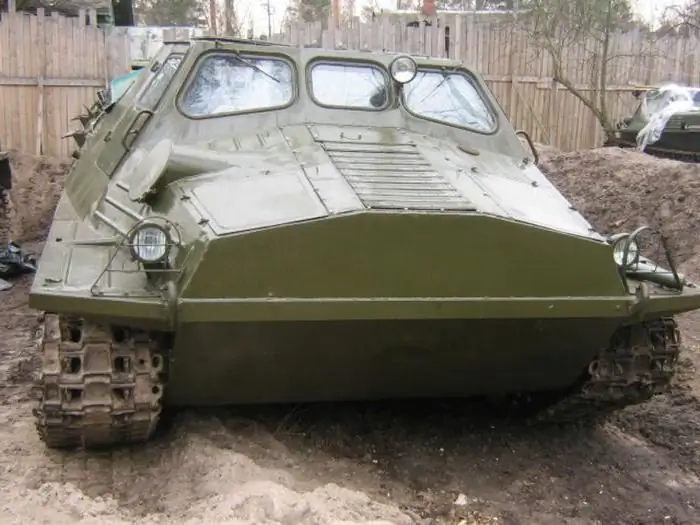
Under such conditions, a special-purpose tracked all-terrain vehicle turned out to be the most suitable vehicle. The development of a universal caterpillar tractor was carried out at KhTZ (Kharkov Tractor Plant) under the in-plant designation "Project 21". The design stage took about four years, and in 1961 the first two products were assembled. The machine received the designation GTT and from the spring of 1962 was mass-produced at the Rubtsovsk Machine Plant. The main customer of the tractor was the army.

The characteristics of the GTT all-terrain vehicle made it possible to abandon the operation of a number of non-tracked tractors, thereby simplifying the maintenance and supply of spare parts for fleets in remote areas of the country. The car, with a dead weight of just over 8 tons, could carry up to 2 tonscargo. If necessary, the cargo compartment measuring 3.5 m1.8 m could accommodate 21 people. The all-terrain vehicle was equipped with a hitch for towing trailers with a total weight of up to 4 tons.
Hull and running gear design
The body of the all-terrain vehicle GTT had a carrier scheme and was manufactured by welding. The body had a power frame to which the outer sheets were attached. Since one of the requirements of the customers was to ensure buoyancy, the lower part of the machine was sealed.
Inside there were two bulkheads that divided the hull into three compartments - compartments of the power unit, passenger and cargo. The gearbox and side clutches were located in the bow of the GTT all-terrain vehicle, the engine was located closer to the central part of the passenger cabin of the body. To the left of the engine cover was the driver's seat. It was separated from the bow by a partition. There were three more passenger seats behind the mechanic and to the right of the engine.

The cargo compartment was located behind the engine and did not have a partition with a passenger one. The compartment was open and could be covered with a tarp.
The undercarriage of the GTT all-terrain vehicle had six road wheels per side. The rollers had external cushioning in the form of a rubber ring on the outer side of the roller. Drive wheels with a gear rim were located in front. The caterpillar consisted of 92 tracks connected by floating pins. The tracks were tensioned using a movable steering wheel located at the rear.
Suspension of track rollers torsion bar. Movement afloatprovided by the rotation of the tracks and facilitated by special removable shields.
Tractor Transmission
A 200-horsepower diesel engine model B6A was used as a power unit on the GTT tracked all-terrain vehicle. The in-line six-cylinder engine was half of the famous B2 tank engine. Due to its tank origin, the motor had a combined starting system - from an electric starter and compressed air. Fuel consumption was quite high - up to 110 liters per 100 km.

The engine was equipped with a five-speed manual transmission. To make a turn on the GTT all-terrain vehicle, partial or complete braking of one of the tracks using friction clutches was used. Final drives were equipped with planetary gears. The maximum speed did not exceed 45 km/h forward and up to 6.5 km/h back.
Modifications and development
In the early years, production was accelerating. By the mid-60s, the plant was assembling up to 120 vehicles per month. At the end of the 60s, a civilian version of the GTT all-terrain vehicle appeared - a timber rafting machine. In addition to it, there was a version of the GTTS, equipped with a fifth wheel coupling from the ZIL-157V truck tractor.
By the end of the 70s, GTT production was completely transferred to Semipalatinsk (Kazakhstan) to a branch of the Rubtsovsk plant.

In the 90s, work was underway to modernize the machine. In particular, a more economical and modern YaMZ-238 diesel engine was installed. The car received the designation GTTB. Myselfthe engine was slightly shifted back, increasing the conditions for accommodating passengers. But thanks to the new engine, the load capacity has increased to 2,500 kg, and the maximum speed to 50-55 km/h.
At the same time, the material of the shock-absorbing rings of the track rollers was changed to a more wear-resistant polyurethane.
In 2007, an elongated version with seven road wheels appeared under the designation GTTBU. This version of the machine is currently being produced.
Recommended:
Real estate development and its role in economic development. The concept, types, principles and foundations of development

In the framework of this article, we will consider the organization of the real estate development system and its role in economic development. The basic concepts, types and principles of organization of the development system are considered. The characteristic features of the system in Russian conditions are considered
VAZ: history of creation and development. OJSC "AvtoVAZ"

Volga Automobile Plant is known as the largest domestic enterprise in the engineering industry. Many decades of work of the auto giant are rich in ups and downs. VAZ, whose history begins half a century ago, today does not lose its positions. It will be discussed in the article
"Renault": manufacturer, history and date of creation, management, country, technical focus, development stages, introduction of modern technologies and car quality
The Renault manufacturer produces high-quality cars that are in demand in many countries of the world. The products were to the taste of Russian motorists. In 2015, the French concern produced the millionth car from the lines of the Russian plant
3M aircraft: history of creation and development, specifications
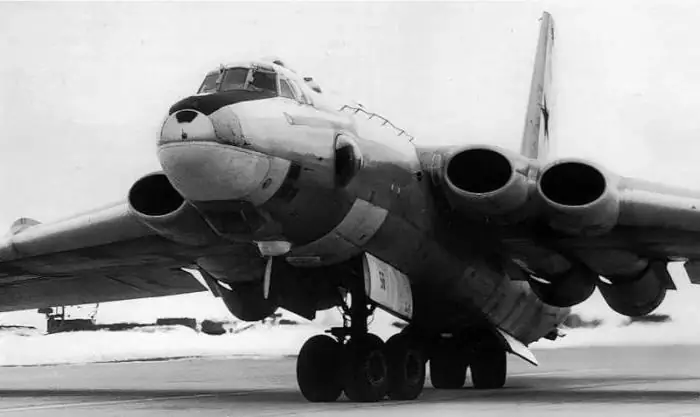

Aircraft 3M - Myasishchev's strategic bomber, which served in the USSR Air Force for over 40 years. Today we will learn how this legendary machine was created and developed
Diesel submarines: history of creation, boat projects, principle of operation, advantages, disadvantages and stages of development
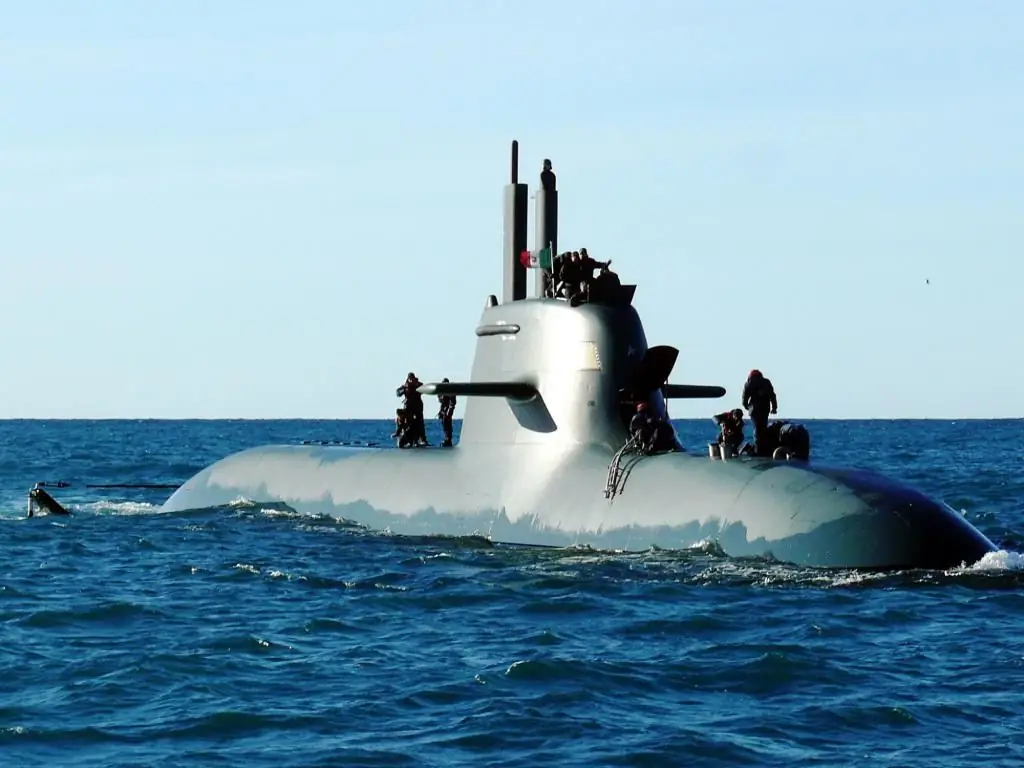

The idea of creating a submersible moving under water, actually a prototype of a submarine (hereinafter referred to as a submarine), arose long before their actual appearance in the 18th century. There are no exact descriptions of underwater vehicles in numerous legends, nor in the Renaissance genius Leonardo da Vinci

