2026 Author: Howard Calhoun | calhoun@techconfronts.com. Last modified: 2025-06-01 07:12:56
The metalworking industry at this stage of development is capable of solving the complex tasks of cutting and drilling workpieces of varying degrees of hardness. This became possible due to the development of fundamentally new ways of influencing the material, including a wide group of electromechanical methods. One of the most effective technologies of this type is ultrasonic processing (UZO), based on the principles of electroacoustic radiation.
Principles of dimensional RCD

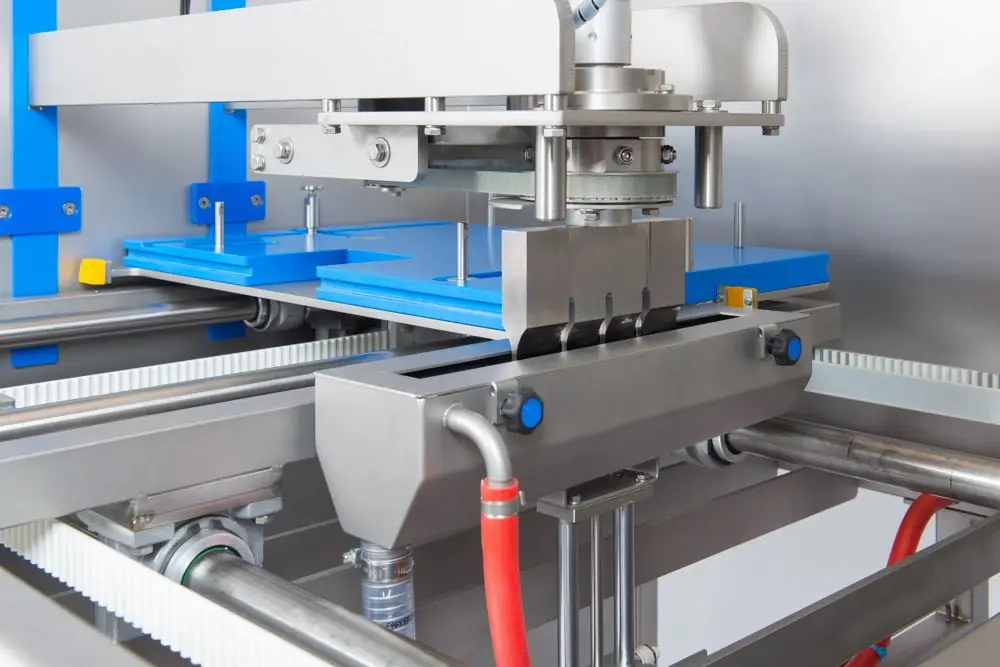
During dimensional processing, the usual mechanical cutters and abrasives act as a direct tool of influence. The key difference in this method lies in the energy source that powers the tool. In this capacity, the ultrasonic current generator operates at frequencies of 16-30 kHz. He provokesoscillations of the same abrasive grains at ultrasonic frequency, which ensures the characteristic quality of processing. Moreover, it is necessary to note the variety of types of mechanical action. This is not only the usual cutting and grinding elements, but also the deformation of the structure while maintaining its volume. What's more, ultrasonic sizing ensures that the particles of the workpiece are kept to a minimum even during cutting. Grains that affect the material dotted out microparticles that do not affect the design of the product. In fact, there is no destruction of the structure by sampling, however, uncontrolled crack propagation may occur.
Differences from plasma technology
In terms of processing quality, ultrasonic and plasma methods have many similar features, providing the possibility of high-precision cutting. But also between them there is a significant difference in the principle of work. So, if UZO involves an intense impact on the abrasive powder from the side of the trimming tool with the energy support of an electric wave generator, then the plasma processing method uses ionized gas charged with ions and electrons as a working medium. That is, the technologies of ultrasonic and plasma processing equally require the support of a sufficiently powerful energy generator. In the first case, this is an ultrasonic electric apparatus, and in the second case, high-temperature gas or isothermal installations capable of bringing the temperature regime of the working medium to 16,000 °C. An important component of plasma treatment is the use of electrodes and plasmasubstances that provide high power of the guided arc of the cutter.
Ultrasonic Treatment Machines

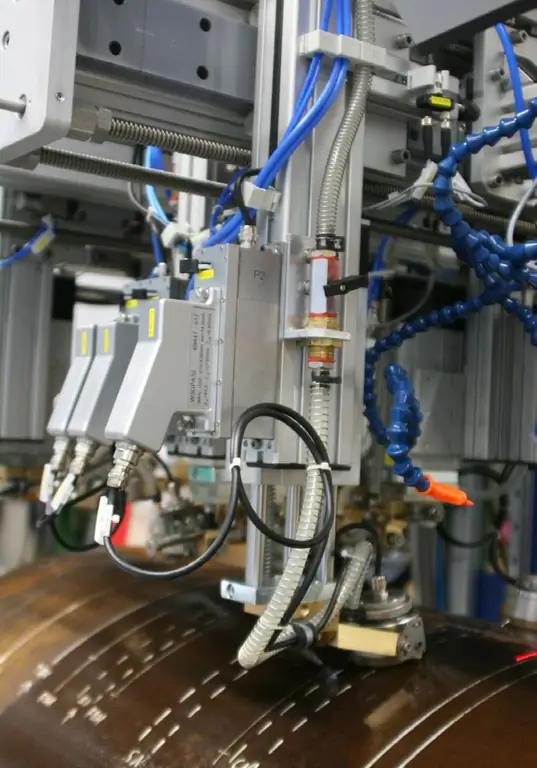
Now it is worth dwelling in more detail on the equipment used in the implementation of the RCD. In large industries, for such purposes, machines are used, provided with a generator set for generating alternating current of ultrasonic frequency. The generated current is directed to the winding of the magnetic converter, which, in turn, creates an electromagnetic field for the working body of the installation. Ultrasonic processing begins with the fact that the punch of the machine begins to vibrate, being in an electromagnetic field. The frequencies of this vibration are set by the generator based on the set parameters that are required in a particular case.
The punch is made of a magnetostrictive material (an alloy of iron, nickel and cob alt) that can change in linear dimensions under the action of a magnetic transducer. And at the final critical stage, the punch acts on the abrasive powder through oscillations guided along the waveguide-capacitor. Moreover, the scale and power of processing can be different. On the equipment considered, industrial metalworking is performed with the formation of massive structures, but there are also compact devices with a similar principle of operation, on which high-precision engraving is performed.
Dimensional RCD technique

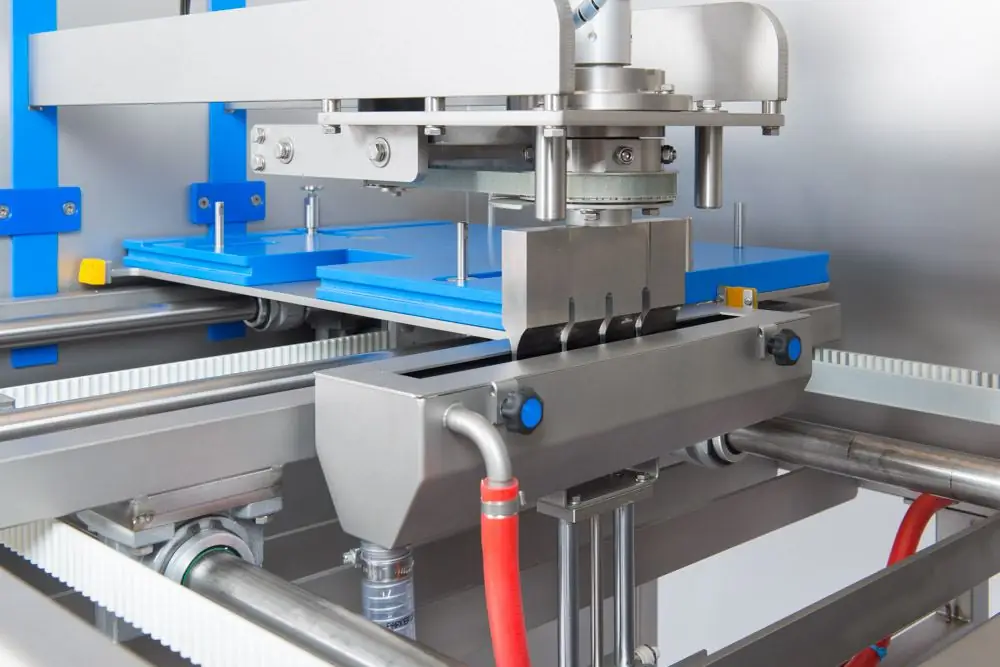
After installing equipment and preparingof the target material, the abrasive slurry is supplied to the area of the operation - that is, to the space between the surface of the product and the oscillating end. By the way, silicon or boron carbides are usually used as the abrasive itself. In automated lines, water is used for powder delivery and cooling. Directly ultrasonic processing of metals consists of two operations:
- Impact penetration of abrasive particles into the intended surface of the workpiece, as a result of which a network of microcracks is formed and microparticles of the product are punctured.
- Circulation of abrasive material in the processing zone - used grains are replaced by streams of new particles.
An important condition for the effectiveness of the whole process is to maintain a high pace in both procedures until the end of the cycle. Otherwise, the processing parameters change and the abrasive direction accuracy decreases.
Process characteristics

Processing parameters optimal for a particular task are pre-set. Both the configuration of the mechanical action and the properties of the workpiece material are taken into account. The average characteristics of ultrasonic treatment can be represented as follows:
- The frequency range of the current generator is from 16 to 30 kHz.
- The oscillation amplitude of the punch or its working tool - the lower spectrum at the beginning of the operation is from 2 to 10 microns, and the upper level can reach 60 microns.
- Saturation of abrasive slurry - from 20 to 100 thousand.grains per 1 cm cube.
- Diameter of abrasive elements - from 50 to 200 microns.
Varying these parameters allows not only individual high-precision linear processing, but also the accurate formation of complex grooves and cutouts. In many ways, working with complex geometries has become possible due to the perfection of the characteristics of the punches, which can affect the abrasive composition in different models with a thin superstructure.
Deburring with RCD
This operation is based on an increase in the cavitation and erosive activity of the acoustic field when ultra-small particles from 1 micron are introduced into the abrasive flow. This size is comparable to the radius of influence of the shock sound wave, which makes it possible to destroy weak areas of burrs. The working process is organized in a special liquid medium with a glycerin mixture. A special equipment is also used as a container - a phytomixer, in a glass of which there are weighed abrasives and a working part. As soon as an acoustic wave is applied to the working medium, the random movement of abrasive particles begins, which act on the surface of the workpiece. Fine grains of silicon carbide and electrocorundum in a mixture of water and glycerin provide effective deburring up to 0.1 mm in size. That is, ultrasonic treatment provides accurate and high-precision removal of microdefects that could remain even after traditional mechanical grinding. If we are talking about large burrs, then it makes sense to increase the intensity of the process by adding chemical elements to the containerlike blue vitriol.
Cleaning parts with RCD
On the surfaces of working metal blanks, various kinds of coatings and contaminations may be present, which are not allowed, for one reason or another, to be removed by traditional abrasive cleaning. In this case, the technology of cavitation ultrasonic processing in a liquid medium is also used, but with a number of differences from the previous method:
- The frequency range will vary from 18 to 35 kHz.
- Organic solvents like freon and ethyl alcohol are used as a liquid medium.
- To maintain a stable cavitation process and reliable fixation of the workpiece, it is required to set the resonant mode of operation of the phytomixer, the liquid column in which will correspond to half the length of the ultrasonic wave.
Diamond drilling supported by ultrasound
The method involves the use of a rotating diamond tool, which is driven by ultrasonic vibrations. Energy costs for the treatment process exceed the volume of required resources with traditional methods of mechanical action, reaching 2000 J/mm3. This power allows you to drill with a diameter of up to 25 mm at a speed of 0.5 mm/min. Also, ultrasonic processing of materials by drilling requires the use of coolant in large volumes up to 5 l/min. Fluid flows also wash out fine powder from the surfaces of the tooling and workpiece,formed during the destruction of the abrasive.
Control of RCD performance

The technological process is under the control of the operator, who monitors the parameters of the acting vibrations. In particular, this applies to the amplitude of oscillations, the speed of sound, as well as the intensity of the current supply. With the help of this data, the control of the working environment and the impact of the abrasive material on the workpiece is ensured. This feature is especially important in the ultrasonic processing of instruments, when several modes of equipment operation can be used in one technological process. The most progressive methods of control involve the participation of automatic means of changing processing parameters based on the readings of sensors that record the parameters of the product.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Technology
The use of RCD technology provides a number of advantages, which manifest themselves to varying degrees depending on the specific method of its implementation:
- The productivity of the machining process increases several times.
- Ultrasonic tool wear is reduced by 8-10 times compared to conventional machining methods.
- When drilling, processing parameters increase in depth and diameter.
- Increases the accuracy of mechanical action.
Flaws of technology
Wide application of this method is still hindered by a number of shortcomings. They are mainly related to the technological complexity of the organization.process. In addition, ultrasonic processing of parts requires additional operations, including the delivery of abrasive material to the working area and the connection of equipment for water cooling. These factors can also increase the cost of the work. When servicing industrial processes, energy costs also increase. Additional resources are required not only to ensure the function of the main units, but also for the operation of protection systems and current collectors that transmit electrical signals.
Conclusion

The introduction of ultrasonic abrasive technology into metalworking processes was due to limitations in the use of traditional methods of cutting, drilling, turning, etc. Unlike a conventional lathe, ultrasonic metalworking is able to effectively cope with materials of increased hardness. The use of this technology made it possible to perform machining operations on hardened steel, titanium-carbide alloys, tungsten-containing products, etc. At the same time, high accuracy of mechanical action is guaranteed with minimal damage to the structure located in the working area. But, as is the case with other innovative technologies such as plasma cutting, laser and waterjet processing, there are still economic and organizational problems when using such metal processing methods.
Recommended:
Plexiglas engraving: advantages and disadvantages, technology, equipment

Plexiglas engraving is considered a painting craft. A souvenir figurine, stained-glass windows or a glass table, which are decorated with exquisite drawings, embody a delicate artistic taste. Pickling and sandblasting technologies are in the past. Today, with the help of a laser machine, each person can create a highly detailed pattern
Letterpress is Letterpress printing technology, modern stages of development, necessary equipment, advantages and disadvantages of this type of printing

Letterpress is one of the typical methods of applying information using a relief matrix. The elements that protrude are covered with paint in the form of a paste, and then pressed against the paper. Thus, various mass periodicals, reference books, books and newspapers are replicated
Meat: processing. Equipment for meat and poultry processing. Production, storage and processing of meat

Information of state statistics show that the volume of meat, milk and poultry consumed by the population has significantly decreased in recent years. This is caused not only by the pricing policy of manufacturers, but also by the banal shortage of these products, the required volumes of which simply do not have time to produce. But meat, the processing of which is an extremely profitable business, is very important for human he alth
Welding of ultrasonic plastics, plastics, metals, polymeric materials, aluminum profiles. Ultrasonic welding: technology, harmful factors
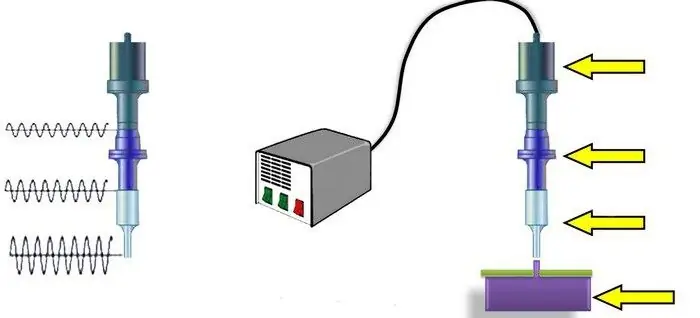
Ultrasonic welding of metals is a process during which a permanent joint is obtained in the solid phase. The formation of juvenile areas (in which bonds are formed) and the contact between them occur under the influence of a special tool
Lost-wax casting: technology, advantages and disadvantages

The use of investment models is a fairly popular method of foundry production. It is used where it is necessary to accurately observe the dimensions and ensure high quality of the surface of the parts. This is how turbine blades and high-performance tools, dentures and jewelry are cast, as well as sculptures of complex configuration. The mold for casting is one-piece, the model of low-melting materials is not removed during molding, but is melted out

